Hemodynamics Flashcards
1
Q
CO (Cardiac Output)
A
4-8 L/min
2
Q
CI (Cardiac Index)
A
2.5-4.5 L/min/m2
3
Q
CVP (Central Venous Pressure)
A
3-8 mmHg
4
Q
RA (Right Atrial)
A
1-7 mmHg
5
Q
RV systolic
A
20-30 mmHg
6
Q
RV diastolic
A
0-5 mmHg
7
Q
PA systolic
A
20-30 mmHg
8
Q
PA diastolic
A
5-15 mmHg
9
Q
PA mean
A
less than 20 mmHg
10
Q
PWCP
A
6-12 mmHg
11
Q
SVR
A
900-1400 dynes/sec/cm5
12
Q
PVR
A
100-250 dynes/sec/cm5
13
Q
SVO2
A
60-80%
14
Q
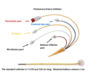
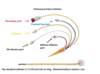
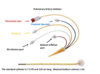
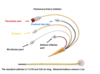
What is the square looking port with the red cap? and what is it for?

A
Thermistor Port for temperature monitoring
15
Q
What is the blue port? and what is it for?

A
Proximal injectatet, CVP monitoring
16
Q
What is the white port? and what is it for?

A
RA Infusion, IVF infusions