Infectious Disease Flashcards
Drug of choice for Syphilis

Penicillin G

When you see Gram(+) cocci in clusters, what do you cover for?
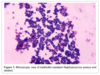
MRSA
Treatment of choice for MRSA?
Vancomycin
Best antibiotic for Methicillin-Sensitive Staph Aureus?
Cefazoline
What bacteria to consider when seeing Gram(+) cocci in pairs and chains?
Streptococcus
Gram(+) bacilli seen in gastroenteritis and meningitis?
Listeria
Tx of choice for Bacillus anthracis?
Ciprofloxacin
Tx of choice for Actinomyces?
Penicillin
What organisms do Cephalosporin NOT cover?
LAME
- Listeria
- Atypicals
- MRSA (except Cefazoline)
- Enterococcus
What is Catalase positive, Coagulase positive cocci?
Staph Aureus
What are alpha-hemolytic Streptococcus?
Strep pneumo and Viridans
What are beta-hemolytic Streptococcus?
S. pyogenes and S. agalactiae
What are gamma-hemolytic streptococcus?
Enterococcus
What type of cocci is Enterococcus?
Gram positive in pairs and chains.
Enterococcus is not covered by ________.
Cephalosporins
Best Tx for group A strep
Penicillin
What anaerobes are resistant to penicillin?
Bacteroides spp.
How does actinomyces present?
Abscess in the mandible, oral lesions
Tx of choice for Listeria?
Ampicillin
What do you need to treat Staph aureus?
Beta lactamase inhibitors + Penicillins
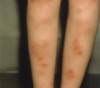
When covering for cellulitis, you cover for what organisms?
Group A strep (pyogenes) and MSSA
Tx of choice for cellulitis
1st gen cephalosporins
Examples of 2nd gen cephalosporins
Cefoxitin and Cefotetan
The only cephalosporins that treat for anaerobes?
2nd generation cephalosporins:
Cephamycins:
- Cefoxitin
- Cefotetan
Which cephalosporin is effective in covering MRSA?
Ceftaroline (5th gen)
Which cephalosporins treat PID?
2nd generations cephalosporins
What does clindamycin cover?
Strep, Staph, and Anaerobes
Best substitute for penicillin if patient has PCN allergy.
Clindamycin
Metronidazole is best for what organisms?
(GET the Metro)
Giardia
Entamoeba
Trichomonas
What is the best Tx for recurrent C. diff?
Fidaxomicin
Best diagnostic test for C. diff?
ELIZA test for C. diff toxin
How effective is fecal transplant?
95% effective
What is the best Tx for SEVERE C. diff?
Oral Vancomycin
How do you define SEVERE C. diff?
Any ONE of the following:
- WBC count over 15,000
- Increase of Creatinine of 1.5 or more
- over 60 y/o
- albumin less than 2.5
What drug, apart from an antibiotic, causes C. diff?
Proton pump inhibitors
What antibiotics increase risk of C. diff?
- Fluoroquinolones
- Broad spectrum cephalosporins
Safer antibiotics that have a low risk of C. diff occurrence
Tetracycline, Macrolides, and Bactrim
What antibiotics can you give to treat atypicals in pneumonia?
Macrolides
Cross reactivity for penicillin allergy and cephalosporins is ____%
less than 5%
What is your Vanco MIC (Minimum inhibitory concentration) cutoff to determine you cannot use Vancomycin?
Over 2.0
Substitutes for Vanco for MRSA?
- Daptomycin (Calcium paralyses cell)
SE: Myositis, neutralized by surfactants (cannot use for pneumonia)
For: cellulitis, right-sided endocarditis, skin infections, bacteremia
- Linezolid (inhibit cell wall synthesis)
SE: cannot use with SSRI, serotonin syndrome risk
For: good for pneumonia
Difference between serotonin syndrome and NMS
Myoclonus and hyperreflexia in serotonin syndrome.
No myoclonus and HYPOreflexia in NMS.
Most common side effect of Vanco
Thrombocytopenia
Ceftaroline is used for:
Pneumonia and Cellulitis
Macrolides are used for:
MILD gram positive infections
GOOD for atypical infections
BAD for serious gram pos infections
What organism must you cover with neutropenic fever?
Pseudomonas
If person has infected chemotherapy line what antibiotic do you give?
Vancomycin
What antibiotics can cover pseudomonas?
- Ceftazidime (3rd gen)
- Cefepime (4th gen)
- Pip/Taz
- Ticarcillin/Sulbactam (Beta lactams)
- Fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin is the best)
- Aminoglycosides
- Carbapenems (if with PCN allergy)
- Aztreonam (if with PCN allergy)
What conditions should you be wary of Pseudomonas?
CF, bronchiectasis
diabetics with malignant otitis externa
hot tub folliculitis
puncture wounds (with a nail)
nosocomial infections
Most common side effects of fluoroquinolones:
- tendinitis / tendon rupture
- peripheral neuropathy
- QT prolongation
- C. diff
Ceftazidime (3rd gen) covers
gram negative but not gram positive (strep/staph)
but good for pseudomonas
Cefepime (4th gen) can cover:
gram pos and gram neg
pseudomonas
Ceftriaxone (3rd gen) covers:
Broad spectrum for gram neg (Neisseria, etc)
can also cover pneumococcus
not good for pseudomonas
Why must you be careful with aminoglycosides?
It is nephrotoxic and ototoxic
What antibiotics have good anaerobic coverage?
Metronidazole
Moxifloxacin
Carbapenems
Beta-lactamases (ampi/sulba)
Which carbapenem does not cover pseudomonas?
