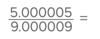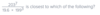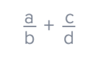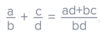GRE Flashcards
(140 cards)
When both quantities of a QC (Quantitative Comparison) problem are unique values, the answer will never be what?
D - cannot be determined
Note: If quantatity A and B are both #’s there will always be a relationship. They will either be equal or one will be greater than the other.
When both quantities of a QC problem want you to calculate the permiter or the area of bounded figures (shapes), and one of them is a circle, the correct answer will never be what?
D
Note: and it is highly unlikely that it will be C
What is an improper fraction?
numerator > or equal to denominator
i.e. 3/2, 4/3, etc.
What is a proper fraction?
Numerator < Denominator
i.e. 3/4, 3/8, etc.
Converting an improper fraction to a mixed number.
7/2 = ?
3 1/2
Note: divide the num. by the den to get a quotient of 3. Put any remainder over the original den. Remainder of 1 is placed over the 2.
Converting a mixed # to an improper fraction:
7 2/3 =
Multiply the den. by the quotient and add the numerator. Put that all over the original den.
3 x 7 + 2 = 23/3
LCD (Least Common Denominator) is what?
LCD is the smallest common mutiple of all the denominators in the list.
1/6 = 6, 12, 18, 24, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60
1/5 = 5, 10, 15…55, 60
1/12 = 12, 24, 36, 48, 60
LCD of 1/6, 1/5, and 1/12 = ?
60
Is 7/56 = 10/80?
Yes.
7 x 80 = 560
56 x 10 = 560
4/7 + 2/7 = ?
6/7
Distributive property of division over addition.
What is the distributive property of division over addition?
A/B = C/B = (A+C)/B
4/7 - 1/7 = ?
3/7
a/b + c/d = ?
Hint: Place in another form
Hint: adding and subtracting with different denominators
(ad + bc) / bd
a/b - c/d =?
Hint: Place in different form
Hint: adding/subtracting fractions with different denominators.
Division with Fractions
3/4 / 1/7 = ?
Hint: Flip and multiply
3/4 * 7/1 = 21/4
Multiplication with Fractions and whole #’s
5 x 4/5 =?
20/5 = 4
2/3 / 6 = ?
Hint: flip and multiply
2/3 * 1/6 = 2/18 = 1/9
Note: remember to always flip the # that comes after the sign.
The product of a # and its reciprocal is always equal to ??
Hint: 1 over that number
Always equal to 1
Note: 4 * 1/4 (Reciprocal) = 4/4 = 1
What is the only number that does not have a reciprocal?
0 is the only number.
Note: any # multiplied by its reciprocal will = 1; however,
0 * 1/0 = 0 and not 1
Explain 3 ways to reduce fractions
1 - multiple all the denominators by the LCD
How do you find the LCM/LCD using prime factorization?
Hint: LCD - Least Common Denominator and LCM - Least Common Mulitple
- Prime factor all denominators within the set
- Multiply every prime # taking the highest exponent of each prime.
ex. LCD/LCM (2,5,8) ==> 23 x 51 = 8 x 5 = 40
2 = 21
5 = 51
8 = 23
More than/ Less than:
is 7/12 > or < 8/12?
7/12 < 8/12
Note: In positive fractions with the same denominator, the larger the numerator, the larger the fraction
Is 3/2 > or < 3/4?
3/2 > 3/4
Note: In positive fractions with the same numerator, the larger the denominator, the smaller the fraction and the smaller the denominator, the larger the fraction
What is the difference between LCM and LCD?
LCD is simply used in fraction form because we want the LCM of the denominator.
LCM is a synonymous term for finding the Lowest common multiple of any set of numbers.