Infection 2.2- Streptococcus and Staphylococcus Flashcards
a) What is staphylococcus?
b) Name a coagulase positive staph bacteria
c) Give 3 virulent factors the above example expresses
d) Give 2 places where it is carried in the human body
a) gram positive cocci
b) coagulase positive staphylocci are S. aureus
c) S. aureus expresses a number of factors that can interfere w host defence mechanism:
- capsular polysaccharide
- protein A
- Leukocidin
* carried in skin and part of nasal cavity
Describe the structure of staphylococcus
- SECRETED FACTORS help make staph virulent
- It produces TOXINS; TTST-1, enterotoxins, alpha-haemolysins; affects RBC’s
- Has invasins; Panton-Valentine Leukocidin; allows staph to invade WBC’s especially neutrophils; by bursting them, this causes the release of granulocytes and enzymes
- These recruit immunie system to that point therefore causing an intense autoimmune response
- Has ADHESINS, binding proteins
Why does staph produce coagulase and kinase and describe the mechanism?
to hide in the body
- Bacteria produce coagulase
- Clot forms around site of bacteria; coagulase recruits clotting proteins to site of infection; immune system does not recognise lot as a bacteria/foreign body
- Bacteria later produce kinase, dissolving clot and releasing bacteria;
release of kinase breaks down the clot therefore allows bacteria to enter bloodstream and circulate.

How can S. Aureus damage the host?
Staph aureus can release:
- Membrane Damaging Toxins
- Superantigens; enterotoxins and TSST
What types of toxins can S. aureus produce?
- Direct tissue invasion; skin infection, pneumonia, endocarditis, osteomylitis
- Exotoxin; toxin-mediated staphylococcal diseases;
- Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSST-1)
- Staphylococcal Scalded skin syndrome
- Staphylococcal food poisoning
What infections does Staph cause by direct invasion?
- Pneumonia
- Skin infections (s . epidermis)
How does S. aureus cause osteomyelitis?
abscess forming on bone—> bacteria move cell into shaft
painful
What does the coagulase test do?
differentiates S. aureus(positive) from Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus (CONS)
How does the coagulase test work?
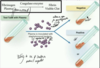
Describe the protective features of the skin against Staph aureus
keratinised cells
multi-layered skin; difficult to enter
sebaceous glands which produce antibacterial peptides
Langhan’s cells ie APC’s
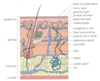
What are the routes of infection for Staph?
- Skin; pores, hair follicles
- Wounds; scratches, cuts, burns
- Insect and animal bites
What is a cutaneous abscess?
localised collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface
What is cellulitis?
- acute bacterial infection of the skin and subcutaenous tissue
- most often caused bys staph and strep
In adults, seen on legs, face, arms
In children, see on face and anus
Cellulitis on face could lead to dangerous eye infection
What can be seen in cellulitis
- warm red extremities on skin
- blisters in skin and waxy appearance because infection is deep in skin
*
Who is at risk of cellulitis?
people with weak immune system
people handling fish, meat, poultry or soil WITHOUT USING GLOVES
Where does cellulitis occur?
adults; face, legs, arms
children; face, anus
cellulitis on face could lead to a dangerous eye infection