Head and Neck Muscles Flashcards
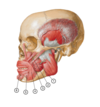
1
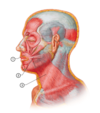
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles does it belong to?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Digastric Muscle
- Suprahyoid Muscles
- Anterior belly - digastric fossa of mandible
Posterior belly - mastoid notch of temporal bone - Intermediate digastric tendon (body of hyoid bone)
- Depresses mandible
Elevates hyoid bone when swallowing and speaking - Anterior belly - nerve to mylohyoid of inferior alveolar nerve (CNV3)
Posterior belly - digastric branch of facial nerve (CNVII)
2
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles is it part of?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Corrugator supercili muscle
- Orbital group
- Frontal bone (medial end of superciliary arch)
- Middle of the eyebrow
- Draws the eyebrows medially and inferiorly (i.e. when squinting)
- Facial nerve - temporal branch
3
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Middle scalene
- Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of vertebrae C3-C7
- Superior border of rib 1 (posterior to subclavian groove)
- Bilateral - neck flexion
Bilateral - elevation of rib 1
Unilateral - neck ipsilateral flexion
Unilateral - neck contralateral rotation - Anterior rami of spinal nerves C3-C8
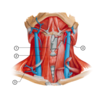
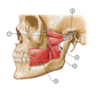
4
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:

A
- Mylohyoid muscle
- Hyoglossus muscle
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Anterior belly of digastric muscle
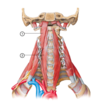
5
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Auricularis anterior muscle
- Epicranial aponeurosis
- Spine of helix
- Draws auricle anteriorly
- Facial nerve - temporal branches
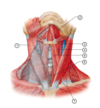
6
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:

A
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Mylohyoid muscle
- Anterior belly of digastric muscle
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Platysma muscle (partially cut)
7
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Trapezius
- External occipital protuberance
Medial third of superior nuchal line (of occipital bone)
Ligamentum nuchae (nuchael ligament)
Spinous processes of C7-T12 - Superior fibres - posterior border of lateral third of clavicle
Middle fibres - medial margin of acromion and posterior border of scapula spine
Inferior fibres - converge at an aponeuosis inserted into the scapula spine - Upper fibres - scapulothoracic joint - draws scapula superiomedially
Upper fibres - atlantooccipital joint/upper cervical vertebrae - extension of head and neck and lateral flexion of head/neck
Upper fibres - atlantoaxial joint - contralateral rotation of head
Transverse/Central fibres - scapulothoracic joint - draws scapula medially
Lower fibres - scapulothoracic joint - draws scapula inferomedially - Motor - Accessory nerve (CNXI)
Sensory - Anterior rami of spinal nerves C3-C4 (via cervical plexus)
8
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles is it part of?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle
- Oral group
- Maxilla (near the bridge of the nose)
- Alar cartilage of the nose
Lateral upper lip (blending with orbicularis oris and levator labii superioris muscles) - Elevates the upper lip
Dilates the nostril - Facial nerve - zygomatic and buccal branches
9
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:
A
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Thyrohyoid muscle
- Sternohyoid muscle
- Omohyoid muscle (superior belly)
- Fibrous loop for intermediate digastric tendon
10
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Platysma
- Skin/fascia of infra- and supraclavicular regions
- Lower border of mandible
Skin of buccal/cheek region
Lower lip
Modiolus
Orbicularis oris muscle - Depresses mandible and angle of the mouth
tenses skin of lower face and anterior neck - Cervical branch of facial nerve (CNVII)
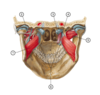
11
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:

