IMMS Flashcards
What is this?

ALCIAN BLUE
- GAG-rich
- mucous
- mast cells
- cartilage
BLUE
What is this?
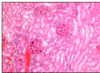
EOSIN
- colloidal proteins
- plasma
PINK
EOSINOPHILIC = ACIDOPHILIC
What is this?

IRON HAEMATOXYLIN
- nuclei
- elastic fibres
BLACK
What is this?

PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF (PAS)
- hexose sugars (complex carbs)
- goblet cell mucins
- cartilage matrix
- glycogen
- basement membranes
- brush border
MAGENTA (DARK PINK)
What is this?

ROMANOVSKY/LEISHMANN’S (BLOOD FILMS)
- Chromatn/nuclei and neutrophil granules (PURPLE)
- eryhtrocytes/eosin granules (RED/PINK)
- lymphocyte/monocyte plasma (PALE BLUE)
- basophil granules (DARK BLUE/PURPLE)

TOLUIDINE BLUE
- nuclei/ribosomoes (DARK BLUE)
- cytoplasm (PALE BLUE)
- cartilage/matrix/mast cell/GAG rich (BRIGHT PURPLE)

VAN GIESON’S TRICHROME WITH HAEMATOXYLIN COUNTER STAIN
- collagen (PINK RED)
- cell cytoplasm (YELLOW/OLIVE GREEN)
- nuclei (BLACK)
- elastic tissue (DARK BROWN)
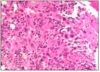
HAEMATOXYLIN
- nuclei
- RNA
BLUE
BASOPHILIC STRUCTURES = BLUE

SILVER STAIN - NEURONS
- neurons are large
- 25-60 microns
- because of slide thickness you cannot see all processes
- 1-5 dendritic processes
- metabolically active
- fully differentiated
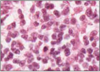
LYMPHOCYTE SIZE
- small = 5 microns
- little cytoplasm as dormant and not fully differentiated
- metabolically inactive
- minimal rER
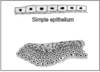
EPITHELIA
- barries
- single layer = simple
- multi layer = stratified
- stratified = protection

SIMPLE COLUMNAR
- height > width
- oval nucleus
- longer axis perp. to base of cell
- often microvilli or cilia at apical membrane
- GUT ENTEROCYTES and RESPIRATORY TRACT
left = gallballder
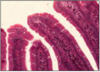
INTESTINAL EPITHELIUM
- enterocytes w/ goblet cells
- epithelia sit on BM - permeability barrier between epithelium and connective tissue
- microvilli at apical surface = BRUSH BORDER
- brush border - increase SA / attachment of exo-enzymes
- samll intestine = simple columnar

MICROVILLI/INTESTINAL WITH PAS AND HAEMATOXYLIN
- microvilli with carb. rich GLYCOCALYX
- goblet cells and BM rich in HEXOSE
- stain magenta

CILIATED SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
- nose/larynx/bronchial tree/fallopian tube
- SIMPLE COLUMNAR EP w/ goblet cells and cilia
- cilia = 2 microns
LEFT = NOSE
stained with H&E and ALCIAN BLUE
cilia movement by tubulin and dynein

CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM
- square
- round nucleus
- @ducts of exocrine glands - sweat glands, salivary, pancreas
- kidney tissue

SQUAMOUS
- outer surface of most thoracic and abdominal organs
- simple squamous epithelium (SEROSA)
- also lines pleural and peritoneal cavities
- air sacs of lungs (alveoli)
- FLATTENED
- CYLINDRICAL/ELLIPTICAL NUCLEI @ base of cell
LEFT = serosa @ outer wall intestine
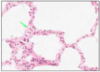
AIR / BLOOD BARRIER
- septa = capillaries covered by simple squamous ep
- typically 1 micron
- overall thickness = 5-10 microns
- with 2x capillary endothelial cells, 2x T1 pneumocytes and capillary lumen

