Infection and Pelvic Pain Flashcards
Inflammation/Irritation of the Vagina
S/s, Dx, Tx
vaginitis / vaginosis
- S/s
- copious, maodorous, or irritating discharge
- Dx
- wet mount prep to analyze vaginal secretions
- Tx
- maintain protective acidic environment
- relieve symptoms (usually pruritis)
- antimicrobial/antifungal meds
- probiotic supplements
- sexually associate (not always STI)
- Gardnerella vaginalis or other anaerobe
- grey vaginal discharge, fishy odor
S/s, Dx, Tx
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
- Dx
- clue cells on wet mount (vaginal epithelial cells covered w/ bacteria)
- Tx**
- Metronidazole (Flagyl) 500mg PO bid 7d
- Tx of partners NOT necessary

- copious, frothy, malodorous, yellow/gray-green discharge**
- internal pruritis**
S/s, Dx, Tx
Trichomoniasis (Trichomonas vaginalis)
anaerobic, unicellular flagellated protozoan that adheres to urethra, vagina, skene/bartholin glands
- Dx
- strawberry cervix**
- Tx
- Metronidazole (Flagyl) or Tinidazole
- MUST tx partners
BV vs. Trich

- vulvar/vaginal pruritis, burning, dysuria, dyspareunia, vaginal discharge
- scant vaginal discharge (20% thick, curdy)
S/s, Dx, Tx

Candidiasis (Candida albicans)
- Dx**
- antibiotics, diabetes, immuno
- 10% KOH prep of vag. discharge
- branching hyphae and spores
- culture on sabouraud’s agar if negative
- Tx**
- Fluconazole (Diflucan) 150mg PO 1 dose
- inflammation of cervix
- yellow-green mucopurulent discharge from cervix
- chandelier sign
Cause
cervicitis / mucopurulent cervicitis (MPC)
- typically STI - gonorrhea/chlamydia MC
- inflammation of external genetalia
- soaps, detergents, lotions, shaving, pads, tight clothing
- vaginal infections spread to labia
Treatment
vulvodynia
(vulvitis, vestibulitis, vulvovestibulitis)
- Tx
- avoid irritants, wear loose clothing
- behavioral tx
- topical xylocaine
- topical or systemic antidressants
- botox of affected nerve
- vestibulectomy
- reddened/painful cyst +/- puss at vaginal opening to ducts
Treatment
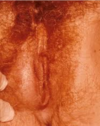
Bartholinitis or Bartholin Cyst
(bartholin or greater vestibular glands)
- Tx
- broad-spetrum antibiotics
- drain cyst w/ hot soaks, needle aspiration, catheter, or marsupialization of gland
STI definition
Sexually Transmitted Infection
- spread by intimate/sexual contact
- includes hepatitis and TB
- prevalent in ALL socioeconomic, racial, ethnic groups
- adolescents at greatest risk of exposure/infection
Gonorrhea
Cause, S/s, Dx, Complications, Tx
Bacterial: Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- S/s
- endocervical canal MC site
- asymptomatic
- dysuria, vag. discharge, dysmenorrhea, lower abdominal/pelvic pain
- fever, mucopurulent discharge from OS
- Dx
- gram stain microscopy
- N. gonorrhoeae cultured (mainstay)
- NAAT is new norm
- Complications
- PID, sterility, disseminated infection (joints- polyarthralgia)
- pass from mother to fetus/infant
- Tx**
- Ceftriaxone (Recephin) 250mg IM
AND
- Azithromycin 1g orally (chlamydia coverage)
- MUST tx partners
- no sex until infection resolved
Syphilis
Cause, S/s, Dx, Complications, Tx
REPORTABLE
Bacterial: Treponema pallidum
(corkscrew spirochete, anaerobic bacteria)
screen in pregnancy: TORCH
- S/s- Stages
- Primary (local manifestations)
- granulomatous rxn: hard, painless chancre w/ yellowish discharge
- firm, large, nontender regional lymph nodes
- Secondary (systemic)
- 6w after chancre appears
- low fever, malaise, sore throat
- anorexia, gen. adenopathy, HA, joint pain, skin/mucous membrane rash
- condylomata lata
- Latent
- 1y - lifetime, asymptomatic but medical evidence
- Tertiary
- most severe, after latent
- gummus formation: destructive skin, bone, soft-tissue lesions
- neurosyphilis- reversible dementia
- Primary (local manifestations)
- Dx
-
Darkfield microscopy and serologic tests
- VRDL antigen and RPR tests
- FTA-ABS if RPR postitive
-
Darkfield microscopy and serologic tests
- Tx
- Benzathine Pen G parenteral injection
- MUST tx partners
- condoms until tx verified

