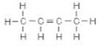Honors -Final Exam Flashcards
How to calculate neutrons:
of Neutrons = Atomic Mass Number - Atomic Number
Electron Configuration
A shorthand method of writing the location of electrons by sublevels.

How do the bulk properties of polymers effect their behavior?
Linear structure - thermoplastics (can be melted and thus recycled.)
Branched chains - strengthen the structure of thermoplastics
Loosely Cross Linked Chains - loosely cross linked structures form an elastomers (rubber)
Tightly Cross Linked Chains - thermoset plastics (can not be melted and thus can not be recycled)
A polymer’s architecture affects many of its physical properties including, but not limited to, solution viscosity, melt viscosity, solubility in various solvents, glass transition temperature and the size of individual polymer coils in solution.
Combustion
Any compound formed from only Carbon an Hydrogen (fuel) added to Oxygen to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
What happens to an exothermic reaction when temperature is increased?
Heat is a product, so the reaction shifts to the left to make more reactant.
How to determine if a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated.
Add more solute and observe the results.

Acids
Electron acceptors.
Yeild H+ Ions in solution.
H+ donor.

Write the formula for Mg²⁺ and PO₄³⁻
Using the criss-cross method and subscripts to insure sum of charges is zero: Mg₃(PO₄)₂
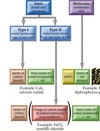
Ionic Compounds
Conduct Electricity when melted or dissolved in water because….

What happens to an endothermic reaction when temperature is increased?
Heat is a reactant, so the reaction will shift to the right to make more product.
The Mole
A unit of measure.
1 mole = the atomic mass of an element
and
1 mole = 6.02 E23 atoms, particles, molecules, units, etc.
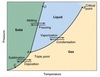
Solid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter. It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume.
Orbital
Sublevels can be broken down into regions called “orbitals”. An orbital is defined as the most probable location for finding an electron. Each orbital holds 2 electrons.

Thermochemistry
The study of energy changes during a chemical reaction or change of state (solid, liquid, gas).
Ionic Compounds
two words, first names cation second names anion. Indicate charge of transition metal cation by Roman Numeral. MgCl₂ = Magnesium Chloride Cr(NO₃)₃ = Chromium(III) Nitrate SnCl₂ = Tin(II) Chloride
Calculate the % Yield of solid silver chromate produced in the following reaction:
K₂CrO₄ + 2AgNO₃ → Ag₂CrO₄ + 2KNO₃
In the reaction there was .500g of the limiting reactant AgNO₃. In the actual experiment, .455g of Ag₂CrO₄ was produced.
Calculating the Theoretical Yield of Ag₂CrO₄ that was produced:
0.500g AgNO₃ x (1 mole AgNO₃ / 169.9g AgNO₃) x
(1mole Ag₂CrO₄ / 2 mole AgNO₃) x (331.7 g Ag₂CrO₄ / 1 mol Ag₂CrO₄) =0 .488g Ag₂CrO₄.
Find the ratio of the actual yield (.455g) to the theoretical yield (.488g) …
% Yield = (.455g Ag₂CrO₄ ÷ .488g Ag₂CrO₄ ) x 100 =
93.2 %
Amphoteric

Acid or Base
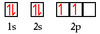
What is the electron configuration of Vanadium?
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d³
[Ar] 4s² 3d³
Intramolecular Forces
Attractive forces WITHIN a molecule (Ionic & Covalent Bonds)
These bonds are stronger than intermolecular forces.
Single Replacement
An element and a compound are located on each side of the equation. The Activity Series must be checked to determine if the reaction will occur. If the reaction occurs, the element on the reactant side switches with the similarly charged ion within the compound on the reactant side.
A + BC –> AC + B

Melting
Make or become liquefied by heat. (Solid to Liquid)
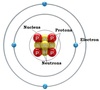
Atomic Number
Identifies an element. The number of protons. For a neutral atom, the number of electrons will equal the number of protons. For an ion (charged atom) the number of electrons will not be the same as the atomic number.

Reactants

Substances being mixed in a chemical reaction. The left side of the equation.
Predict the products of and write a balanced equation from the following statement:
H₂O₂ →
H₂O₂ → H₂ + O₂
DECOMPOSITION
Is the solution unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated, if I have 60g of Potassium Nitrate in 100g of Water at 30 C?

Supersaturated

What is the orbital diagram for Magnesium?

Naming Ionic Bonds
State the name of the metal followed by the nonmetal with the ending changed to “ide”. If the metal is a transition metal, add a (Roman numeral). AlCl₃ = Aluminum Chloride CuCl₃ = Copper (III) Chloride
The three types of radiation and their penetration abilities:

Non Polar Covalent
A type of covalent bond between two atoms in which electrons are shared equally.
Percent Yeild
A measure of the efficiency of a reaction carried out in the laboratory.

Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
A. nitrogen B. oxygen C. fluorine D. neon
N
(least number of protons attracting the electrons on the energy levels)
CaCl₂ + K₂CO₃ →
CaCl₂ + K₂CO₃ →CaCO₃ + 2KCl Double Replacement
Writing Formulas for Ionic Bonds
Absolute Value Criss Cross Oxidation #’s
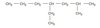
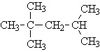
What is the IUPAC name of


Products of an acid/base reaction
Salt + Water
Unsaturated
Contains less solute than it can at that temperature.

Atomic Mass Number
Also known as the Mass Number or Atomic Mass.
Ionic Bond
Metals GIVE electrons, Nonmetals TAKE electrons
Coefficients
The large numbers in front of chemical formulas. Represents the number of molecules of the substance.
2Al

What element is represented by this orbital diagram?

Carbon
Quantum of Energy
Absorbed when an electron moves from its ground state to its excited state.
Lone Pairs
Electron pairs which are not involved in bonding. They do however, affect the shape because electron pairs repel other electron pairs.
Oxidation Number
Ion Charge - number of electrons transferred to or away from an atom when it becomes an ion.

Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy can not be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction
Calculate the volume required to prepare the diluted solution: Given 6.0M NaOH; need 5.0L of 0.10M NaOH.
M1V1 = M2V2
V1 = (M2V2)/(M1)
V1 = 0.083L
Predict the products and write a balanced equation from the following word statement:
Methane (CH₄) plus Oxygen Gas forms:

The Dissolving Process
- The solvent surrounds the outer surface of the solute.
- Individual Solute Ions are “stripped” away from the surface due to their attraction to the solvent particles.
- This exposes more particles to the solvent and thus the process continues.

Intermolecular Forces
Attractive forces BETWEEN molecules.
Van Der Waals or London Dispersion Forces are the weakest type of intermolecular force and hydrogen bonds are the strongest.

C₄H₆ + O₂ →
2C₄H₆ + 7O₂ →4CO₂ + 6H₂O Combustion
How to determine if a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated.
Add more solute and observe the results.

Write a chemical equation from the following word equation:
Lithium chloride reacts with magnesium nitrate to form lithium nitrate and magnesium chloride.
2LiCl + Mg(NO₃)₂ –> 2Li(NO₃) + MgCl₂
Describe crosslinking.
A process that makes a polymer more rigid and resistant to heat. The cross links in slime are hydrogen bonds.

Write a chemical equation from the following word equation:
Magnesium reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
2Mg + O₂ –> 2MgO
How can you make things dissolve faster?
- Agitation (stirring)
- Temperature
- Increase Surface Area (Grind or Crush)
Is the solution unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated, if I have 60g of Potassium Nitrate in 100g of Water at 30 C?

Supersaturated

Specific Heat
the amount of energy in the form of heat, calories or joules, required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance 1°C
What is the solubility of Potassium Nitrate at 50 C?

86 g Potassium Nitrate

In the equation:
4Al + 3O₂→ 2Al₂O₃,
how many moles of Al₂O₃will be produced if there are 3.75 moles of O₂?
- 75 moles O₂ x (2 moles Al₂O₃/ 3 moles O₂) =
- 50 moles Al₂O₃
Subscripts
Small numbers to the lower right of chemical symbols. Represent the number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
0₂
Photon
Energy given off in the form of light by an excited electron. Otherwise known as a “quanta of light”.

Ions
Atoms or groups of atoms with a charge. To have a charge an atom must have gained or lost electrons. If an atom gains electrons it becomes negatively charged. If an atom loses electrons it will become positively charged.

Heat
Energy that transfers from one object to another due to a difference in temperature between them. Heat always flows from the warmer to the cooler object.
Orbital Diagram
Shorthand method of writing the location of electrons by orbital.

Activation Energy
The minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction

Rules for Writing Lewis Dot Structures
- Total the Valence Electrons and Update during each step.
- Form a single bond between the central atom and each surrounding atom (each bond uses two electrons).
- Place electrons around the outer atoms until you run out or they each have eight electrons around them. (Hydrogen and Helium can only have two electrons around them).
- Place any remaining electrons around the central atom.
- Does each atom other than hydrogen have eight electrons around it?
- Rearrange (share) electrons so that all atoms other than hydrogen have eight electrons around them.
Which has the smallest atomic radius?
A. fluorine B. chlorine C. bromine D. iodine
F
(least number of energy levels)
Half Life
The time it takes for the amount of a radioactive element to decay by half.
immiscible
Will not dissolve in water.
What at problems where there with the Rutherford model of the atom?

