Instruments Flashcards

Allis Tissue Forcep
intermeshing teeth at tip are used to grasp tissue
grasps tissue at right angles of tension application
only used on tissue that will be resected
used: positioning of suction tubing and electocautery wire on patient drape

Babcock Tissue Forcep
smooth flat tips grasp tissue
grasps tissue at right angles of tension application
less traumatic than Allis forceps
Grasp and retract robust soft tissues (stomach, bladder)

Straigh Doyen Intestinal Tissue Forcep
thin, slightly bowed jaws
fine, longitudinally oriented grooves
Intestinal lumen occlusion

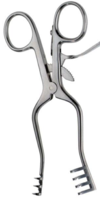
Straight Rochester-Carmalt Hemostatic Forceps
designed for jaw clamping
used for clamping pedicles/tissue
longitudinally oriented serrations with cross-hatched tips
jaws can be straight or curved
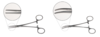
Straight and Curved Kelly Hemostatic Forceps
Transversely orientated serrations (do not extend the entire length of the jaw)
designed for tip clamping of small to medium vessels

Straight and Curved Halsted Mosquito Hemostatic Forcep
Transversely oriented serrations (along the entire length of the jaw)
tip clamping of small vessels
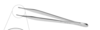
Brown Adson Tissue Forcep
Tips consist of fine teeth in two parallel rows
Used frequently for general tissue handling but can crush tissue

Adson Tissue Forcep
Tips consist of fine teeth (2x1)
Results in less crush injury
Poor grip of fat or other friable tissue

Debakey Tissue Forcep
Parallel ribbed tips
most frequently used thumb forcep in soft tissue surgery
less traumatic

Bishop-Harmon Forcep
Tips consist of fine teeth (2x1) at a right angle
Smaller than other thumb forceps
Used to grasp tissue in ophthalmologic surgery

Bard-Parker Number 3 Scalpel Handle
most commonly utilized scalpel handle
Ribbed grip

10 most widely used- long flat blade used for making longer incisions
Blades

62, 64, 65, 67
Beaver Blade Scalpel Handle
blades extends around tip allowing press cutting
*used with pencil grip at all times
used to incise the limbus for intraocular surgery

Straight Mayo Dissecting Scissors
Plain edge
thick blades (~1/3 of instrument)
straight blade: greater mechanical advantage
Curved blade: improved visualization of tissue, more versetile

Straight Metzenbaum Scissors
Plain edge
Thin, delicate blades (~1/4 length)
used to incise soft tissues
straight blade: greater mechanical advantage
curved blade: improved visulization of tissue, more versatile

Stevens Tenotomy Scissors
Narrow, delicate tipped precision scissors
Used for precision cutting, such as in ophthalmic and urologic surgery
straight or curved

Spencer Stitch Scissors
hooked tip used to entrap suture for cutting
used for post-op suture removal

Vernon Cartilage and Wire Scissor
Smooth or serrated blades
used to incise thick, tough tissue and orthopedic wire
used to cut suture intra-operatively

Mayo-Hegar Needle Holders
various sizes- driver jaws should match needle size
textured tungsten-carbon jaw inserts provide intermediate needle holding security over smooth jaws or jaws with teeth- limits twisting and rotation of needle

Olsen-Hegar Needle Holders
combined needle driver/scissor

Derf Needle Holders
Ophthalmic needle drivers
small size useful for suturing smaller structures (eyelids, conjunctiva)

Castroviejo Needle Holders
Microsurgery needle driver
used for ophthalmic and vascular surgery
spring loaded handle- releases and grabs needle with minimal motion of hands
locking and non-locking styles

Balfour Retractor
blunt blades used to retract abdominal wall laterally
various sizes
central “bladder blade” can be used to retract rib cage cranially (access to liver and diaphragm)
caution

Finochietto Retractor
adjustable rib retractor
various sizes
used for retraction of chest wall during intercostal thoracotomy and median sternotomy
flat retractor blades are perpendicular to instrument