Histology of the Cardiovascular System Flashcards
What are the functions of the cardiovascular system?
- Maintenance of adequate blood flow (cardiac output)
- Delivery of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, electrolytes, and water to peripheral tissues
- Removal of carbon dioxide and other metabolic waste products
- Maintenance of normal thermoregulation and GFR –> urine output
Picture of a normal circulatory system

Relationship between blood pressure, vascular permeability and structural characteristics of different types of blood vessels (bottom)

Describe the normal vascular pattern
Artery –> arteriole –> metarteriole –> capillaries –> venule –> vein
Endocardium
Endothelial lining of the heart chambers surface; also covers the surface of the valves; subendocardium contains a thin layer of connective tissue; Purkinje fibers may be found in this area
Myocardium
- cardiac muscle mass
- central single nucleus
- intercalated disks
- gap junctions
- anchoring junctions
- lipofuscin
- sarcoplasmic reticulum
- many mitochondria, up to 20% cell volume –> requires a lot of O2
Epicardium
Formed by a single layer of flattened epithelial cells, the mesothelium (simple squamous epithelium), supported by connective tissue including fat; a similar mesothelial layer lines the opposing parietal surface of the pericardial sac; mesothelial cells secrete a small amount of serous fluid that lubricates the movement of the epicardium on the opposite parietal pericardium; the epicardium represents the visceral layer of the pericardial sac
The cardiac skeleton
- consists of 4 dense bands of fibrous connective tissue that encircles the base of the pulmonary trunk, aorta, and the AV valves - provides structural support to the heart
- a triangular mass of fibrous connective tissue - the fibrous trigon - connects the the aortic arterial ring and the left and right atrioventricular ring; this area undergoes osseous differentiation and forms the “Os Cordis” - primarily seen in cattle
Tunics of vessels
- tunica intima
- innermost layer
- endothelium, internal elastic membrane, subendothelial connective tissue
- tunica media
- middle layer
- smooth muscle and elastic lamellae/fibers
- tunica adventitia/externa
- outermost layer
- CT, primarily collagen, may contain blood vessels, nerves, capillaries
Vascular endothelium
- role in homeostasis
- anti-thrombotic and pro-fibrinolytic in the normal state
- pro-thrombotic and anti-fibrinolytic during injury
- modulates perfusion
- nitric oxide relaxes and causes vasodilation
- endothelin casues vasoconstriction
- role in inflammation
- regulates the traffic of inflammatory cells
- produces pro-inflammatory cytokines
- control angiogenesis and tissue repair
Elastic artery
- best example is aorta
- all 3 tunics exist:
- tunica media - consists largely of repeating elastic lamellae
- tunica intima - endothelium and loose CT
- tunica adventitia - contains vasa vasorum to assist in supplying nutritional needs of thick tunica media
Muscular arteries
- tunica media is primarily smooth muscle (it’s the thickest tunic)
- generally have a round appearance in XS
- prominent internal elastic membrane

Vascular smooth muscle
- smooth muscle cells are circumferentially arranged within the tunica media
- regulates diameter and tone (vasodilation/vasoconstriction)
Arterioles

- 1-3 layers of smooth muscle
- greatest effect on blood pressure
- nuclei bulge into lumen
- round appearance of vessel
- no internal elastic membrane in the smallest arterioles with 1 smooth muscle cell
- metarteriole is a terminal vessel, has precapillary sphincters that can regulate flow to the capillary bed
Pericytes (Rouget cells)
- mesenchymal-like contractile cells (contain acitn, myosin, tropomyosin) that wrap around capillaries and venules and “communicate” with endothelial cells by physical contact and paracrine signaling
- have own basal lamina
- proliferate after injury; may be repalcement stem cell source; important in angiogenesis
What does each letter represent?
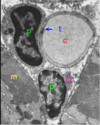
- P = pericyte
- T = tight junction, capillary endothelial cell
- M = skeletal muscle
- C = capillary
- Cl = collagen fibers in transverse section
Capillaries
- thin walled tubules of mesenchymal origin; in a cross section they are made of only one endothelial cell rolled into the tube
- represent the site of exchange between blood and surrounding tissue
- 3 types:
- continuous
- fenestrated
- discontinuous (sinusoidal)
Continuous capillary
- most common
- found in muscle, brain, bone, lung, etc.
- nucleus of endothelial cell
- pinocytotic vesicles
- tight junctions
- basement membrane/lamina
Glomerular capillary (example of fenestrated)
The renal corpuscle/glomerulus is a tightly coiled network of fenestrated capillaries and is responsible for the filtration of plasma
Discontinued/sinusoidal capillaries
- lumen is enlarged and irregular
- lining endothelium is discontinuous and fenestrated
- basal lamina may be absent (hence discontinuous)
Venules
- called postcapillary venules
- very ‘leaky’ vessels
- no smooth muscle
- leukocyte diapedesis possible here
Veins
- large, wide lumen, thin walls in comparison to same-size arteries
- valves present
- thin tunica media
- the tunica adventitia is the thickest tunic
- large veins may have vasa vasorum
Lymphatic vessels
- very thin wall, very low pressure, may contain valves
- no RBCs in lymph, so appear clear


