Histological Images Flashcards
1
Q

A
Renal corpuscle
- a = vascular pole
- b = parietal epithelial layer of Bowman’s capsule
- c = urinary pole
- d = visceral epithelium with podocyte
- e = peritubular capillary
- f = proximal tubule
- Blue arrow = macula densa

2
Q

A

3
Q

A

4
Q

A

5
Q

A

6
Q

A

7
Q

A
- Af = afferent arteriole
- Ef = efferent arteriole
- Pt = proximal tubule
- Ilu = interlobular u?
*

8
Q

A
Renal corpuscle
- V = arteriole (afferent OR efferent)
- Green arrow = RBC
- Between white arrows: parietal epithelial layer of Bowman’s capsule
- BS = capsular space of Bowman

9
Q

A
Kidney undergoing compensatory hypertrophy with podocyte and capillary loop
- N = podocyte nucleus
- M = major processes
- F = filtration slits

10
Q

A

11
Q

A

12
Q

A
Renal corpuscle
- Ef = efferent arteriole
- Af = afferent arteriole with renin granules in its wall
- Green arrow: renin granules
- Po = nucelated cell body of podocytes
- PE = parietal epithelium
- US = urinary space
- EN = endothelial cell nucleus
- MC = mesangial cells
- CL = capillary lumen
- JG = juxtaglomerular call
- FM = filtration membrane
- PCT = proximal convoluted tubule
- PCa = pertitubular capillary

13
Q

A
Podocyte
- Np = podocyte nucleus
- BS = capsular space of Bowman
- M = major processes
- F= foot processes
- Ne = endothelial nucleus
- Ms = mesangial cell
- C = capillary lumen
- R = RBC

14
Q

A
- BS = capsular space of Bowman
- CL = capillary lumen
- Large arrows: pore in the endothelial lumen
- Small arrows: diaphragm spanning the foot processes
- In between the two = thick basement membrane

15
Q

A

16
Q

A
Unilobular rat kidney
- C = cortex
- OS = outer stripe of the outer medulla
- IS = inner stripe of the outer medulla
- IM – inner zone of the medulla

17
Q

A
Kidney
- Blue arrow = thin renal capsule
- C = cortex
- M = medulla
- Small arrows = glomeruli (darker ones are capsules without glomerulus)
- Large arrows = medullary rays

18
Q

A
Renal circulation
- Interlobular artery at the bottom center
- Intralobular arteries that branch from it.
- Afferent arterioles can be seen branching to the right at the top of the field
- Round, dark red-staining glomeruli
- Peritubular capillary plexus is demonstrated at the upper and lower right-hand corners of this slide
19
Q

A
Renal cortex containing a renal corpuscle
- Green arrow = macula densa
- Blue bracket = vascular pole
- Gray arrows = S1 of proximal convoluted tubule
- Purple brackets = urinary pole
- Red arrow = microvillous brush border
- Pink arrows = distal convoluted tubules

20
Q

A
Renal cortex
- a = capsular space of Bowman
- b = distal convoluted tubule
- c = macula densa
- d = proximal convoluted tubules
- e = peritubular capillary
- f = distal convoluted tubules
- g = parietal epithelial layer of Bowman’s capsule
- h = urinary pole

21
Q
A
22
Q

A
- Black arrow = macula densa
- Blue arrow = renal corpuscle
23
Q
A
24
Q

A
Vascular pole of renal corpuscle
- Ea = efferent arteriole
- Md = macula densa
- Aa = afferent arteriole
- PS1 = S1 of proximal tubule

25
26

**Renal corpuscle**
* BS = space of Bowman
* C = lumen of glomerular capillaries
* P = podocytes
* V = vascular pole of renal corpuscle
* Between 2 arrows = parietal epithelium
* Blue arrow = visceral epithelium podocytes reflecting back from the glomerular vessels and transforming into a layer of simple squamous cells at the vascular pole
* Brackets = macula densa
* Small black arrow = mesangial cells

