How to Manage Orthopaedic Conditions Flashcards
(70 cards)
What are the 3 causes of bone disorders?
- Trauma
- Stress
- Pathological

What are the two categories of mechanisms of bone fractures other than trauma?
- Abnormal stresses on normal bones
- Normal stresses on abnormal bones
How does abnormal stress on a normal bone cause a bone fracture (5 steps)?
- Overuse
- Stress exerted on bone > Bone’s capacity to remodel
- Bone weakening
- Stress fracture
- Risk of complete fracture

What are the activity related causes of abnormal stress on normal bone that cause bone fracture (3)?
- Athletes
- Occupational
- Military

What are the pathological causes of normal stress on abnormal bones fractures (5)?
- Osteopenia / Osteoporosis
- Vitamin D deficiency / Calcium deficiency
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- Pagets disease
- Malignancy

What is the pathophysiology of osteopenia / osteoporosis?
- Osteoclast activity > Osteoblast activity → Disrupted microarchitecture
What are the causes of osteopenia / osteoporosis (3)?
-
Secondary osteoporosis:
- Hypogonadism
- Glucocorticoid excess
- Alcoholism
- Associated with fragility fracture (hip / spine / wrist)
- Low energy trauma (fracture)

What T score on a DEXA scan diagnoses osteoporosis?
- < -2.5

What is the gender epidemiology of osteopenia / osteoporosis?
- Female:Male 4:1
What is the pathophysiology of Rickets / Osteomalacia?
- Vitamin D facilitates calcium, magnesium & phosphate absorption
- Inadequate calcium or phosphate leeds to defect in osteoid matrix mineralisation
- Osteomalacia / Rickets

What is the cause of Rickets / Osteomalacia?
- Vitamin D or calcium deficiency in children (Rickets) or adults (osteomalacia)

What are the effects of Rickets / Osteomalacia?
- In rickets (paeds), the epiphyseal growth plates can become distorted under weight of the body
- In osteomalacia (adults), increased risk of fracture

What is the physiology of osteogenesis imperfecta?
- There is a reduction in type I collagen secretion
- Collagen is an extracellular matrix protein secreted by fibroblast & osteoblasts
- Collagen provides mechanical strength and rigidity to bone

What is the causes of osteogenesis imperfecta?
- Autosomal recessive (20%) / dominant (80%) condition

What are the effects of osteogenesis imperfecta (3)?
- Increased fragility of bones
- Increased bone deformities
- Increased blue sclera
- Affect hearing

What is osteogenesis imperfecta often mistaken as in children?
- Can be mistaken as NAD in children – diagnosis is important medicolegally

Outline the pathophysiology of Paget’s disease (7 steps).
- Increased osteoclastic activity
- Mixed osteoclastic - osteoblastic activity
- Excessive bone break down & disorganised remodelling
- Deformity, pain, fracture or arthriti
- Osteoblastic activity
- Deformity, pain, fracture or arthritis
- Malignant degeneration
- Excessive bone break down & disorganised remodelling
- Mixed osteoclastic - osteoblastic activity

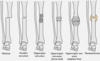
What kind of fracture pattern is this?

Transverse
What kind of fracture pattern is this?

Oblique
What kind of fracture pattern is this?

Spiral
What kind of fracture pattern is this?

Comminuted
What is an impacted fracture?
- One fracture is driven into the other as a result of compression

What is a greenstick fracture?
- Partial fracture in which one side of the bone is broken

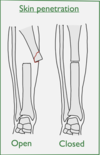
What is an open fracture?
- A fracture in which at least one end of the bone penetrates the skin - presenting a potential risk of infection