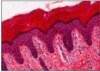
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS
- mouth, throat, oesophagus, anus, vagina
- cells replaced from below
- stem cells (mitosis capable) at basal layer
- sloughed off from top
this slide = moist non-keratinised stratified squamous epithelium at mouth
(moist from glandular secretion)
KERATINISED STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS
- epidermis
- lower layers epidermis similar to stratified squamous
- upper layers syntehsise unique collection of proteins - interact with cytoskeleton of cell to produce keratin
- keratine - dense protein, fills cytoplasm of cells = tough and waterproof
- when full of keratin cells die and are sloughed off
this slide - hairless skin @ lower lip
blue/purple = living
pink = dead keratinised squames
@ boundary =layer with blue keratohyaline granules
STRATUM GRANULOSUM - intermediate with blue grans
STEM CELLS @ basal layers
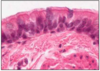
PSEUDOSTRATIFIED
- multilayered but when stretched flattens
- TRACHE AND BRONCHI
- @urinary tract = specialised UROTHELIUM
distinguish from stratified
all cells in contact with BM
cells replaced by lateral migration not vertical
this slide - trachea
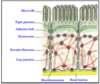
CELL JUNCTIONS
- bound tightly together to prevent macromolecule or fluid movement
- DESMOSOMES
- TIGHT (ADHERENT) JUNCTIONS
- GAP JUNCTIONS

GLANDS
- epithelial in origin - develop as ingrowths
- exocrine glands to surface by ducts
- fluid, lubricants, enzymes
MUCUS - separate acini from serous, occasionally mixed
PALE - flattened nucleus at base of cell
SEROUS
DARK - round nuclei

CONNECTIVE TISSUE - INTRO
- extracellular fibre scaffold - COLLAGEN/ELASTIN
- jelly-like matrix - hydrophilic polysaccharide polymer - GAG - glycosaminoglycans
- GAG - synthesises @ epithelial cells, muscle, cartilage, bone
- COLLAGEN/ELASTIN synthesised by fibroblast

CONNECTIVE TISSUE - TERMINOLOGY
SOFT - flexible/gel-like
- fibrous - collagen/elastic/reticulin (with silver = black lines)
LOOSE IRREGULAR - few visible fibres/random orientate
DENSE IRREGULAR - large number of fibres/little matrix
DENSE IRREGULAR - large number of fibres - long parallel bundles
- fatty - mainly fat cells with intervening capillaries
HARD - bond

DENSE IRREGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE
- dermis of scalp
- long fibres of collagen in many directions
- fibres stain pink
- fibres with dark nuclei (fibrobalsts) alongside
- collagen fibres not uniform thickness
- INSET - fibroblast
- COLLAGEN FIBRES = EXTRACELLULAR

DENSE REGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE
- ligament
- thick ribbons of parallel collagen
- fibroblasts at layer between
- compact and regular
COLLAGEN NEITHER ELASTIC NOR CONTRACTILE
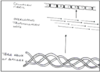
COLLAGEN (TROPOCOLLAGEN = 300n)
- 12 types
- NEITHER ELASTIC NOR CONTRACTILE
TYPE
- SKIN/BONE/TEETH/ORGAN CAPSULES
- CARTILAGE
- LIVER/KIDNEY/SPLEEN/ARTERIES/UTERUS (reticulin)
- BASEMENT MEMBRANES (sheet like)
- PLACENTA
STRUCTURE - overlapping linear strands TROPO-COLLAGEN
TC secreted from fibroblasts - arranged to fibrils extracellularly
overlapping gives rise to characteristic banding
TC = 3 linear polypeptide chains @ alpha helix

LOOSE AND DENSE
- dense irregular at penis erectile compartment (inner) forms a capsule/sheath
- this is common between cells of most organs and tissue
- outside = loose
@ penis - an inextensible capsule around erectile compartments means extra blood makes it turgid
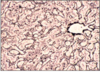
RETICULIN (TYPE 3 COLLAGEN) - SILVER STAIN
- shape and intergrity of many organs by extracellular fibres
- coarser elements = T1
- fine frameworkd = T3/reticulin
TISSUE OF RETICULO-ENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM ie. lymph nodes, spleen, liver
RETICULIN FORMS BRANCHED FIBRES
- most collagen forms linear fibres

