History + Exam Flashcards
Diarrhoea?
Diarrhoea is an increase in the amount of stool passed daily to over 300g, usually accompanied by increased frequency and loosening of stools.
Malaena?
dark, tarry, smelly stools caused by digested blood

Haematochezia?
bright red stools due to frank blood

Steatorrhoea?
pale, floating stools from undigested lipid

Loose Stools?
soft faeces with no increase in frequency or quantity
Diarrhoea can be caused by?
- infection of the bowel (infectious diarrhoea),
- inflammation of the bowel (IBD or diverticular disease),
- increased bowel motility (hyperthyroidism, anxiety, IBS),
- malabsorption of nutrients (coeliac disease, pancreatic insufficiency),
- obstruction overflow due to mass that only allows liquid stool to pass beyond it (hard faeces stuck in the bowel is a common cause of overflow diarrhoea, colon cancer and ovarian cancer can also cause overflow diarrhoea),
- medications (laxatives, colchicine, digoxin, metformin, thiazide diuretics).
Diarrhoea common diagnoses?

Diarrhoea diagnoses in elderly?
Neoplastic Disease - villous polyps, colonic adenocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer
Diverticular disease
Overflow diarrhoea secondary to constipation
Ischaemic colitis
Microscopic colitis
Bacterial overgrowth
Diarrhoea acute management?
ABC
Dehydration; main cause of mortality in this group, check HR, BP (postural drop, low BP, narrow mean arterial pressure), mucous membranes.
Electrolyte or pH disturbance; either excessive loss of ions in faeces or secondary to hypovolaemia.
Consequences of severe diarrhoea?
Shock (tachycardiac and hypovolaemic)
Acidosis (pH<7.35); This can be due to loss of ions or due to the presence of extra acidic ions (e.g. lactic acidosis due to tissue ischaemia).
Hypokalaemia; due to loss in faeces, can be corrected with fluid rehydration if kidney function is normal.

Characterise the stool; mucoid or jelly like?
infection by Salmonella or villous polyps in the colon, can be any disease causing inflammation of the bowel wall.
Characterise the stool; foul smelling and floating?
suggests malabsorption,
due to coeliac disease, pancreatic duct obstruction (pancreatic cancer, cystic fibrosis) or biliary insufficiency (recent cholecystectomy).
Characterise the stool; unusually pale?
lack of bile salts due to obstruction of biliary or pancreatic ducts (chronic pancreatitis, gallstones).
Characterise the stool bloody faeces?
if on toilet paper then anal pathology (anal fissure, haemorrhoids). If mixed in and red suggests colorectal pathology (UC, dysentery, colorectal carcinoma).
Change in bowel habit nocturnal diarrhoea?
suggests organic aetiology (rather than functional like IBS)
Change in bowel habit; do they rush to the toilet?
Urgency to defecate likely infectious diarrhoea or IBD.
Change in bowel habit; variable bowel habit?
IBS (in younger)
colorectal carcinoma (in older)
present as alternating normal, diarrhoea and constipation.
Change in bowel habit; tenesmus?
space occupying lesion in rectum (carcinoma).
Change in bowel habit; suffer from frequent diarrhoea?
infectious diarrhoea is typically one off.
Diarrhoea + vomiting?
infectious gastroenteritis.
Diarrhoea + abdo pain?
RIF pain is suggestive of terminal ileum inflammation (Crohns, Yersinia enterocolitica infection).
LIF pain is suggestive of diverticular disease.
Pain relieved by passing motion is IBS.
Diarrhoea + significant weight loss?
chronic=IBD, acute=infection.
Diarrhoea + eye problems, skin rashes, joint pain?
uveitis, scleritis, episcleritis, erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum, aphthous ulcers, enteric arthritis
= all features of IBD.
Risk factors Travelled abroad, eaten something unusual, know anyone else with similar symptoms?
infectious diarrhoea.
Risk factors stress/diet?
stress and low fibre are associated with IBS
Risk factors medications?
diarrhoea is most common medication side effect, look out for PPIs.
family history?
Of bowel disease; Crohns, UC, coeliac disease or rarer conditions like HNPCC
Exam clubbing (4)?
Crohns disease, UC, hyperthyroidism, coeliac disease are all causes.
Exam iritis, episcleritis, scleritis?
associated to Crohns and UC.
Exam mouth ulcers?
Crohns produces ulcers anywhere from mouth to anus.
Exam erythema nodosum?
(raised, tender, red nodules) Crohns or UC. But OCCP can also produce this is young women.

Exam overview
1
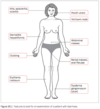
Exam Dermatitis herpetiformis?
itchy rash associated with coeliac disease, typically found over extensor surfaces of limbs.

Exam Virchow lymphadenopathy?
in left supraclavicular fossa is strongly suggestive of bowel malignancy that has spread.
Exam Abdominal masses?
in right lower quadrant is often found in Crohns.
Exam Anal ulcers or fistulae?
Crohns causes both ulcers and fistulae around the anus.
Exam DRE?
look for causes of obstruction that could lead to overflow diarrhoea.


