Hemoglobin and Oxygen Flashcards
(31 cards)
Why is it beneficial for the body to use hemoglobin for oxygen transport?
Oxygen is poorly soluble & diffusion is ineffective over long distances
What is the function of the heme ring present in hemoglobin?
Transition medals have a strong tendency to bond oxygen
Proteins side chains on their own do not
What is the danger with free iron in the blood?
Promotes the formation of highly reactive oxygen species
What is a heme?
Protein bound prosthetic group that includes iron
porphyrin ring bound to a single iron atom in its ferrous (Fe2+) state
How many cooridnation bonds does the iron in a heme have?
- 6 coordination bonds
- 4 to nitrogen atoms in porphyrin ring
- 2 perpendicular to the ring
- side chain nitrogen of His residue
- binding site for molecular oxygen (O2)
What is the function of the coordination bonds that iron has in a heme?
coordinated nitrogen atoms help prevent converstion of heme iron to the ferric (Fe3+) state
Why is it beneficiation to have the ferrous state of iron (Fe2+) in a heme rather than the ferric state (Fe3+)?
Iron in the Fe2+ state bind oxygen reversibly
Iron in the Fe3+ state does not bind oxygen
In addition to hemoglobin, where else can heme be found?
many oxygen-transporting proteins
proteins such as cytochromes that participate in redox reactions
What reaction can cause in irreversible conversion from Fe2+ to Fe3+?
Free heme molecules (not bound to protein) leave Fe2+ with two “open” coordination bonds. Simultaneous reactin of one O2 molecule with two free heme molecules can result in irreversible converstion of Fe2+ to Fe3+.
How do heme-containing proteins prevent the conversion of Fe2+ to Fe3+?
keeping the heme deep within the protein
access to the two open coordination bonds are restricted
Why is arterial blood red and venous blood blue?
When oxygen binds, the electronic properties of heme iron change
Why is CO highly toxic?
CO has a higher affinity for heme than does O2
When a molecule of CO is bound to a heme, O2 is excluded and the body loses its ability to transport oxygen
What are the 4 globin proteins & their general function?
- myoglobin
- monomeric
- oxygen diffusion in muscle tissue
- hemoglobin
- tetrametric
- oxygen transport in the blood stream
- neuroglobin
- monomeric
- expressed largely in neurons & protects brain from hypoxia or ischemia
- Cytoglobin
- monomeric
- regulates levels of NO in the walls of blood vessels
How much larger is the affinity of CO for free heme than the affinity of O2 for a free heme?
How does this magnitude of difference change when the heme is a part of myoglobin?
CO binds 20,000X better to free heme than O2
CO binds 40X better to heme part of myoglobin than O2 - (only 250x for myoglobin)
What factor is responsible for the change in relative affinity of CO and O2 for heme?
geometric structure of the binding site- the distal His & rapid molecular flexing
a partial negative change exists on the oxygen atoms that stabilized by forming a hydrogen bond with the imidazole side chain of His E7
What is the main function of erythrocytes?
Red blood cell
carry hemoglobin
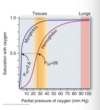
About what fraction the oxygen carried by hemoglobin is release to tissue in a single circulation of blood?
one third
leaves lung: 96% saturated
returns to heart: 64%
Why is myoglobin a good oxygen -storage protein?
relatively insensitive to small changes in dissolved oxygen b/c its hyperbolic binding curve for oxygen
Why is hemoglobin best at transporting oxygen?
Highly sensitive to changes in oxygen demand
What is it called when the normal ligand & allosteric modulator are identical?
homotropic
What is it called when the normal ligand & allosteric modulator are different?
heterotropic
What is diagnostic of cooperative binding?
sigmoid binding curve
How does binding O2 lead to cooperative binding in hemoglobin?
There is only one binding site for O2 on each subunit, so the allosteric effect are b/c conformational changes transmitted from one subunit to another by subunit-subunit interactions
How is CO2 transported through the blood?
bicarbonate (HCO3-)
carbamates (CO2 bound to Hb and other proteins)
not as CO2 b/c poor solubility