Intro Flashcards
(25 cards)
Define the following:
- Prenatal period:
- Perinatal period:
- Postnatal period:
- Neonatal period:
- Infancy:
- Childhood:
- Puberty(girls &boys are dif.):
- Adolescence:
A.Prenatal period: the period of gestation that is prior to birth
B. Perinatal period: 22 Weeks gestation to 28 days after birth
C. Postnatal period: after birth
- Neonatal period: up to 1 month after birth
- Infancy: first postnatal year
- Childhood: 12 months to 12-13 years
- Puberty: 10-15 years (girls); 12-17 years (boys)
- Adolescence: 3-4 years post-puberty
A clinician might say a pregnancy lasts for how long? what would a patient say?
- 40 weeks
- 9 months
To an embryologist, what are the stages of fetal development?
1.
2.
3.
- preimplantation
- embryonic
- fetal stage
Describe what happens during the Prenatal weeks:
- Week 1:
- Week 2:
- Week 3:
- Weeks 3-8:
- Week 9 to term:
•Week 1: Preimplantation stage: zygote, morula, blastocyst
•
•Week 2: Inner cell mass forms bilaminar embryo
•
•Week 3: Bilaminar embryo becomes trilaminar embryo
•
•Weeks 3-8: Embryonic period – organogenesis (all organs are made)
•
•Week 9 to term: Fetal period - Growth and differentiation
The first 2 weeks after fertilization are the ____ _ ____ period which means?
What is common in this phase?
“all or nothing”
If something goes wrong, the embryo will not survive.
Miscarriages/spontaneous abotions
The ______ stage starts at week 3 and goes until week 8, _____ will be formed. This is a _____ period; what does this mean?
- embryonic
- organs
- critical period
- harmful agent of any sort (physical, chemical, radiation) can cause then a major anomally. This is where things can go very wrong.
Weeks 9-38 are called the _____ _____. what would happen if an injury were to occur during this time?
- fetal period
- the injury is most likely to produce minor structural defects or functional abnormalities
what is Gestational age (GA)?
the age of the embryo/fetus from the presumed first day of the last menstrual period – clinical notion
what is Fertilization age?
Which is longer Fertilization age or GA? Why?
The age of the embryo/fetus from the fertilization day – not used as such
GA is approximately 2 weeks longer than the fertilization age because the oocyte is not fertilized until about 2 weeks after the last Menstrual Period (around ovulation time) when gestational age is counted.
EDD is what?
What is the Naegele’s rule?
___% of women deliver on their due date while 60-70% deliver within 13 days from their due date. Why the variation?
Expected Delivery Date
- first day of LMP – 3 months +1 year +1 week
- 5%
- different time length of the period prior to ovulation; after ovulation, the period between ovulation and menstruation is fairly constant, at 14 days
What is an Abortion? An abortion happens before what time in development?
expulsion/removal of the embryo/fetus from uterus prior to age of viability- does not matter how it happens
22-23 weeks gestation
What is a misscarriage?
What is it a synonym for?
What are the majority caused by?
Miscarriage is spontaneous expulsion from uterus of embryo/fetus relatively early (usually < 20 weeks);
synonym = spontaneous abortion
à majority are caused by chromosomal abnormaliti
Premature infants are born between stage of _____ and ___ weeks. A majority are caused by ______ _____ of the pregnancy.
What is a still born?
viability (22-23 wks) and 37 weeks
Maternal complications
A baby that is born dead but after 22 wks?
what are PGCs?
These are Identified during the ___ week in the ____ ____ and are important for ______. During week 4-6, they migrate to the ____ ____ ___ area. PGCs wil then continue to multiply by _______ during their migration.
Primordial Germ cells
4th
yolk sac
Gametogenesis
future genital ridge
mitosis during their migration
After moving to the primitive genital ridge, PGCs stimulate the surrounding ______ to create the ____ ____ ___. The swelling becomes the ______ _____. The PGCs are now called _____ (same cells w/ new name). In females the somatic support cells will become ____ ____ while in males they will become ____ ____ .
