Histology (Caridac) Flashcards
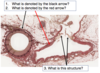
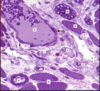
What tissue is this (yellow arrow)?

Smooth muscle
Compared to other muscle types, smooth muscle is ______________ & ______________.
non-striated and involuntary
The contractile proteins in smooth muscle are ____________ & ____________.
Actin and myosin
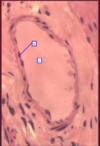
What type of tissue is this and what are it’s characteristics?

- Caridac muscle
- Striated and involuntary
What are the contractile proteins found in cardiac muscle?
Actin and Myosin
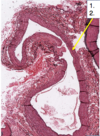
1) Give both names for the layer (blue arrow)?
2) What is it (#1) comprised of?
3) What is the structure (yellow)?

1) Epicardium & visceral serous pericardium
2) Dense fibrocollangenous CT, lined with mesothelium
3) Myocardium
4) What is the outmost layer lined with?
5) What is this structure?

4) Mesothelim (simple squamous epithelium)
5) Purkinje fibers (subendocarial branches)
- What are these structures (arrows)?
- What is the purpose of them and in what layer of the heart wall are they located?

1) Intercalated discs
2) Specialized junctions that bind cells together and allow spread of excitation; located in myocardium
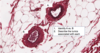
What are these structures (yellow arrows) and where are they located in realation to sarcomere?

- Intercalated discs
- Coincide with Z-lines
What are the 2 regions of intercalated discs?
1) Transverse region
2) Lateral region
What are the components and function of transverse region of intercalated disc?
- Fascia adherentes: anchoring site for actin filaments of terminal sarcomeres to the plasma membrane
- Maculae adherentes (desmosomes): hold contractile cardiocytes tightly together
What are the components and funtion of the lateral region of intercalated discs?
- Gap junctions
- Allow ions to travel cell-to-cell
- Causes ionic coupling allowing connected cells to function as one unit
Label 1, 3, and 5 and state which region of the intercalated disc they are found in and their function?
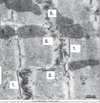
1) Fascia adherentes (transverse region) - anchoring site for actin filmanents of terminal sarcomeres
3) Gap junction (lateral region) - excitation to pass b/w cells
5) Desmosome (transverse region) - anchor contractile cardiocytes tightly together
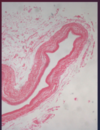
What is this structure and what is it comprised of?
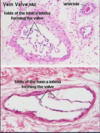
Heart valve; core of fibroelastic CT, covered with endothelium
- What is this portion of the valve
- What is found lining heart valves (bottom arrow)?

- Cardiac/fibrous skeleton
- Endothelium
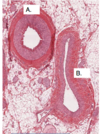
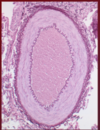
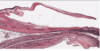
What is this a picture of and label 1-5.

- Elastic artery (due to extensive thickness of tunica media)
1) Tunica media
2) IEL (internal elastic lamina)
3) Tunica intima
4) Endothelium
5) Vaso vasorum