Imaging Flashcards
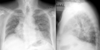
ILD

COPD - emphysema

NRDS
ground glass and low lung volumes

ILD

ILD

consolidated lobar pneumonia with empyema

pleural effusion

ARDS: bilateral opacities

ARDS (L); normal (R)
Which lobe(s) can silhouette the RH border?
RML or RLL
Which lobe(s) can silhouette the LH border?
Lingula of LUL
Which lobe(s) can silhouette the posterior heart border and/or posterior L hemidiaphragm?
LLL
Which lobe(s) can silhouette the anterior R hemidiaphragm?
RML
Which lobes can silhouette the posterior R hemidiaphragm?
RLL
Interpretation of a silhouette sign
Atelectasis or consolidation

Atelectasis: upward displacement of minor fissure due to RUL collapse w/ mediastinal silhouette sign.

Resorption atelectasis of LUL caused by tumor compressing airway; tracheal/mediastinal shift towards collapse
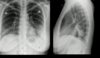
LLL pneumonia; consolidation w/ silhouette sign

Consolidation due to cardiogenic pulmonary edema (silhouette sign)
Atelectasis vs. consolidation?
Both produce airless lung; atelectasis causes decreased lung volume, while consolidation does not.

air bronchogram: seen with consolidation or atelectasis

Interstitial fibrosis: perilymphatic interstitial fluid, forming Kerley B lines in secondary septations between lobules.

Pulmonary fibrosis, causing reduced lung volume

emphysema

Pleural effusion: opacity spanning enitre chest, loss of RML volume due to compression, and meniscus

sarcoidosis

Sarcoidosis: adenopathy

lymphoma

Lymphoma