ELASTIC FIBRES
- microfibres of fibrillin set in amorphous matrix of elastin
- fine fibres or sheets
- PINK WITH H&E - tough to distinguish collagen
- DARKER STAINING
this slide - large elastic artery
concentric sheets of elastic tissue (in vessels near heart)
stain pink with eosin
difficult distinguish collagen (GLISTENS)
perforated elastic sheets with snake-like character

ELASTIC FIBRES 2
- with elastic Van gieson’s trichrome
- DARK BROWN

FATTY CONNECTIVE - DIPOSE
- white and brown
- white fat more abundant
- large cells with single fat droplet
- protect vital organs and energy store (INSULATION AND PACKING)
- usually deposited alongside capillaries therefore many vessels
- brown fat abundant in new born
- limited in later life (chest and shoulder-blade)
- multi-locular - many droplets per cell
- generation of heat via oxidation of FAs

NERVES
- supporting cells OLIGODENDROCYTES (CNS), SCHWANN CELLS (PNS) produce myelin (insulate/conductive)
- cell bodies mainly at CNS or sensory at DRG
- myelin lost in tissue processing
this slide - axons in transverse section
- each axon surrounded by Schwann cell cytoplasm
- with dark staining lamina = myelinated
- A - Schwann cell nucleus
- B - axon w/myelin sheath
- C - unmyelinated axon
- D - myelin sheath
Schwann cells may contain many unmyelinated axons
Myelin linkage: adhesion proteins
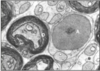
SCHWANN CELLS AND AXONS SUPPORTED
- each axon with continuous Schwann cell chain
- MYELINATED - 1:1 relationship with Schwann
- UNMYELINATED - several:1
MYELINATED AXONS - generally larger (greater diameter) with increased velocity of conduction
MYELIN
membranous, bilipid (phospholipid), proteins inserted between layers
Predominantly phospholipid = SPHINGOMYELIN
MESAXON - where 2 limbs of Schwann/Oligo around axon fuse = focal point where myelin inserted in myelin sheath

PERIPHERAL NERVES
- mix of motor/sensory axons
- surrounded by Schwann cells
- between axons = connective tissue network (fibres and cells)
CONNECTIVE TISSUE NETWORK
- endoneurium
- perineurium
- exoneurium
5 NERVE FIBRES - with many axons - surrounded by endoneurium and perineurium
Flattened nuclei = fibroblasts
Rounded nuceli = Schwann
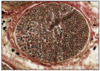
ISOLATED PERIPHERAL NERVES (OSMIUM TETROXIDE STAIN) - TRANSVERSE
- lipid of myelin sheath extracted in processing
- if treat nerve with osmium tertroxide renders myelin insoluble
- myelin = brown/black
this slide - osmium tetroxide and H&E
various diameters
many axons = nerve fibre (w/perineum)
many nerve fibres = nerve (peripheral) w/epineurium

ISOLATED PERIPHERAL NERVES (OSMIUM TETROXIDE STAIN) - LONGITUDINAL
- worm-like
- constrictions = NODES OF RANVIER - boundary between one Schwann cell and next
MYELINATED = 10-100 m/s
UNMYELINATED = 1-20 m/s

SYNAPSE
- large number of neuro-secretory vesicles @ presynaptic space
- dark staining either side of synapse

NERVE CELL BODIES (SILVER)
- either @ CNS or in discrete ganglia close to spinal cord
- exception is PNS with clusters close to organ innervated
- silver stain has affinity for cytoskeleton of cells
- neurons have developed cytoskeleton, therefore stain heavily
GOLDEN BROWN - nucleus pale but nucleolus black
cytoskeleton - mictrotubules (tubulin and dynein) = axonal transport i.e. vesicles from golgi to end and back/neurofilaments (intermediate architecture) = axonal diameter
no. processes
unipolar - sensory
bipolar - interneurons
multipolar - motor neurons

NERVE CELL BODIES (H&E)
- sensory cell bodies at DRG
- large
- one axon
- one major dendrite
- appear more rounded than motor neurons
this slide - DRG with large cell bodies
DARK STAINING PATCHES IN PERIKARYON (cytoplasm around nucleus) = NISSL SUBSTANCE (aka rER)
nissl substance synthesis of proteins for export from cell or inclusion in membrane