A
- Sternothyroid muscle
- Thyrohyoid membrane
- Hyoid bone
- Thyroid cartilage
- Cricoid cartilage
- Thyroid gland
- Trachea
12
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles does it belong to?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Sternohyoid
- Infrahyoid muscles
- Manubrium of sternum
Medial end of clavicle - Inferior border of body of hyoid bone
- Depresses hyoid bone (from an elevated position)
- Anterior rami of spinal nerves C1-C3 (via ansa cervicalis)
13
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles is it part of?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Masseter muscle
- Muscle of mastication
- Inferior and medial border of the zygomatic arch
Maxillary process of the zygomatic bone - Angle of mandible
Ramus of the mandible
Coronoid process - Elevates mandible
Protrudes mandible
Aids in lateral excursion of the mandible - Masseteric branch - of the anterior division of the mandibular of the trigeminal nerve (CNV3)
14
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles is it part of?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Procerus muscle
- Nasal group
- Nasal bone (lower portion)
Lateral nasal cartilage - Skin of the forehead between the eyes
- Brings skin together creating transverse wrinkles on the bridge of the nose (e.g. when frowning)
- Facial nerve - temporal and zygomatic branches
15
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:
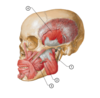
A
- Masseter muscle
- Parotid duct
- Buccinator muscle
- Temporalis muscle
16
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles is it part of?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Temporalis muscle
- Muscle of mastication
- Entire temporal fossa
- Coronoid process
Anterior border of the mandibular ramus - Elevates and retracts mandible
Aids in lateral excursion of the mandible - Anterior and posterior deep temporal branches
(branch of anterior division of mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve - CNV3)
17
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles is it part of?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Orbicularis oculi muscle
- Orbital group
- 3 parts: orbital, lacrimal, palpedbral
- Orbital - frontal process of maxilla; nasal portion of frontal bone; medial palpebral ligament
- Lacrimal - lacrimal bone
- Palpebral - medial palpebral ligament
- 3 parts:
- Orbital - around the orbit
- Lacrimal - lacrimal fascia around the lacrimal canaliculi
- Palpebral - lateral palpebral raphe
- Orbital - voluntary closure of eye (e.g. squinting)
Lacrimal - pulls lacrimal pupilla and eyelids medially, aids in flow of tears
Palpebral - closure of eyelids gently (e.g. sleeping/blinking) - Facial nerve - temporal and zygomatic branches
18
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles does it belong to?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Thyrohyoid
- Infrahyoid muscles
- Oblique line of thyroid cartilage
- Inferior border of body of hyoid bone
Greater horn of hyoid bone - Depresses hyoid bone
Elevates larynx - Anterior ramus of spinal nerve C1 (via hypoglossal nerve - CNXII)
19
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Auricularis superior muscle
- Epicranial aponeurosis
- Superior surface of auricle
- Draws auricle (ear) superiorly
- Facial nerve - temporal branches
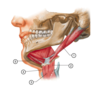
20
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:
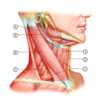
A
- Omohyoid muscle (superior and inferior belly)
- Sternohyoid muscle
- Thyrohyoid muscle
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Scalene muscles (anterior, middle and posterior)
21
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:

A
- Temporalis muscle
- Masseter muscle insertion (cut away)
- Buccinator muscle
- Orbicularis oris muscle
22
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles does it belong to?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Stylohyoid
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Styloid process of temporal bone
- Body of hyoid bone
- Elevates and draws hyoid bone posteriorly
- Stylohyoid branch of facial nerve (CNVII)
23
Q
Identify the following structures in this image:

A
- Orbicularis oculi muscle
- Nasalis muscle (transverse and alar parts)
- Buccinator muscle
24
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What group of muscles is it part of?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Levator anguli oris muscle
- Oral group
- Canine fossa of maxilla (inferior to infraorbital foramen)
- Angle of mouth
Some fibres belnd and provide origin for orbicularis oris m. - Elevates angle of the mouth - e.g. smiling
Makes nasolabial furrow more pronounced - Facial nerve - zygomatic and buccal branches
25
Q
- What is this muscle?
- What is its origin?
- What is its insertion?
- What is its function?
- What is its innervation?

A
- Frontalis muscle (part of occipitofrontalis muscle)
- Skin and superficial fascia along eyebrows
Adjacent facial muscles - corrugator supercili, orbicularis oculi and procerus - Epicranial aponeurosis
- Elevates eyebrows
Wrinkles forehead - Facial nerve - temporal branch