In the equation:
2Na + Cl₂→ 2NaCl
How many grams of NaCl are produced from 3.75 moles of Cl₂?
- 75 moles Cl₂ x ( 2moles NaCl/1 mole Cl₂ ) x ( 58.5g NaCl / 1 mol NaCl =
- 75 g NaCl
pH Scale
pH = (-) log [H+]
pOH = - log [OH-]
pH + pOH = 14
[H+] = 2nd Log (-) pH
[OH-] = 2nd Log (-) pOH
[H+] [OH-] = 1E-14

Products

Substance(s) being made. Right side of the equation.
Exothermic
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of light or heat.
Anion
Negatively charged Ions. Anions are negatively charged because they have gained an electron(s) (electrons are negative). In general, anions are nonmetals.

Predict the element formed and write a balanced nuclear equation for the following statement:
Uranium-238 decays by alpha emission to form __________.

Solvent
The component doing the dissolving.
The component in the largest amount.
Water is the universal solvent.

Endothermic
Reaction in which the system absorbs energy from its surroundings in the form of heat.
Heat of Fusion
The energy required to change a gram of a substance from the solid to the liquid state without changing its temperature.
Le Chatlier’s Principle


Properties of Bases

Bitter and slippery
Kinetic Energy
The energy an object has due to its motion.

What is the orbital diagram for Silicon?

Nucleus
The center of an atom. Contains the protons and neutrons. Since neutrons have no charge and protons are positively charged, the nucleus has an overall positive charge.

Gas
One of four main states of matter, composed of molecules in constant random motion. Unlike a solid, a gas has no fixed shape and will take on the shape of the space available. Unlike a liquid, the intermolecular forces are very small; it has no fixed volume and will expand to fill the space available.
Vapor Pressure
The pressure of the vapor resulting from evaporation of a liquid (or solid) above a sample of the liquid (or solid) in a closed container.
How much solute will not dissolve if I have 80g of Potassium Nitrate in 100g of Water at 30C?

35g Potassium Nitrate



What is the electron configuration of Krypton?
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶
[Ar] 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶
Properties of Acids

Sour
What is the molarity of a solution in which 58 g of NaCl are dissolved in 1.0 L of solution?
1.0 M
Polyatomic Ionic Formulas
- Metal written first, Polyatomic Ion is written second 2. Use criss-cross method and subscripts to insure sum of charges = 0 3. When using a subscript for polyatomic ions: place a parentheses around the polyatomic formula, put the subscript outside of the parentheses
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created or destroyed during a chemical reaction - it is conserved.
Mass Reactants = Mass Products

How does a reaction at equilibrium shift when reactants are removed?
Reaction shifts to the left to make more reactant.
How does a reaction at equilibrium shift when products are removed?
Reaction shifts to the right to make more product.
IUPAC Rules for Alkane Nomenclature
IUPAC Rules for Alkane Nomenclature
- Find and name the longest continuous carbon chain.
- Identify and name groups attached to this chain.
- Number the chain consecutively, starting at the end nearest a substituent group.
- Designate the location of each substituent group by an appropriate number and name.
- Assemble the name, listing groups in alphabetical order using the full name (e.g. cyclopropyl before isobutyl).
The prefixes di, tri, tetra etc., used to designate several groups of the same kind, are not considered when alphabetizing.
Which has the largest atomic radius?
K
Na
Rb
Li
Rb
(most energy levels)
Plastic
Long chain organic compounds that can be molded or formed into shapes, films, or fibers.
What do the symbols in the following equation represent:
Q=mC(Delta T)

How many atoms are in 2.7 moles of iron?
2.7 moles Fe x (6.02x10²³ atoms Fe/1 mole Fe) =
1.6 x 10²⁴atoms Fe
Diatomic Molecule
If these elements appear by themselves in an equation, the must be in pairs with the subscript 2.
Na + MgCl₂ →
2Na + MgCl₂ →2NaCl + Mg Single Replacement
Intramolecular Forces
Attractive forces WITHIN a molecule (Ionic & Covalent Bonds)
These bonds are stronger than intermolecular forces.
miscible
Will dissolve in water.
Predict the products of and write a balanced equation from the following statement:
HCl + Zn →
2HCl + Zn →ZnCl₂ + H₂
Single Replacement
Principle Energy Level
The possible locations around an atom where electrons having specific energy values (quantum number) may be found. Divided into sublevels s, p, d, and f.
K + Cl₂ →
2K + Cl₂ →2KCl Synthesis
Weak Acid
Weak acids are not fully ionized or dissociated.

