Hip, buttock and thigh Flashcards
What happens to the lower limb during development?
It twists during develop and you get a permanent pronation at the mid-thigh level just below the hip joint
What specific words are given to the flexion and extension of the foot?
Dorsiflexion (pointing toes up) - true extension Plantarflexion (pointing toes down) - true flexion
What are the three parts of the pelvis (hip bone)?
Ilium Ischium Pubis
What marks the ends of the iliac crest?
ASIS and PSIS
What is the name given to the surface of the hipbone that articulates with the sacrum?
Auricular Surface
What lies in between the greater and lesser trochanters of the femur?
Intertrochanteric crest
What short ridge is found just inferior to the lesser trochanter?
Gluteal tuberosity
A long ridge downwards along the shaft of the femur and originates from the short ridge below the lesser trochanter. What is this long ridge called?
Linea aspera
Which tubercle is found just superior to the medial epicondyle of the femur?
Adductor tubercle
What is the anterior protrusion between the ilium and the pubis called?
Iliopubic eminence
What are the two notable parts of the ischium onto which ligaments attach?
Tuberosity and spine
Which pelvic bones make up the acetabulum?
All three of them (ilium, ischium and pubis)
What notches are present on the posterior aspect of the pelvis?
Greater sciatic notch and lesser sciatic notch
What is the angle of inclination?
The angle that the long axis of the shaft makes with the long axis of the head and neck
What determines the size of the angle between the long axis of the shaft and the vertical plane?
The width of the hips
What structures form the greater and lesser sciatic foramina?
Sacrospinous ligament Sacrotuberous ligament
What are the two fascia found in the thigh?
Superficial fascia – e.g. subcutaneous tissue Deep fascia – fascia lata
What is the name given to the lateral thickened area of the fascia lata?
Ilio-tibial tract
What are the four compartments of this region?
Gluteal compartment Anterior compartment of the thigh Medial compartment of the thigh Posterior compartment of the thigh
What movements are the muscles of the gluteal region responsible for?
Extension, abduction and external rotation of the femur
What are the gluteal muscles?
Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus (tensor fasciae latae – this is neurologically a gluteal muscle (innervated by superior gluteal nerve) but functionally it is more of an anterior compartment muscle)
What are the short external rotators of the hip?
Piriformis Obturator internus Quadratus femoris Gemelli (superior and inferior)
Describe the attachments of gluteus maximus.
Proximal – posterior part of the iliac crest and thick fascia of the sacrum and coccyx Distal – gluteal tuberosity and ilio-tibial tract
What proportion of the gluteus maximum fibres attach to the gluteal tuberosity?
About 25% attach to the gluteal tuberosity and the rest are attached to the ilio-tibial tract
What does the ilio-tibial tract insert into?
Anterolateral tubercle of the tibia NOTE: there is a lateral intermuscular septum that goes between the iliotibial tract and the posterior surface of the femur
Describe the attachments of gluteus medius.
Proximal – broad attachment to the external surface of the ilium (between the anterior and posterior gluteal lines) Distal – greater trochanter
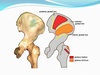
Describe the attachments of gluteus minimus.
Proximal – broad attachment to the external surface of the ilium (between the anterior and inferior gluteal lines) Distal – just below the greater trochanter

What movement are gluteus medius and gluteus minimus responsible for?
Abduction
What movement are the deep muscles of the gluteal region responsible for?
External rotation
Describe the attachments of tensor fasciae latae.
Proximal – ASIS Distal – ilio-tibial tract
Which compartment is tensor fasciae latae in?
Neurologically it is more like a gluteal compartment muscle because it is innervated by the superior gluteal nerve In terms of action, it is a flexor of the hip so it functions more like an anterior compartment muscle
Describe the attachments of obturator internus.
Rim of the obturator foramen Greater trochanter of the femur
What movement are the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh responsible for?
Hip flexion Knee extension
Which muscles are in the anterior compartment of the thigh?
- Tensor fasciae latae
- Pectineus
- Ilio-psoas
- Sartorius
- Quadriceps (rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis)
What is the most powerful flexor of the hip?
Ilio-psoas
Describe the attachments of Ilio-psoas.
Psoas major attaches to the lateral parts of the lumbar vertebrae and T12 and Iliacus attaches to the iliac fossa and crest The two muscles then come together to form a common tendon that attaches to the lesser trochanter
Describe the attachments of Sartorius. What movement is it responsible for?
Sartorius comes off ASIS and descends inferiorly and medially. It crosses the knee and attaches to the upper part of the shaft of the tibia
Crossing the legs
Describe the arrangement of the quadriceps muscles.
Rectus femoris is most superficial with vastus medialis and vastus lateralis on either side of rectus femoris Vastus intermedius is deep to rectus femoris
Where do the quadriceps attach distally?
They come together to form a quadriceps tendon, which attaches to the patella There is a patellar tendon between the patella and the tibial tuberosity on the anterior of the tibia The patellar tendon is part of the quadriceps tendon with the patella in between as a sesamoid bone
What small muscle is found underneath vastus intermedius?
Articularis genu
What bursa is found just above the knee joint?
Suprapatellar bursa
What movement are the muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh responsible for?
Adduction of the hip
Which muscles make up the medial compartment of the thigh?
- Obturator externus
- Gracilis
- Adductor brevis
- Adductor longus
- Adductor magnus
Where do most of the muscles of the medial compartment attach proximally?
Pubic bone
Describe the structure of adductor magnus.
It has a broad attachment to the shaft of the femur (medial lip of the linea aspera) and then a smaller attachment to the adductor tubercle (just superior to the medial epicondyle) The gap in between is called the hiatus of adductor magnus
What movements are the muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh responsible for?
Hip extension Knee flexion
Which muscles make up the posterior compartment of the thigh?
Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Biceps femoris
Where do the muscles of the posterior compartment attach proximally?
Ischial tuberosity
Describe the attachments of biceps femoris.
The long head of biceps femoris comes from the ischial tuberosity and the short head comes off the shaft of the femur (lateral lip of linea aspera) They cross over laterally to attach to the head of the fibula
What are the borders of the femoral triangle?
Superior – Inguinal Ligament Lateral – Sartorius Medial – Adductor Longus
What are the contents of the femoral triangle (medial to lateral)?
- Deep inguinal lymph nodes
- Femoral Vein
- Femoral Artery
- Femoral Nerve
What is the name given to the opening in the fascia lata over the femoral triangle and what is its purpose?
Saphenous Opening – it allows the draining of the long saphenous vein into the femoral vein The margin of the saphenous opening is called the Falciform Margin
What structures form the Adductor Canal?
Anterior – Vastus Medialis Posterior – Adductor Longus and Adductor Magnus Medial – Sartorius
What are some other names for the Adductor Canal?
Hunter’s Canal Subsartorial Canal
What are the contents of the Adductor canal?
Femoral artery Femoral vein Saphenous nerve (major branch of the femoral nerve)
Where does the sciatic nerve lie within the gluteal region?
Inferior medial quadrant (NOTE: there are variations in terms of the emergence of the sciatic nerve relative to piriformis)
What two nerves does the sciatic nerve consist of?
Tibial Nerve Common Peroneal Nerve
Where would you perform an intramuscular injection into the gluteal region?
Superior lateral quadrant
What does the sciatic nerve supply?
Muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh (hamstrings) All the muscles below the knee (supplies by the two branches of the sciatic)
What test is used to assess the function of the hip abductors?
Trendelenberg test When a patient lifts one foot off the floor, their hip abductors (gluteus medius and gluteus minimus) should contract to keep the pelvis level despite the extra weight of the raised foot on the opposite side
Describe the structure of the acetabulum.
The acetabulum has a depression in the middle (acetabular fossa) and a lunate surface (surrounding the fossa) There is an acetabular notch, which is filled in by the transverse acetabular ligament
What is the small depression on the head of the femur called?
Fovea capitis
What are the ligaments of the hip joint?
- Iliofemoral ligament (Y shaped)
- Ischiofemoral ligament
- Pubofemoral ligament
- Transverse acetabular ligament
Describe how the arrangement of these ligaments changes when the hip is flexed and extended.
When the hip is flexed, these ligaments are relaxed When the hip is extended (e.g. when standing) the ligaments wind, which pulls the head of the femur into the acetabulum and helps stabilise the joint when in the standing position
Describe the blood supply to the head of the femur.
The main blood supply is via the medial circumflex femoral artery and the lateral circumflex femoral artery (both from profunda femoris) There is a small blood supply from the artery of the head of the femur (branch of obturator artery - this is more important in children)
What type of hip fracture is most likely to need a hip replacement and why?
Intracapsular – this is more likely to disrupt the blood supply and cause avascular necrosis of the head of the femur
When does the external iliac artery become the femoral artery?
As it passes under the inguinal ligament
What main branch does the femoral artery give off that gives rise to the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries?
Profunda femoris
At what point do the superficial femoral artery and the femoral vein become the popliteal artery and vein?
As they pass through the hiatus of adductor magnus
Which arteries, that supply the buttock and thigh, are branches of the internal iliac?
Superior gluteal and Inferior gluteal arteries Obturator artery
What is the main superficial vein of the thigh?
Long saphenous vein
What other veins drain into the saphenous vein before it enters the sapheno-femoral junction?
- Superficial circumflex iliac
- Superficial epigastric
- Superficial external pudendal
- Lateral cutaneous
What are the deep veins of the thigh?
- Popliteal vein
- Femoral vein
- External iliac vein
- Sapheno-femoral junction
- Venae comitantes of the profunda femoris artery
What are the main groups of lymph nodes in the thigh?
Deep inguinal lymph nodes Superficial inguinal lymph nodes External iliac lymph nodes
Which nerve supplies the anterior compartment and which division of the lumbosacral plexus gives rise to this?
Femoral nerve – posterior division of the lumbosacral plexus (L234)
Which nerve supplies the medial compartment and which division of the lumbosacral plexus gives rise to this?
Obturator nerve – anterior division of lumbosacral plexus (L234)
State which roots are responsible for: Hip flexion Hip extension Knee extension Knee flexion
Hip flexion: L23 Hip extension: L45 Knee extension: L34 Knee flexion: L5S1
Which nerve supplies the posterior compartment of the thigh and which nerve roots give rise to this nerve?
Sciatic nerve (L45S123)
Which nerves supply the gluteal muscles and which nerve roots give rise to these nerves?
Superior gluteal nerve (L45S1) Inferior gluteal nerve (L5S12)
Which nerve roots are responsible for the sensory supply to the: Front of the thigh Back of the thigh Buttock
Front of the thigh: T12, L123 Back of the thigh: S123 Buttock: S234
Which nerve roots give rise to the following sensory peripheral nerves:
Subcostal nerve: T12 Ilio-hypogastric nerve: L1 Ilio-inguinal nerve: L1 Genito-femoral nerve: L12 Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh: L23 Sensory branches of the femoral nerve: L234 Sensory branches of the obturator nerve: L234 Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh: S123 Saphenous nerve: L234 Buttock nerves from the sacral plexus: L1-S3
What are the types of hip fracture?
Intracapsular Fractures – break occurs below the ball or in the neck of the femur (most commmon) Intertrochanteric Fractures – break occurs between the greater trochanter and lesser trochanter Subtrochanteric Fractures – break occurs below the lesser trochanter or further down the femur


