Hepatitis Flashcards
How many Hepatitis C genotypes are there and which is most common in Canada? (PBSG)
- 6 major genotypes
- Genotype 1 >60% of cases in Canada
What is more infectious by blood, HCV or HIV? (PBSG)
- HCV 10x more infectious than HIV
How is Hepatitis C most commonly transmitted? (PBSG)
- Parenterally (IVDU)
In which years were blood transfusions a known risk factor for HCV? (PBSG)
- Before 1992
What are 3 questions to ask patients with abnormal liver function tests?
- New Prescription Drugs
- Alcohol
- Travel history
What are 6 risk factors for viral hepatitis B? (USPSTF)
- Persons born in countries and regions with a high prevalence of HBV infection (≥2%)
- Asia, Africa, Middle East, Eastern Europe
- HIV positive
- IVDU
- Household contacts or sexual partners of persons with HBV infection
- MSM
- Persons receiving hemodialysis or cytotoxic or immunosuppressive therapy (e.g. chemotherapy for malignant diseases and immunosuppression related to organ transplantation and for rheumatologic and gastroenterologic disorders
What are 8 risk factors for viral hepatitis C? (USPSTF)
- Blood-borne exposure and Transfusions and Organ Transplant (before 1992 in Canada)
- High-risk sexual activity (e.g. sex with IVDU)
- Incarceration/Imprisonment
- IV drug use
- Snorting cocaine with shared equipment
- Tattoos or body piercing
- Long-term hemodialysis
- Being born to a mother with HCV infection
What are 8 symptoms of liver disease? (DFCM Open)
- Fatigue (most characteristic symptom)
- Pruritus
- Nausea (more severe liver disease)
- Poor appetite with weight loss (common in acute, rare in chronic disease)
- Diarrhea (with severe jaundice)
- Jaundice
- Dark urine
- Light stools (severe cholestasis)
What are 7 signs that can be seen with liver disease? (DFCM Open)
- Icterus
- Hepatomegaly
- Hepatic tenderness
- Splenomegaly
- Spider angiomata
- Palmar erythema
- Excoriations
What are 13 signs associated with severe or advanced liver disease? (DFCM Open)
- Muscle wasting
- Ascites
- Edema
- Dilated abdominal veins
- Hepatic fetor
- Asterixis
- Loss of male-pattern hair distribution
- Enlarged Virchow’s (left supraclavicular) or Sister Mary Joseph’s (umbilical) nodes
- JVD or Rt pleural effusion
- Mental confusion
- Stupor/coma
- Gynecomastia
- Testicular atrophy
Where are ALT and AST found in and which is more specific for hepatocellular damage? (AFP)
- ALT primarily in the liver
- AST also found in skeletal muscles and erythrocytes
Which blood tests are markers of liver damage? (TN)
- AST
- ALT
- ALP
Which blood tests are markers of liver function? (TN)
- PT or INR
- Albumin
- Bilirubin
Which clotting factors are not synthesized in the liver? (TN)
- Factor VIII
- VWF
Does liver dysfunction cause elevated direct (conjugated) or indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin? (TN)
- Direct bilirubin
IF the ALP is elevated out of proportion to the ALT/AST elevation, what are 4 diagnoses to consider? (TN)
- Obstruction of CBD
- Extraluminal = pancreatic cancer, lymphoma
- Intraluminal = stones, cholangiocarcinoma, sclerosing cholangitis, helminths
- Destruction of microscopic ducts
- PBC
- Bile acid transporter defects
- Drugs
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
- Infiltration of the liver
- Liver metastases
- Lymphoma
- Granulomas
- Amyloid
What are the 3 different abnormal Liver Lab patterns?