- epithelium
- somatic support cells
- Primitive Gonad
- gonocytes
- ovarian follicles (female)
- Sertoli cells (male)
Gonocytes will undergo _____. In a female, they will become _____ and they will become ____ in males. The basic chromosomal events of the process are the same in the two sexes afterwards. Both will undergo Several ______ divisions and two _____ divisions. However, the timing of the _______ of germ cells is different in the male and female
- mitosis
- oogonia
- spermatogonia
- mitotic
- meiotic
- maturation
•Gonocytes have ____ pairs of chromosomes for a total of ___ chromosomes this makes them _____ cellls. One chromosome from of each pair comes from each parent. There are __ pairs of matching, homologous chromosomes called ______ and two ____ ______ that determine sex of the individual.
- 23
- 46
- diploid
- 22
- autosomes
- sex chromosomes (X&Y)
Mature gametes are ____ cells which means they have ___ copy(ies) of each chromosome(s). This is because during _______, the number is _____ by____ during the _____ division.
haploid
1
gemetogenesis
reduced
half
meiotic
Describe Gametogenisis. Label the process in each blue box and label the teal box and say if diploid or haploid
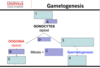

Oogonias divide by MITOSIS by the ___ week of pregnancy& the number of germ cells in the ovary reaches its max (7 mil); Most of them ________. Surviving cells have entered _______ of ____ ___ and each is tightly enclosed in a ______ ________. By ____, only 700,000 to 2 million oogonias remain and even more degenerate. By puberty, only about ________ remain
- 20
- degenerate
- prophase of meisis 1
- primary follicle
- birth
- 400,000
Before birth, all primary oocytes are suspended in _____ of ____ ____ . ____ primary oocytes form after birth
•The primary oocytes remain dormant in the _____ _____ until _____. At puberty, __-___ _____ develop/month, but one is _____. The primary oocyte will _____ in ___ and shortly before _______ completes the first _____ division. It now is a ______ ____ and a ____ ____ that are both _____, but the secondary follicle takes almost all of the _____. At ovulation, the nucleus of the secondary oocyte begins the second _____ division, but progresses only to ______, when division is arrested. If a _____ penetrates the secondary oocyte, the second meiotic division is completed
prophase of meiosis I
No
ovarian follicles until puberty
5-12 follicles
dominant
increase in size
ovulation
meiotic
secondary follicle
polar body
haploid
cytoplasm
meiotic
metaphase
sperm
______ inside the embryonic male gonad remain dormant from 6th week until ______ and does not end until _____. 200-300 million sperms are produces per ___. Simpler process that is prone to less errors! The entire spermatogenesis process takes about ___ _____.
- Spermatogonias
- puberty
- death
- day
- 2 months
In spermatogenesis, at puberty, _____ will cause _____ ____ differentiate into _____ ______. _______ (which are still PGC’s) resume development and divide several times through _____ to become primary _____ which are ___ cells. The cells are gradually translocated from the basal to the ____ side of the _______ ______ while spermatogenesis takes place. Primary spermatocytes complete, without interruption, ___ _____ divisions to form 2 ___ ____ followed by 4 ______. As they migrate, the spermatids undergo maturation and go through _______ or the differention of the ___ ___.
- testosterone
- sertoli cells
- seminiferous tubules
- spermatogonias
- mitosis
- spermatocytes
- diploid
- luminal
- seminiferous epithelium
- 2 meiotic
- secondary spermocytes
- spermatids
- spermiogenesis
- sperm cell.
*
In the Embryp….
- Proximal and distal mean?
- Superior and inferior are equivalent to ____(____) and _____
- A median plane is ____ section down the _____
- Anterior and posterior are equivalent to_____ and___

- close or far away from center
- Cranial (rostral) and caudal
- logitudinal,middle
- Dorsal and ventral


