Histo Exam 1 Flashcards
(151 cards)
Acid reflux disease can result in what type of cell change?
Metaplasia of stomach mucosa
Peptic ulcer can result in what type of change?
Destruction of stomach mucosal lining
Celiac Disease results in what type of change in the stomach?
Alteration of normal absorptive surface of small intestine
Describe secretory cells
- Clear cytoplasm
- Round/oval nuclei
- Without nucleoli
Describe Basal Cells in the prostate
- Numerous
- Produce high molecular keratin
Describe the epithelial bilayer in the prostate
- Consists of columnar and basal cells –> psuedostratified
- Abundant fibro-muscular stoma
Describe the microscopic structure of the prostate
- Many wide, irregular tubules (well-differentiated)
- Epithelium is folded
- Glands not closely spaced
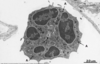
Identify the organ and condition

Appendicitis
What are some pathological findings consistent with appendicitis?
- Gray, shaggy exudate
- Pus
- Ulcerated mucosal surface
- Neutrophilic infiltrate
What are the seven staining methods?
- Gomori
- Feulgen
- Masson
- Romanovsky
- Golgi
- Geimsa
- Cajal
What does H&E stain show?
Generalized picture of a cell and structure of an organ
What does PAS show?
Mucus secretions and basement membranes
What does Masson’s Trichrome show?
Collagenous architecture of organs
What does Wright’s Stain show?
Complete blood cell counts
What does Sudan Black “B” show?
Lipid droplets, lysosomes, and mitochondria
What do silver stains show?
Polypeptide hormone-producing cells and basement membranes
What is shown in this picture?

Kidney in Eosin
What is shown in this picture?

Kidney in hematoxylin
What is shown in this picture?

Kidney shown in H&E stain
What kind of stain is being used?

PAS
What kind of stain is being used?

Silver stain
What kind of dye is hematoxylin and what does it stain in the nucleus?
Basic dye, stains RNA and DNA

What type of dye is Eosin and what does it stain?
- Acidic dye
- Stains:
- Cytoplasm
- Skeletal muscle
- Secretion granule
- Connective tissue cells (fibroblasts)
- Collagen fibers
- Thyroglobulin
What does H&E dye help show the contrast between?
Nucleus, nucleolus, and mitochondria