Solute
The component being dissolved.
The component in the smallest amount.

How can hydrogen bonding affect the properties of polymers?
Different side groups on the polymer can lend the polymer to ionic bonding or hydrogen bonding between its own chains. These stronger forces typically result in higher tensile strength and higher crystalline melting points.
Radioactivity
When the nucleus of an atom becomes unstable and decays. This tends to happen to large atoms (larger than atomic number 83) becuase the number of protons to neutrons in the nucleus is unbalanced.

Boiling
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point.
Predict the products of and write a balanced equation from the following statement:
CuCl₂ + H₂S →
CuCl₂ + H₂S →CuS + 2HCl
Double Replacement
Balance the following chemical equation:
__C + __O₂ → __CO₂
1C + 1O₂ → 1CO₂
Mg + I₂ →
Mg + I₂ →MgI₂ Synthesis
IUPAC Rules for Alkyne Nomenclature
IUPAC Rules for Alkyne Nomenclature
- The yne suffix (ending) indicates an alkyne or cycloalkyne.
- The longest chain chosen for the root name must include both carbon atoms of the triple bond.
- The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest a triple bond carbon atom. If the triple bond is in the center of the chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where numbering starts.
- The smaller of the two numbers designating the carbon atoms of the triple bond is used as the triple bond locator.
- If several multiple bonds are present, each must be assigned a locator number. Double bonds precede triple bonds in the IUPAC name, but the chain is numbered from the end nearest a multiple bond, regardless of its nature.
Roman Numerals
Above groups/families Roman Numerals represent the number of valence electrons.
When writing the name of an ionic compound which includes a transition metal a Roman Numeral is used to denote the quantity of positive charge associated with that transition metal.
What element is represented by the following orbital diagram?

Fluorine

Polymers
Very long chains of repeating units (monomers)
(Simplest polymer: -(-CH₂CH₂CH₂CH₂CH₂-)- =Polyethylene)
Bases
Electron donator.
Yeilds OH- in solution.
H+ Ion acceptor.
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to change the temperature of a substance
Atmospheric Pressure
Pressure resulting from the collisions of atoms and molecules with objects.

How does a reaction at equilibrium shift when more reactants are added?
Reaction shifts to the right to make more product.
When is a photon emitted from an atom?
A photon is emitted as an excited electron returns to its ground state.

9.08 g of Al₂0₃ is equal to how many moles?
9.08 g Al₂0₃ x (1 mole Al₂0₃/101.96 g Al₂0₃) = 0.0890 moles Al₂0₃
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Crystalline Structure High Melting Point Rigid Strong Bond Conduct Electricity (when dissolved or melted) Good Insulators
9.08 g of Al₂0₃ is equal to how many moles?
9.08 g Al₂0₃ x (1 mole Al₂0₃/101.96 g Al₂0₃) = 0.0890 moles Al₂0₃
Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
A. nitrogen B. oxygen C. fluorine D. neon
N
(least number of protons attracting the electrons on the energy levels)
Ionic Compound Formulas
- Metal written first Nonmetal written second 2. Use criss-cross method and subscripts to insure sum of charges = 0
Liquid
Liquid is one of the four fundamental states of matter, and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds.
Summarize how to write formulas for ionics and covalents.

Gases deviate most from ideal behavior under conditions of very ______ temperature and very _______ pressure
low; high
Describe the Bohr Model of an atom.

VSPER
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
Most important aspect of determining the shape or geometry of a molecule. The molecule will adopt the shape which minimizes te electron pair repulsion.
Chemical Potential Energy
The energy stored in chemical bonds. (Lines with no Slope on the Heating Curve)
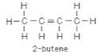
What is the IUPAC name of


How many atoms are in 2.7 moles of iron?
2.7 moles Fe x (6.02x10²³ atoms Fe/1 mole Fe) =
1.6 x 10²⁴atoms Fe
Kinetic Energy
In Thermochemistry, the energy an object possesses due to its change in temperature is called kinetic energy. (Sloped lines on the Heating Curve)
How many grams of KNO₃ should be used to prepare 2.00 L of a .500 M solution?
101 g KNO₃
How many moles are in 3.67 x 10²⁴ molecules of SO₂?
- 67 x 10²⁴ molecules SO₂ x (1 mole SO₂/6.02x10²³ molecules SO₂)=
- 10 moles SO₂
Compound Formation
Compounds are the result of the formation of chemical bonds between two or more different elements, whose atoms lose, gain or share valence electrons to complete their outer shell and attain a noble gas configuration.
This tendency of atoms to have eight electrons in their outer shell is known as the octet rule.