27
28

**Glomerular wall**
* Purple arrow = lamina rara interna
* Black arrow = amina densa
* Yellow arrow = lamina rara externa
* Blue arrow = filtration slit with diaphragm
* Green arrow = foot process
* Gray arrow = endothelial pore

29

**Uriniferous tubules in cortex**
* PT = proximal tubule with debris filled lumen due to ischemia
* DCT = distal convoluted tubule
* CD = collecting duct

30
List characteritics while identifying.

**Proximal and distal convoluted tubules**
* DCT = distal convoluted tubule
* No microvillous brush border
* No debris
* Cells are not as broad =\> more nuclei seen in a cross section
* Does not stain as dark
* PT = proximal tubules
* Microvillous brush border
* Debris in lumen during ischemia
* Stains darker
* Less visible nuclei
*

31

**Uriniferous tubules in cortex**
**Lower panels = proximal convoluted tubule**
* Nu = nucleus
* MI = mitochondria
* Mv = microvillous brush border
* AV = apical vesicle
* JC = juxtaglomerular cells
* Ly = lysosomes
* Tubule most to the right = S2 proximal tubule (larger brush border)

32

**Proximal convoluted tubules**
* N = nucleus
* Ly = lysosomes
* V = apical vesicles
* C = capillaries
*

33

Transition from the descending thick (with microvillous brush border) to the descending thin segments of the loop of Henle aka from the inner stripe to the outer stripe of the outer medulla
* Blue arrow = ascending segment

34

**Inner/outer strip transition in the outer medulla**
* Large arrow = descending thick section with microvillous brush border changing into a descending thin segment with no microvillous brush border(small arrow) of the loop of Henle
* ADT = ascending distal tubule
* PS3 = third segment proximal tubule
* VR = vasa recta

35

**Inner stripe of outer medulla**
* a = vasa recta with blood in them
* b = ascending thick segments
* c = collecting ducts
* d = thin segments of Henle’s loop

36
**Inner/outer medulla transition:** ascending thin to ascending thick segment of Henle's loop

37

**Inner stripe of the outer medulla**
* CD = collecting ducts
* DT = descending thin segment
* AD = ascending distal tubule (aka thick segment)
* Small arrows = cilia on the intercalated cells lining the collecting duct
* P = principal cell types

38

**Medullary ray**
* Blue arrow = thick descending segment of loop of Henle
* Green arrow = ascending thick segment of loop of Henle
* Black arrow = collecting duct

39

**Inner medulla**
* Red arrows = vasa recta
* Yellow arrows = collecting ducts
* Blue arrows = descending thin segments of loops of Henle

40

**Collecting ducts in inner medulla**

41

**Inner medulla**
* Red arrows = vasa recta
* Yellow arrows = collecting ducts
* Blue arrows = thin segments of loops of Henle

42

**Collecting ducts in papilla with taller columnar cells**

43

**Collecting duct**

44

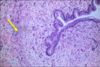
Ureter lined by transitional epithelium and surrounded by lamina propria and smooth muscle continuous with an adventitia

45

Ureter lined by transitional epithelium and surrounded by lamina propria and smooth muscle (yellow arrow) continuous with an adventitia
46

**Bladder**
The upper portion of this field depicts the transitional epithelium that
lines the urinary bladder.
Note the superficial dome cells which are sometimes binucleated.
The connective tissue of the lamina propria can be seen at the bottom of the field.

47

* P = podocyte
* U = urinary pole
* C = capillary loop
* Arrows = parietal epithelial layer
* PS1 = S1 segment of the proximal convoluted tubule with its microvillous brush border
* N = nucleus
* Blue arrows = mitochondria

48

Proximal tubule
* Mb = microvillous brush border
* Arrows = basolateral folds

49

S3 segment of the proximal tubule
* Mb = microvillous brush border
* N = nucleus

50

* AT = ascending thin
* AD = ascending thick
* \* = transition from inner to outter zones of the medulla

51

* MI = mitochondria
* LC =
* DC =

52

* Md = macula densa
* Aa = afferent arteriole
* Ea = efferent arteriole
* Small arrow = renin containing granules
* Large arrow = extraglomerular mesangial cells
* PoN = podocyte nucleus



