IC's, Utility (+maximisation), and Budget Flashcards
Budget constraints, indifference curves, utility. Utility maximisation with calculus
What does this mean?

Strict preference for a over b
What does this mean?

Indifferent between a and b
What does this mean?

Weak preference for a over b
What is an indifference curve?
An indifference curve shows the preferences of one consumer
What are the properties of indifference curves? (5)
- Bundles on indifference curves farther from the origin are preferred to those on indifference curves closer to the origin
- Every bundle lies on an indifference curve
- Indifference curves cannot cross
- Indifference curves slope downwards
- Indifference curves cannot be thick
What is a utility function?
A function that tells us about the relative ranking of various consumption bundles.
It:
- Describes the location and form of all IC curves
- Assigns each IC curve a utility value
E.g - The Cobb Douglas Utility Function:
U(q1,q2)=q10.5q20.5
Utility is an ordinal measure, what does this mean?
This means that each value of utility doesn’t directly represent something, a utility of 8 doesn’t equal double the happiness of a utiltiy of 4, we just know that it is better.
What is the marginal rate of substitution (MRS)?
The willingness to substitute between goods (for one consumer)
In context, the maximum amount of one good that a consumer will sacrifice to obtain one more unit of another good.
It is the gradient at a particular point on the indifference curve.
What does the MRS depend on?
The marginal rate of substitution depends on the marginal utility of consuming each good for the consumer.
What is marginal utility?
The extra utility a consumer gets from consuming one more unit of a good. Ceterus parabus.
In maths the marginal utility of one good (q1) is the partial differential of the utility function with respect to q1
(the gradient of q1 in the utility function)

How do you calculate the Marginal Rate of Subtitution?
Explanation of the maths:
The partial differential of the utility function with respect to q1
over
The partial differential with respect to q2
all multiplied by -1.
This is the same as -1 multiplied by the marginal utility of 1 over the marginal utiltiy of 2. (-1*MU1/MU2)

Draw an indifference curve for perfect substitutes, why is it shaped this way?
Perfect substitutes create diagonal lines as they cannot be consumed together.

Draw indifference curves for perfect complements
Perfect compliments must be consumed together.
Therefore the indifference curves are straight.

What is the budget constraint?
A line that shows the consumers budget
Underneath the line the consumer can afford all the bundles of goods.
(p1*q1)+(p2*q2)
Name the 6 assumptions of the budget constraint
- There are only 2 goods the individual might consume
- The prices of those goods are p1 and p2
- M is the amount of income available to the consumer
- It is for one period only, there is no saving for the future.
Solve the budget constraint for q2

What does the slope of the budget line represent and what do the values mean?
The slope is -p1/p2
It represents the Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT), this is the rate at which the market substitutes one good for another.
A value of -1/3 means that the market is willing to give up 1 of good one for 3 of good two.
What happens if the price of one or both goods changes?
If the price of one of the goods changes the budget constraint will shift only on that axis, thus affecting the MRT (logically if one good is cheaper you’ll be willing to give up less to get it).
If the price of both goods decreases equally then the budget constraint will shift on both axis’ and the slope will not change.
How does a consumer maximise their utility when choosing a bundle of goods between lots of indifference curves?
The bundle of goods that is on the highest indifference curve and tangential with the budget constraint is the optimal bundle.
The point at which this happens is where MRS = MRT (the gradient of the budget constraint and indifference curve are identical).
so: -MU1/MU2 = -p1/p<span>2</span>
How are the rules of choosing an optimal bundle different for perfect substitutes?

How are the rules of choosing an optimal bundle different for perfect compliments?

Explain the difference in effect on the budget constraint between giving a consumer cash versus giving them food stamps

What is the MRS? Definition, equation, explanation.
The MRS is the Marginal Rate of Substitution, the willingness to give up one unit of one good in order to get more of another good (for one consumer).
Starting with a Utility function , U(q1, q2)
Take a partial derivative of U to obtain the marginal utilities, U1 and U2
The formula for the MRS comes from the total derivative of U
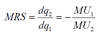
How can you find the consumers optimal choice (by maximising their utility)?
Maximise U subject to the budget constraint using the Lagrangian function. The first term will be the utility function, the budget constraint must be arranged into c=xy and then entered in also.
- After partial differentiation get rid of lambda from the x and y derivates by dividing the first equation by the second (dividing the x derivative by the y).
- Then use this new equation you just created with the lambda partial derivative (equation 3) to solve for quantities q1 and q2.