-
Pre-Hepatic
- Elevated UNconjugated (indirect) bilirubin
- AST & ALT normal
-
Hepatocellular – Increased AST and ALT
- Alcohol = 2:1 AST:ALT (Shots, Shots, Shots)
- Viral = 2:1 ALT:AST
- Elevated CONjugated bilirubin
-
Biliary/Obstructive – Increase ALP and GGT
- Elevated CONjugated bilirubin
- ALP found in bone, liver and placenta
- If elevated, check Anti-Mitochondrial Antibody and get Abdo U/S
- Refer for surgery if obstruction found
What is the differential diagnosis for acute or chronic liver disease with either a hepatocellular or cholestatic pattern? (DFCM Open)
Hepatocellular
Cholestatic
Acute (<6 months)
- Hepatitis A/B/C
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Mononucleosis associated hepatitis
- Wilson’s disease
- EtOH/drug use
- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- Drug abuse
- Gallstone
- Biliary duct dilation
- Fatty liver
- Masses
- Ampullary lesions
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Chronic
- Hepatitis B/C
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson’s disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Alcohol abuse
- Drug abuse
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
What does jaundice without dark urine indicate and what are 3 possible diagnoses? (DFCM Open)
- Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia
- Hemolytic anemia
- Genetic disorders
- Gilbert’s syndrome
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome
What does a normal and low albumin (measure of protein synthesis) indicate in the context of liver disease? (DFCM Open)
- Low albumin = chronic process
- Cirrhosis
- Cancer
- Normal albumin = acute process
- Viral hepatitis
- Choledocholithiasis
What does the INR (measure of protein synthesis) indicate in the context of liver disease? (DFCM Open)
- Elevated INR = vitamin K deficiency due to prolonged jaundice and malabsorption or significant hepatocellular dysfunction
What does the failure to correct a prolonged INR with IV vitamin K indicate? (DFCM Open)
- Severe hepatocellular injury
What is the differential diagnosis (10) for elevated liver enzymes?
- Infectious
- Hepatitis A, B or C (ALT>AST)
- Liver abscess
- Toxic
- Tylenol, Statins, INH
- Alcohol (AST>ALT)
- Cirrhosis (AST>ALT)
- Biliary obstruction
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or NASH
- Autoimmune – Hepatitis or Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- Metabolic
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson’s
- Right-sided CHF
- Neoplastic – Hepatocellular or Metastatic
- Extra-Hepatic – Heart or Skeletal Muscle injury
What is the differential diagnosis (5) for when the AST or ALT is > 500 to 1000?
- Tylenol overdose or other toxin ingestion
- Viral Hepatitis – particularly Hepatitis A
- Liver shock or Hepatic ischemia
- Budd-Chiari syndrome
- Right-sided CHF
How does alcoholic hepatitis typically present? (TN)
- History of recent alcohol
- RUQ abdominal pain
- AST:ALT >2
- AST usually <300
- Low grade fever
- Mildly elevated WBC
In an asymptomatic patient with elevated LFTs, what would be your approach?
- I wouldn’t wait 6 months, probably 1 month

In an asymptomatic patient with an elevated ALP, what would be your approach?
- Antimitochondrial Ab positive in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
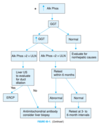
If an elevated ALT returns to the normal range on repeat testing, what still needs to be screened for? (AFP)
- Hepatitis C
What is the most common cause of mild elevations of LFTs? (AFP)
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
What % of the population is affected by NAFLD? (AFP)
- 30%
Combined, what % of mildly elevated liver transaminase levels were hepatitis B, hepatitis C and hemochromatosis in NHANES? (AFP)
- 31%
What AST:ALT ratio is usually found in NAFLD? (AFP)
- 1:1
What could an AST:ALT ratio >4 suggest? (AFP)
- Wilson’s disease
In addition to an AST:ALT ratio >2, what other blood test supports a diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease in this setting? (AFP)
- Elevated GGT
What % of the population has NASH? (AFP)
- 3-6%
What % of healthy nondrinkers can have elevated liver transaminase levels after dosages of 4g per day of acetaminophen for 5-10 days? (AFP)
- 58%
What % of elevated transaminase levels spontaneously resolve in persons taking statins? (AFP)
- 70%
In which persons is autoimmune hepatitis more common? (AFP)
- Women
- History of thyroid disease or other autoimmune conditions

