Gout PCOL Sharpe Flashcards
Which patients have a greater incidence of gout? (select all)
A. Obese patients
B. Male gender patients
C. Older patients
D. Female gender patients
E. Patients with decreased levels of serum urate
A, B, C
What foods or beverage will potentially increase incidence of gout? (Select All)
A. Rice
B. Alcohol
C. Fish
D. Vegetables
E. Meat
B, C, E
All of these factors lead to overproduction of Uric Acid except
A. Purine metabolization
B. Increased breakdown of tissue nucleic acids
C. Excessive dietary purines
D. Enzyme abnormalities
E. Decreased kidney function
E
What does the term “Denovo” mean in terms of uric acid in the body?
A. Refers to the consumption of urates that lead to increased levels in the blood stream.
B. Referse to the production of uric acid within the body.
B
Which of these can cause an increase in breakdown of tissue nucleic acids?
A. Myeloprloiferative disorders
B. Lymphoproliferative disorders
C. Cytotoxic drugs
D. All of the above
D
Which of the following factors leads to hyperuricemia? (select all)
A. Endogenous purine synthesis
B. Tissue nucleic acid breakdown
C. Over-excretion of uric acid
D. Dietary purines
E. Underexcretion of uric acid
A, B, D, E
What other clinical manifestations can be present in Gout? (Select All)
A. Tophi deposits
B. Constipation
C. Nephrolithiasis
D. Chronic Urate Nephropathy
E. Acute arthritis
A, C, D, E
How are Tophi deposits caused?
A. An inflammation of the joint due to pannus formation
B. Uric acid crystalize and deposit in the joints and causes damage, deformity to surrounding tissue.
C. Worn cartilage causes inflammation and attracts uric acid
D. None of the above
B
What are some non-pharmacologic treatments of gout? (Select All)
A. Diet higher in proteins
B. Diet consisting of liver and sweet breads.
C. Diet lower in sweetbreads and liver
D. Decreased alcohol consumption
E. Physlical activity, wegith loss, rest
C, D, E
Which medications for gout treatment are used to Terminate Acute Attacks? (Select All)
A. Xanthine Oxidase inhibitors
B. Corticosteroids
C. Uricosurics
D. Colchicine
E. NSAIDs
B, D, E
T/F Gout is a type of arthritis that is associated with hyperuricemia
T
Metabolism of ____ bases will lead to the formation of uric acid in the blood and increase the incidence of gout.
A. Purine
B. Pyrimidne
A
T/F Purine bases can come from cell breakdown and dietary intake
T
Based on the picture provided lable the boxes in the appropriate order from top to bottom:
I. Purine base
II. Xanthine
III. Hypoxanthine
IV. uric Acid
A. I, II, III, IV
B. I, III, II, IV
C. I, IV, III, II
D. II, I, III, IV
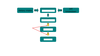
B
What enzyme is responsible for converting Hypoxanthine to Xanthine and Xanthine to Uric Acid?
A. MAO
B. CYP2C19
C. Xanthine Oxidase
D. UGT

C
Why do cancer patients have an increased chance of developing hyperuricemia?
A. Cytotoxic medications (chemo) that kills cells in the body
B. Increased Xanthine oxidase sensitivity
C. Higher levels of dietary intake of purines
D. Cancer naturally produces more uric acid than normal patients
A
Cytotoxic drugs destroy cells and cause them to break down. Cancer patients taking these medications or undergoing therapies will have more cell destruction and lead to more purines in the body.
Which of the following statements is true regarding Uric Acid solubility?
A. A drop in body temperature will lead to a decreased solubility.
B. An increase in pH will cause a decrease in solubility of uric acid.
C. An increase in body temperature will increase uric acid solubility.
D. A decrease pH will decrease solubility of uric acid
A,C, D
T/F Areas such as the big toe and ear are at an increased risk of developing uric acid crystalization due to lower body temperatures in those areas
T
What is the purpose of URTA1 transporters in the kidney?
A. Reabsorption of Uric acid back into the blood
B. Excretion of uric acid in the urine
C. Chemically eliminates uric acid from the body
D. Allows crystallized uric acid to pass through the tubules and into the urine.
A
Hyperuricemia will lead to crystal deposition in the organs of the body and cause inflammation. The inflammation is caused by all of the following except:
A. Cytokine Release
B. Vasodilation
C. Influx of Polymorphonuclear
D. Vasoconstriction
D
What are risk factors of gout (Sharpe)? (Select All)
A. Age
B. Female gender
C. Hyperuricemia
D. Obesity and Insulin resistance
E. Male gender
A, C, D, E
Which of these risk factors could possibly bring about a gout attack?
A. Stress and trauma
B. Consumption of high purine foods
C. Aspirin and alcohol
D. Cytotoxic drugs and diuretics
E. All of the above
E
(Short Answer) How does alcohol cause an increased risk of gout?
Dehydration: Alcohol causes dehydaration and decreases blood volume. This increases the concentration of uric acid in the blood and it will crystalize more easily as a result.
Elimination: Will impair elimination of uric acid from the body.
Patients are at a higher risk of uric acid nephrolithiasis if their urine is at a ____ pH
A. Higher
B. Lower
B


