GU Flashcards
(37 cards)




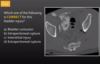



most common form of bladder rupture
extraperitoneal
extravasated contrast limited to perivesical space
SIMPLE extraperitoneal bladder rupture
extravasated contrast from the bladder extends to the thigh, scrotum, and perineum
COMPLEX extraperitoneal rupture
treatment for extraperitoneal bladder rupture
Foley catheter placement

Simple EXTRAperitoneal bladder rupture
contrast is confined to the perivesical space

simple extraperitoneal bladder rupture
“MOLAR TOOTH” accumulation of extravasation contrast
type of bladder injury and spaces indicated by the arros

COMPLEX extraperitoneal bladder rupture
red arrow = prevesical space
Blue arrow = perivesicular space

bladder neck injury
treated conservatively with FOLEY CATHETER
intraperitoneal bladder ruptures are secondary to rupture at what anatomic location in the bladder?
injury to the bladder dome
management of intraperitoneal bladder rupture
SURGERY

intraperitoneal bladder rupture
extravasated contrast outlining multiple bowel loops










most specific sign for testicular rupture
contour abnormality

extraperitoneal rupture

most common mechanism of injury causing bladder injury
blunt trauma is most common (70-80%)

INTRAperitoneal bladder rupture
injury to the bladder dome
