Ertapenem
Carbapenems cover mostly gram negs, pseudomonas (except ertapenem), and anaerobes except:
MRSA
Enterococcus faecium
Stenotrophomonas maltophila (can be covered by bactrim)
What do we use to treat extended spectrum beta lactamases (ESBLs),
highly resistant gram negs.
Examples: E. coli, Klebsiella
Carbapenems (ertapenem)
Tigecycline
We can treat carbapenemase Klebsiella with:
Tigecycline or
Ceftazidime/avibactam (new beta lactamase inhibitor)
These mostly used for complicated UTIs and intrabdominal
How to treat multi drug resistant (MDR) pseudomonas?
Ceftolozane/Tazobactam
Where is doxycycline used?
Early lyme disease
Rickettsia
Chlamydia
Ehrlichiosis
What are the side effects of doxycycline?
Photosensitivity, pill esophagitis (drink lots of water)
Bactrim mostly used for:
PCP
Uncomplicated cystitis
Side effects of bactrim:
rash
SJS
thrombocytopenia, anemia, pancytopenia
kernicterus
hyperkalemia
decreased creatinine clearance
Do not give Bactrim with:
Ace-inhibitor
ARB
spironolactone
(Inhibit RAAS) - you can get arrhythmias due to hyperkalemia
Age cut off for covering listeria in patient’s with meningitis?
Over 50 years old
(Give ampicillin for listeria)
Why give vancomycin in patient’s with meningitis?
20% of strep is penicillin resistant
What type of meningitis patients can get it from listeria?
HIV, steroids, lymphoma, leukemia, chemoTx, neonates and people over 50
How do you dx cryptococcal meningitis?
cryptococcal antigen
In patient’s with HIV and cryptococcal meningitis, what is Tx algorithm?
Treat with HAART lifelong then star with induction phase of antigungals:
such as amphotericin and flucytosine then maintain with
fluconazole until CD4 count is >100 for 3 months
Why give dexamethasone in strep meningitis?
Improves morbidity and mortality
Main causes of brain abscess in normal patient (non HIV): (organisms)
60-70% is Streptococcus
20-30% is Bacteroides
25-35% is Enterobacter
10% is Staphylococcus
Empiric Tx for brain abscess:
Penicillin (for the Strep, 60-70%) / or 3rd gen cephalosporin
Metronidazole (for the Bacteroides, 20-30%)
Main causes of brain abscess in HIV patients:
90% - Toxoplasmosis
How to Tx Toxo brain abscess in HIV patients
pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine for 10 days
If brain abscess comes from sinusitis infection, add ___ to treatment.
Add vancomycin (to cover MRSA)
With Herpes encephalitis, what happens if you have a negative PCR from your LP?
Repeat after 5 days, results may be negative in the early stages.
What indicates a West Nile encephalitis?
Happens in the summer
Lower extremity paralysis
First line Tx for otitis media?
Amoxicillin
then Augmentin or Macrolides
Sinusitis caused by:
90-98% caused by VIRUSES
When do you give antibiotics for sinusitis?
If symptoms persist for more than 10 days
if symptoms are severe (102 deg fever, facial pain for 3-4 consec days)
if symptoms worsen
Which organisms do you cover for sinusitis?
- Strep pneumo
- Haemophilus
- Morzaxella
Antibiotics for sinusitis?
Augmentin (covers for s. pneumo and haemophilus, moraxella)
Doxycycline or New fluoroquinolone (if with PCN allergy)
What is the life-threatening side effect of augmentin?
Fulminant hepatotoxicity (antidote is NAC)
Which antibiotics can cause QT prolongation?
Macrolides and Fluoroquinolones
CENTAUR Criteria for pharyngitis
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Tonsillar Exudates
Fever
Lack of cough
When do you do a CT for meningitis?
FMD
seizures
papilledema
severe AMS
immunocompromised
When do you start empiric abx for meningitis?
IMMEDIATELY
When you see gram pos bacilli in CSF which sbx do you give?
Ampicillin (for listeria)
How to treat TB meningitis?
RIPE + steroids
How to treat TB pericarditis?
RIPE + steroids
Antibiotic Tx for Meningitis?
Ceftriaxone + Vancomycin
(Strep pneumo + PCN resistant strep)
Tx for pharyngitis
Penicillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin
Macrolide, 1st gen ceph, clindamycin
CENTAUR for pharyngitis:
0-1 = ?
2-3 = ?
4 = ?
0-1 = do nothing
2-3 = rapid strep test
4 = treat
What drugs cover atypicals?
Fluoroquinolones
Macrolides
Doxycycline
What kind of rash do you see with coccidiomycoses?
Erythema nodosum
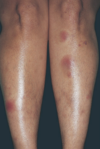
Tx for Chlamydia psittaci?
Doxycycline
Pneumonia with:
pancytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, hilar lymphadenopathy, and NO RASH
Histoplasmosis
(Histoplasma capsulatum)
Tx for CAP pneumonia?
New fluoroquinolones
(covers atypicals and PCN resistant pneumococcus)
Why not give macrolide only for pneumonia?
Does not cover PCN resistant pneumococcus
When can you give Macrolide monotherapy for pneumonia patients?
young, healthy, no comorbidities
If pneumonia patient has QT prolongation problems, and you can’t give fluoroquinolones…
Give:
Ceftriaxone and Doxycycline
What are you covering in ventilator-assisted pneumonia?
Pseudomonas and MRSA
What pneumococcal vaccine do you give with patients >65 y/o or immunocompromised?
Give covalent 13 then PPSV 23 a year later
Pneumococcal vaccine in lung, cardiac, liver, alcohol, smokers, diabetics but <65?
PPSV 23
Pneumococcal vaccine in HIV, renal disease, hematological malignancies, transplant recipient, immunosuppressants, <65 y/o
Covalent 13 now, then PPSV 23, 8 weeks later