Interstitial Lung Disease Flashcards
What is interstitial lung disease?
What are the common causes?
What may all show on xray?
Disease that affects the space between the endothelium and epithelium in the air sacs. Fibroblasts proliferate and excrete excess collagen which affects air transfer
Common causes -
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Idiopahtic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Sarcoidosis
May all show reticulo (lines) nodular (dots) appearence

Electron micrograph of an alveolar wall

- What is hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
- What often causes it?
- What are the symptoms?
- What are the clinical signs
- How is it diagnosed?
- What is the management?
- Hypersensitivity reaction to something in the environent causing an immune response and pulmonary fibrosis.
- Mould, feathers, pigeon feathers/poo, farmers lung
- Progessive SOB, cough, weight loss
- Inspiratinal squeaks (like bronchiolitis) and scanty crackles
- Alveolar lavage shows lymphocytosis, non caseating granulomas on histology. CT shows ground glass and mosaic of light and dark
- Remove cause

What does this show?
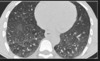
Mosaic pattern in HP
- What is sarcoid?
- What are the symptoms?
- What are the clinical signs?
- How is it diagnosed?
- What is the treatment and when do you treat?
- Multi system disorder of unknown aetiology and causes non causeating granulomas anywhere in the body with lungs being the most affected organ.
- None, to malaise, arthralgia, joint pain, SOB
- Erythema nodosum, hilar lymphadenopathy
- Alveolar lavage shows lymphocytosis (less than HP), non caseating granulomas
- Corticosteroids if systemic involvement or severe pulmonary

What is this?

Diffuse reticulonodular apperence on CXR
?IPF or any Interstitial lung disease
What are some extra pulmonary symptoms of sarcoid?
Basically anything - any lump can be caused by granulomas
- retina
- bone
- skin
- nervous system- mononeuritis multiplex/meningitis/myopathy
- CVS - arrythmias due to granulomas
What are these?
What causes them?
What are the symptoms?

Calcified pleural plaques
Asbestos exposure - approx 20 years after
Often none
What are these?
What causes them?

Calcified pleural plaques
Asbestos exposure - approx 20 years after
- What is the typical presenation of mesothelioma?
- What are the xray signs?
- What causes it?
- How do you diagnose?
- Pleuritic pain and breathlessness
- Massive pleural effusion
- Asbetos exposure (not from plaques)
- Histologically

- What is asbestosis?
- What are the symptoms?
- What are the clinical signs?
- What are the radiological signs?
- Fibrosis of the lung
- SOB, dry cough
- CLubbing, inspirational crackles and Increased VF (same as IPF)
- Diffuse retiulonodular markings on XRAY, honeycombing on CT

What is folded lung?
Presents as a mass on xray with vessels feeding it - caused by asbestosis of pleural effusions.
Asymptomatic

- What is idipathic pulmonay fibrosis?
- What are the symptoms?
- What are the clinical signs?
- What are the investigations?
- How is it managed?
- Pulmomany fibrosis of unknown cause
- Progressive SOB and cough
- Clubbing and Inspirational lung crackles/Increased TVF at base
- Low Fev1 and FVC (normal ratio) and low transfer coefficent. Also honeycombing on CT and reticulo nodular (lines and dots) XRAY
- Only transplant shows benefit
What are some common drug causes of pulmonary fibrosis?
LOADS
Methotrexate
Bleomycin
Amioderone
What collagen vascular diseases are associated with pulmonary fibrosis?
SLE
RA
Scleroderma (diffuse)
What are the common occupational lung diseases?
Asthma
Hypersentivity pneumonitis
Pneumoconiosis (coal, asbestos)
What does asbestos do to the lung?
Mesothelioma
Pleual plaques
Lung cancer
Asbestosis
Diffuse pleura thickening


