Inter- and Intracellular Neurotransmission Flashcards
True or False
These natural products (Nicotine, D-Turbocurarine, Alpha-bungartoxin) bind to nAChR.
For instance, Nicotine has a higher affinity towards CNS nAChR than muscle.
Alpha-bungartoxins will cause victims to become paralysis and respiratory failure.
True
True or False
GlyRs and GABA-Rs are members of the same family.
True
What do GABA-Rs have in common with nAChR?
What is the difference between the two?
They are both heteropentomes –> made out of different subunits.
nAChR is excitatory channels and GABA and GlyRs receptors are inhibitory channels
What are two drugs that affect GABA?
Barbiturates - bind near GABA binding sites (accentuate the effects of GABA or can activate the receptor without the presence of GABA)
and
Benzodiazepines (Positive allosteric modulators)
Have no impact in the absence of GABA

What is the mechanism and regulation of glutamate release and uptake?
Made in neuronal cytoplasm by the biosynthetic mechanism.
Uptake into vesicles by vesicular transporters
mGluRs are autoreceptors –> trigger negative feedback
Glutamate transporters are the uptake mechanisms
What are the different types of Glutamate receptors?
AMPA
NMDA
Kainate (less abundent)
What is the major difference between NMDA-Rs and AMPA-Rs as related to their activation and inactivation kinetics and their voltage dependence?
AMPA is the fast kinetics of activation and inactivation (desensitization).
only needs Glutamate to activate the channel.
NMDA is slow kinetics of activation and inactivation.
Mg2+ blocks the channel, lead to a requirement for stimulation depolarization
Ca2+ permeable.
Why NMDA-Rs are coincidence detectors and the two criteria required for channel activation?
Need activity in presynaptic neurons -yields glutamate release from its nerve terminals
and
need activity in postsynaptic neurons - yield depolarization of its membrane potential.
Fill in the blanks for the NMDA mechanism of action of coincidence activation.
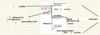
A. Glutamate
B. Fast
C. Activation gate
D. Inactivation gate
E. AMPA current
F. inactivating current
G. NMDA and AMPA
H. NMDA
True or False
NMDA passes Ca2+ and Na+ ions
and
AMDA passes only Na+ ions
True
True or False
____ A silence receptor only contain NMDA receptors
____ NMDA receptors are dependent on AMPA for depolarization
___ Depolaorization leads to Mg2+ removal from NMDA
___ The increase in cytosol Ca2+ will insert new AMPA receptors, increase the sensitivity to Glutamate (increase Bmax) which is also known as Long Term Potentiation
All True
True or False
LTP leads to phenotype change and is important for memory.
The early phase of LTP is translation-independent on existing proteins and the Late phase places transcription inhibitors leading to a change in phenotype.
True