Chancroid
Cause, S/s, Dx, Complications, Tx

Bacterial: Haemophilus ducreyi (G- bacillus)
- S/s
- painful, tender, soft chancre
- women: asymptomatic, dysuria, dyspareunia, vag. discharge, painful defecation, rectal bleeding
- Tx
- 3rd gen cephalosporin
- MUST tx partners
- condom use
Granuloma inguinale (donovanosis)
Cause, S/s, Dx, Complications, Tx
Bacterial: Klebsiella granulomatis
(G-, non-spore forming, encapsulated bacteria)
- S/s
- commonly concurrent w/ syphilis
- rare in US
- painful nodule w/ itching, ulcers on labia
- Dx
- donovan bodies- bacteria filled vacuoles within white cells of ulcer smear
- Tx
- Abx for at least 3 weeks
Chlamydia
Cause, S/s, Dx, Complications, Tx
Bacteria: Chlamydia trachomatis
MC STI in U.S.**
- S/s
- can be asymptomatic
- acute urethral syndrome (dysuria, frequency, sterile pus in urine)
- mimics UTI
- Dx
- NAATs of genital swab recommended
- Complication
- leading cause of tubal infertility
- C. trachomatis MCC cervicitis
- infects:
- cervix, urethra, rectum, conjuntiva***
- Tx
- Azithromycin 1 dose
- MUST tx all sexual contacts
- abstinence/condoms during tx + 7 days
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Cause, S/s, Dx, Complications, Tx
Chlamydial Infection
- S/s
- skin lesion spreading to lymphatic tissue
- inflammation, necrosis, abscesses
- buboes- pus draining lymph node
- 1’: cervix, vaginal wall, labia
- 2’: large buboes that rupture and drain
- Tx
- Doxycycline or Erythromycin PO 21d
- MUST tx partners
Nongonococcal / Nonspecific Urethritis
Cause, S/s, Dx, Complications, Tx
(Nonreportable STI)
Chlamydial infection MCC
- S/s
- asymptomatic
- dysuria w/ mild to moderate white or clear urethral discharge
- Tx
- Azithromycin 1 dose or Doxycycline 7d
Genital Herpes
S/s, Dx, Tx
(non-reportable disease)
HSV Type 1 and HSV Type 2
(Type 2 is 80% of initial and 98% or recurrent)
- S/s
- vesicles that progress to ulceration w/ pain, lymphadenopathy, fever
- persists in latent stages
- recurrent infections milder
- Dx
- serum PCR test
- Tx
- no cure- symptom management
- Acyclovir
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
S/s, Dx, Tx
Viral STD
- S/s
- condylomata acuminata (genital warts) - soft, skin-colored, whitish pink-to-reddish brown benign cauliflower painless growths
- Dx
- Papanicolaou test (Pap smear)
- Tx
- patient applied
- Podofilox, Imiquimod, Sinecathechin
- provider applied
- cryotherapy, Podophyllin resin, Trichloroacetic acid (TCA), Bichloroacetic acid (BCA), surgery
- vaginal/urethral/anal warts
- TCA, BCA, cryotherapy, surgery
- patient applied
Molluscum Contagiosum
S/s, Dx, Tx
- S/s
- benign viral infection of skin of face, hands, lower abdomen, genitalia
- taken into epithelial cells by phagocytosis
- Dx - clinical
- Tx
- spontaneous healing after months - but contageous until then
- curettage, liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy), silver nitrate, topical creams
- lifetime immunity once lesions heal
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Approach During Pregnancy
retrovirus that infects CD4 (helper) T cells - destroys T and B cell function
- perinatal transmission around L&D MCC of HIV infection in children
- HAART: highly active antiretroviral therapy
- initiated if viral load > 1,000 copies/mL
- undetectable load is the goal
- C-section and NO breastfeeding
- screen all pregnant patients w/ consent
Pediculosis Pubis
S/s, Dx, Tx

Parasite - Phthirus pubis (the crab louse)
- S/s
- mild to severe itching
- allergic sensations
- 2’ infections from scratching
- Dx - clinical
- Tx
- creme rinse
- shampoo
- lotion
- tx of clothes and bedding
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
S/s, Complications, Tx
accute inflammation caused by infection -
possibly migrated STI (untreated C/G MCC)
- S/s
- sudden, severe ab pain w/ fever or no sx
- cervical motion, uterine, adnexial tenderness
- salpingitis- inflammation of fallopian tubes
- oophoritis- inflammation of ovaries
- Complications
- infertility, ectopic pregancies
- Tx
- Admit if failed PO, questionable compliance, severe systemic illness, tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA)
- IV Cefotetan or Cefoxitin + Doxy
- IV Clindamycin + Gentamycin
- 25% require drainage
- MUST tx partners
- Admit if failed PO, questionable compliance, severe systemic illness, tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA)
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Classifications, Pathogens, Protective
inflammation of urinary epithelium after colonization
- Classification
- complicated vs. uncomplicated
- cycstitis- bladder inflammation
- pyeloneprhitis- upper urinary tract
- MC pathogens
- E. coli, Staph. saprophyticus
- virulence: evade/overwhelm defense, adherance to uroepithelium (pili, fimbriae), resist defense (biofilms)
- Protective mechanisms
- washed out during micturition
- low pH, high osmolality of urea
- Tamm-Horsfall proteins
- uroepithelium secretions
- ureterovesical junction
- women: mucus-secreting glands
Acute Pyelonephritis
S/s, Dx, Tx
infection of ureter, renal pelvis and/or parenchyma
- S/s
- flank pain
- fever, chills
- CVA tenderness
- purulent urine
- Dx
- WBC casts
- Tx
- antibiotics


