Helminthology Flashcards

Moniezia expnasa

Diphyllobothrium latum - Broad or fish tapeworm
- One set of genitalia
- genital openings are on the middle line of proglottids

Dipylidium caninum - flea or cucumber tapeworm
- anapolytic: can move in feces and push eggs out

Moniezia expansa
- triangular shape
- 6 hooked oncoshophere is central

Lancet fluke egg
- detected by flotation
- with two eye-like excretory cells of the miracidium inside.
- the egg is hard-shelled

Liver fluke: big lesions
Lancet fluke: smaller lesions

2nd larval form: sporocyst, produces redia
- develops in the body of the snail

Moniezia benedeni
- quadrangular eggs
- 6 hooked oncoshaera is eccentric

Liver: big lesions: T. tenuicollis.
Small lesions: pisiformis / echinococcus

Strobilocercus fasciolaris
- with seperated bladders
- in liver of rodents
only taenia that can infect cats

Egg of rumen fluke
- unembryonated egg. collected from fresh feces
- the eccentric zygote is surrounded by coarse yolk granules

primary biotope for intermediate host snail of liver fluke

Liver fluke adult, hemorrhages

Cysticercus longicollus
- short neck
- predilection site: body cavity of rodents

Lancet fluke adult
- food source: absorbs nutrients from bile
- two larger testicles and the smaller ovary are behind the ventral sucker while yolk glands are lined up on both sides of the worm

Egg of liver fluke
- non-embryonated egg. observed in fresh feces.
- the eccentric zygote is surronded by a finely granulated yolk
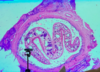
Liver fluke with blood inside

Blood fluke, egg

Cercaria of Fasciola hepatica
- develops inside the body of a redia
- after rain the cercaria swarm out of the snail and swim to find a solid surface.
- cercariae attaches to vegetation, shed their tail and encyst as metacercariae (the infective stage)

Egg of anoplocephala

Anoplocephala

Cercaria of blood fluke

Schematic drawing of T.multiceps

Galba truncatula with metacercariae around

Liver fluke. food source: blood

Heart, can be Su or Bo
- Cysticercus cellulosa or c. bovis

Hemorrhages on liver due to larval migration (similar to liver fluke)

C. pisiformis

Taenia type egg (thick wall)

Small rodent: foamy cyst/bladders, connected to eachother
–> E. multicolaris

E. hydatisus

Cirrhosis, hemorrhages

C. tenuicollis

Echinococcus granulosus
- 3 segments, adult
- Larvae: e. hydatidosus
- armed scolex with 4 suckers and hooked rostrellum
- one set of genitalia
- E. granulosus predilection site of larvae:
- most parenchymal organs and bone marrow
- Liver: in cattle, pig, horse, humans
- Lungs: in sheep and goat

Miracidium: free-living, wants to infect snails
- developed from zygote containing eggs in water usually within 2 weeks
- larva hatches and swims in water to find and penetrate into a freshwater snail

Formica spp., ant
secondary intermediate host of lancet flukes

Liver surface
- C. pisiformis

Liver fluke egg: aber/goldish with operculum

small: lancet fluke
Big: liver fluke

Adult tapeworms

Hemorrhages, liver fluke

C. tenuicollis/C. pisiformis
- differntiate based on size

Brain
- T. muticeps

Cysticercus
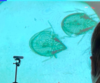
soil mites with cysticercoid inside the body cavity

Rumen fluke cross section
- Paramphistomum (I.H: planorbids - freshwater snails)
- Calicophoron (I.H: Galba truncatula
- It has eggs and not intestine containing blood
- Morphology: Bean like, reddish worms having a sucker on the oral end and another bigger on the opposite end
- Similar lifecycle as liver fluke. except Juvenile fluke never leave the intestinal canal.
- Definite host:
- Cattle: C. daubneyi
- Sheep and goat: P. cervi

secondary biotope for liver flukes
- main source of heavy fasciolosis

Rumen fluke cross-section
- Paramphistomum (I.H: planorbids - freshwater snails)
- Calicophoron (I.H: Galba truncatula
- Morphology: Bean like, reddish worms having a sucker on the oral end and another bigger on the opposite end
- Similar lifecycle as liver fluke. except Juvenile fluke never leave the intestinal canal.
- Definite host:
- Cattle: C. daubneyi
- Sheep and goat: P. cervi

Rumen fluke
- Paramphistomum (I.H: planorbids - freshwater snails)
- Calicophoron (I.H: Galba truncatula
- Morphology: Bean like, reddish worms having a sucker on the oral end and another bigger on the opposite end
- Similar lifecycle as liver fluke. except Juvenile fluke never leave the intestinal canal.
- Definite host:
- Cattle: C. daubneyi
- Sheep and goat: P. cervi

adult blood fluke (male big, female small)

Lancet Fluke in liver
- Dicrocoelium dendriticum
- lives in hyperthrophic biliary ducts of the liver.
- I.H: 1st: small landsnails. 2nd: formica genus
- Life cycle:
- adult worms produce eggs, shed in the feces, contains miracidium
- egg eaten by landsnail -> miracidum hatches
- Larva hatches in the intestine of snail and develops into sporocyst
- the sporocyst produces more generations of daughter-sporocysts
- inside the sporocyst, cercaria develops by asexual budding (padeogenesis). Cercaria hava long tail and a stylet on the head.
- Cercariae leave the snail by its expelled mucous
- the ants ingest the mucos and then they get infected with the larval lancet fluke
- after penetration of the intestine the larvae turn into metacercaria
- reach the ganglion of the ants -> modify their behaviour
- grazing animals ingest the ants
- encapsulated metacercariae gets out of their own capsule in the small intstine of the final host and turn into juvnile flukes
- emerging juvenile flukes reach the liver through the biliary ducts and then develops into adults.

Evaginated cycticercus

Adult rumen fluke in rumen
- Paramphistomum (I.H: planorbids - freshwater snails)
- Calicophoron (I.H: Galba truncatula
- Similar lifecycle as liver fluke. except Juvenile fluke never leave the intestinal canal.
- Definite host:
- Cattle: C. daubneyi
- Sheep and goat: P. cervi

skeletal muscle
C.ovis/c.cervi

Rumen fluke cross-section
- Paramphistomum (I.H: planorbids - freshwater snails)
- Calicophoron (I.H: Galba truncatula
- Morphology: Bean like, reddish worms having a sucker on the oral end and another bigger on the opposite end
- Similar lifecycle as liver fluke. except Juvenile fluke never leave the intestinal canal.
- Definite host:
- Cattle: C. daubneyi
- Sheep and goat: P. cervi

tapeworm egg w oncoshphere

The scolex of a Taenia species usually have strong hooks on the rostrellum.
two suckers

Redia
- the third larval form, develops by asexual budding in the sporocyst
- redia has amouth and a blind sac of intestine and actively consume the tissue of the snail host.
- after some time the cercariae (4th larval stage) develops inside the body of redia

E. multicolaris (alveolaris)

Gall bladder: adult liver fluke
- Life cycle:

Diplydium caninum - flea or cucumber tapeworm
- 2 sets of genitalia
- genital openings on both sides of the longitudinally narrow proglittids

Hydatid cyst, E.graulosus (thick wall)


