guide.rubyonrails.org Part1 Flashcards
(23 cards)
What is Rails and what 3 benefits do most rails programmers appreciate the most?
Rails is a web development framework written in the ruby language, used by programmers to create complete web apps. The top 3 benefits of rails:
a) Fun. It makes programming more fun.
b) Less code. Programmers write less code but do more.
c) Makes Assumptions. Rails makes assumptions of what you need to get started.
http: //guides.rubyonrails.org/getting_started.html
What is the rails way?
The rails way refers to the rails philosophy of programmers following two guiding principles when coding: DRY COC.
Don’t repeat yourself is a principle within software development that states “Every piece of knowledge has a SAD (single, authoritative, dictatorial) representation within a system”. Avoid writing the same code over and over again, this way your code is easy to maintain and more extendible.
Convention over configuration means as long as programmers learn and follow rails conventions programmers wouldn’t need to specify every thing about their apps through endless configure files.
The first step (in creating your rails app) is create a folders and files to store your files, how does Rails make this easy?
Rails creates the majority of your files and folders for you. Rails comes with a number of scripts called generators, which basically build up your MVC components with necessary files and folders.
How do you create a rails app to start working in?
Think “new app” when you decide on creating a new rails app.
$ rails new nameOfApp
Rails creates your app, and Rails’ generators download all the gem dependencies you need.
What CLI command reveals the many CLI options Rails provides?
The new keyword use below is odd, but necessary.
$ rails new -h
This command returns all the CLI options that your Rails app builder accepts.
Explain what the purpose of the following files/folders are:
app/
bin/
config/
config.ru
db/
Gemfile Gemfile.lock
lib/
log/
public/
Rakefile
README.rdoc
test/
tmp/
vendor
app/ - Contains the MVC HAM (models, views, controllers, helpers, assets, mailers) for your app.
bin/ - Contains the rails script that starts your app and can contain other scripts you use to setup, deploy or run your app. Contents: bundle, rake, rails, setup, spring.
config/ - Configure your application’s routes, db, and more.
config.ru - Rack configuration for Rack based servers used to start the application.
db/ - Contains your current db schema, as well as the db migrations.
Gemfile Gemfile.lock - These files allow you to specify what gem dependencies are needed for your Rails app. These files are used by the bundler gem (see bundler.io).
lib/ - Extended modules for your app.
log/ - Application log files.
public/ - The only folder seen by the world as-is. Contains static files and compiled assets.
Rakefile - This file locates and loads tasks that can be run from the CL. Task definitions are defined throughout the Rails components. Rather than changing Rakefile try adding your own tasks by adding files to the lib/tasks directory of your app.
README.rdoc - Brief intro to your app. You should edit this to say what your application does, how to set it up and so on.
test/ - Unit tests, fixtures and other test apparatus
tmp/ - Temp files (ex- cache, pid, session files)
vendor - a place for all third-party code. In a typical Rails app this includes vendored gems.
How do you start your rails server?
$ bin/rails server
Typing in the above code will fire up WEBrick, a web server distributed with Ruby by default. To see an app in action, visit the url http:localhost:3000 in your browser while the rails server is running.
What is WEBrick?
WEBrick is a Ruby library providing a simple HTTP server that serves your rails app. It’s also open source.
What are RubyGems?
The RubyGems software is a package manager that allows easy download and installation of Ruby packages or Gems. Gems extend functionality of your app, gems are libraries or other forms of reuseable code other programmers found worthwhile to incapsulate, note the Rails philosophy of DRY.
Some gems contain command line utilities to help automate tasks and speed up your work.
http://guides.rubygems.org/
If after starting your rails server your localhost:3000 browser page shows a ‘Welcome Aboard’ page you’ve successfully served a webpage with your current rails app confiuration. Successful running of the ‘Welcome Aboard’ page is called a smoke test. Explain this term further.
It answers the question of correct configuration. In computer programming and software testing a smoke test (or confidence test or sanity test) is a preliminary test. Preliminary tests would obviously reveal any failures severe enough to reject a software release.
What is the purpose of the controller and the view?
To get Rails to say anything such as “Hello world” you need at minimum a controller and a view.
A controller receives requests from the browser, collects information and responds to the browser.
The view responds to the controllers request and displays information in a human readable format.
How would you create a new controller?
Funny thing about creating controllers- once you create a controller you can also create a view!
(Note rails uses its generators to create all parts of its MVC)
$ bin/rails generate controller welcome index
The controller is called ‘welcome’
The view is called ‘index.’
welcome_controller.rb is the name of our controller.
index.html.erb is the name of our view file.
(The extension .erb stands for embedded Ruby)
Rails will also go on to create several other files and routes for you.
If you’d like to edit the app to say ‘Hello world’, edit your view at:
app/views/welcome/index.html.erb
But how do you go about having your ‘Hello world’ message show up as the main homepage in your rails app localhost:3000 page rather than our ‘Welcome Aboard’ page?
If we want Rails to navigate to or index page as our root URL of our site, instead of the ‘Welcome aboard’ page, we’ll need to tell Rails where the homepage is located. Go to your apps routing file and change the root destination to what you’d like it to be.
Locate and open the routing file by heading back to your apps root folder, you’ll find the routes.rb file in your config folder.
Find the file that starts with ‘root,’ uncomment it. Once this is done running your rails server should show an updated root (home) page.
In your rails application what does the term ‘resource’ mean, and how is it used?
A REST Resource is a term for collection of similar objects.
Ruby collects lots of things like articles, people or animals.
You can CRUD resources anytime you want.
(CRUD: create, read, update, destroy)
Ruby provides a resources method that’s really easy to use and is used in the config/routes.rb page.
So we understand that we store our ‘articles’ in ‘resources’, but what are articles?
To my knowledge articles in ruby are like components in React, they are used to contain html content and/or content in general.
I’m not very clear on what ‘articles’ in this instance refers to. I understand that it serves as a resource or a collection of similar things and it can be created, read, updated or destroyed (CRUD) just as well as we can get, post, put and delete it (GPPD). But what it represents isn’t immediately understood. We created our resource in the routes.rb page, but it seems we can create html content out of it, such as a form? Are resources really similar to components in REACT?
What are resources?
Resources are a fundamental concept in all RESTful APIs. The resource acts very much like an object (in OOP languages) in all ways except its methods aren’t as varied. The resource has a type, associated data, relationships to other resources, and its own set of methods.
Resources can exist as singletons, alone in the ether. They can also exist in collections. Resources can also exist in sub-collections within one collection, this is where relationshiops come into play.
http://restful-api-design.readthedocs.io/en/latest/resources.html
Assuming you create a resource named articles, how do you go about seeing the details of the resource?
Run $ bin/rake routes
You simply deploy the routes. $ bin routes
(remember resources are created inside the routes.rb file)
Rails defines routes for all your standard RESTful actions.
Assuming you created a resource named articles in your config/routes.rb file Rails should have defined several route lists. One of those URI patterns ends in articles/new. You’ll be able to create a new article at this address. How do we do so?
If we opened up to the localhost:3000/articles/new address we’d see a routing error page. The error: our controller is not defined and cannot serve the request.
To define a controller enter the following:
$ bin/rails generate controller articles
The above code will generate a new RAILS controller named articles.
(Note however you had the option of also creating a view by simply having a name follow the ‘articles’ designation, but we chose not to do so here)
What steps were taken in the Rails tutorial to ensure the routes, controller and action components of our app worked?
See section 5.1: Laying the groundwork.
?
How does one create a form builder in Rails?
Rails offers a method to help you create a form. The helper method is called form_for.
(think of the form_for method as you would an html tag)
To use this method head to your views/articles/new.html.erb file and enter the following code:

How do we create an action for our article?
Easy. We go to our controllers/articles_controllers.rb file and define our create ruby function (In rails it seems functions are called actions). The create action helps save our new article to the database.
def create
end
The create action/function helps us save our new article to the database, and we know the article is saved as parameters. How do we see this data on screen?
Go into your controller and inside your create function simply add another line of code to render your parameters!
render plain: params[:article].inspect
The render method above takes a key and a value. The key is ‘plain,’ the value is a method called params with a passed in ‘:article’ and a params method.
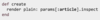
Models in rails are classes and use a singular name, and their corresponding database tables use a plural name. Rails provides a generator for creating new models. What CLI command must you run to create a new model?
The CLI command to run a new model:
$ bin/rails generate model Article title:string text:text
Above we generate a model named Article, with a title and text.
(Note: Models are classes and use a singular name. Class names must always begin with Capital letters.)


