Gmat Prep Flashcards
Least Common Multiple
Used when adding or subtracting fractions
Use prime facorization and then multiply the numbers. **“multiply pairs and singles” **
84= 2x2x3x7
66=2x3x11
2x2x3x7x11 = 924
Greatest Common Factor
used to simplify a fraction
You only multiply the “paris” on each side
Adding & Subtracting Fractions
Denominators must be the same to add or subtract across
When using large numbers find the
Least Common Multiple to get the denominators to match!
Multiplying Fractions
Reduce diagonally and the multiply across
Divide Fractions
Flip and multiply
Exponents
- Multiplying
- Dividing
- Parenthesis
- Multiplying Parenthesis
- Negative Reciprical
Multiplying - Add Across 22x 23= 22+3= 25
Dividing - Subtract 44 =44-2 = 42
42
Parenthesis - multiply (32)4= 32x4 - 38
MultiplyParenthesis - (23)(33) = (2x3)3
Neg Reciprical a-n = 1 or (_1)_n
an or (a)
What happens to positive fractions with the same numerator but different denominators…
As the denominator increases…
As the denominator decreases…
Denominator increases the fraction gets smaller
Denominator decreases the fractions get larger
Inequalitities Multiplied or Divided by a negative you…
flip the inequality sign
Radicals/Square Roots
Follow same rules as exponents

Distance
speed x time
Prime #’s
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47
Distinct Prime Numbers
“different”
ex: 1,050 = 2 x 3 x 5 x 5 x 7
5, Prime #’s
4, Distince Prime #’s
Simple Interest
Only applied to the principal, not the interest that has already been accrued
Principal x (1 +rt)
R = interest rate per time period expressed as a decimal<br></br>T = # of time periods
Compound Interest
Interest applied to the principal and any previously accrued interest
principal x (1 +r)t
R = interest rate expressed as a decimal T = # of time periods
Rate
quantity A
quantity B
Combined Rate or Work
Rate =
# of tasks
time to complete tasks
if more than 2 : <u>1</u> =<u>1</u>+ <u>1</u>+<u>1</u><br></br> t a b c
Combined Rate or Work
- 2 ppl or 2 machines
Total Time =
AB
A + B
Speed
Distance
Time
Decimal or Percent 2 a Fraction
Multiply by 100
0.17 x 100% = 17%
1/4 x 100 = 25%
% to a Decimal
drop % sign and move decimal points
2 places to the left
0.8% = 0.008
% Increase
Amount Increase x 100%
Original
% Decrease
Amount Decrease x 100%
Original
Standard Deviation
how close or far the termas are from the average
To find the sum of any set of #’s
Multiply the average by the # of terms
Extra Practie. Page. 804
To find the sum of a sequence of consecutive integers
Multiply the average of the largest and smallest term by the # of terms
To find the # of terms in a consecutive sequence
take the difference between largest and smallest and add 1
Combinations Formula
Page. 805
Used when solving for a # of K unordered selections one can make from group N
nCk = n!
k! (n-k) !
Permutations Formula
Page 806
Used when solving for a # of K ordered selections one can make from group N
nPk = _ __n! _
(n-k) !
Probabilty
Number of desired outcomes
_______________________________
Number of total possible outcomes
Multiply the fractions by one another.
Average Formula
sum of terms
__________________
number of terms
Balanced Average
The difference between the average and every # below and above it
Weighted Average
used when you know the average of different portions of the whole
Ex: 2/5 of the studens have a gpa 79 and the remaining 3/5 have an average of 84
(0.4)(79) + (0.6)(84)
31.6 + 50.4
82
Average Speed
Total Distance
____________________
Total Time
What do you do when you have multi-part journey “average” questions
you use a chart to organize the data

Divisibility Test
A number is divisibly by 2 if…
the units digit is even
128 is divided by 2 because 8 is even
177 is not divisiblye by 2 because 7 is not even
Divisiblity Test
A number is divisible by 3….
if the sum of the digits is divisible by 3
4,317 is divisible because 4 + 3 + 1 + 7 = 15
Divisiblity Test
Divisible by 4 if….
if the last two digits compose a two-digit number that is divisible by 4
1,732 is divisible by 4 because 32 is divisible by 4
Divisibilty Test
Divisible by 5 if….
if its units digit is either a 5 or a 0
26,985 is divisible by 5
Divisiblity Test
Is divisible by 7 if…
the difference between its units digit multiplied by 2 and the rest of the # is a multiple of 7
147 is divisible by 7 because 14 - 7(2) = 0
(which is divisible by 7)
Divisiblity Test
Divisible by 8 if…
its last three digits compose a three-digit number that is itself divisible by 8
76,848 is divisible by 8 because 848 is divisible by 8
Divisiblity Test
Divisible by 9 if…
the sum of its digits is divisible by 9
16,956 is divisible by 9 because 1+6+9+5+6=27 which is divisible by 9
Divisiblity Test
Divisible by 10 if…
its units or digits is zero
67,890 is divisible by zero
What is a Supplementary Angle?
if two angles when together make a straight line aka 180 degrees
What is a Complimentary Angle?
if two angle’s together make 90 degrees
Area of a Triangle
1/2 x base x height
Perimeter of a Triangle
Add all sides together
What are congruent triangles?
When different triangles have corresponding angles with the same measure and corresponding sides with the same length.
They’re proportional to one another
Pythagorean Theorem ?!
holds for ALL right triangles
A2 +B2 = C2
“Pythagorean Triples”
Right triangles with the lengths (sides)
32+ 42 = 52
6, 8, 10
5, 12, 13
Special Right Triangles Ch. 18
For Isosceles Right Triangles
aka 90º 45º 45º
90º 45º 45º
X2root2 X X
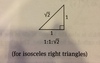
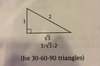
Special Right Triangles Ch. 18
For 30º 60º 90º
30º 60º 90º
X X2root3 2X
The sum of the interior angles of a Polygon is….
(number of sides - 2)180º
How do you measure each interior angle in a Regular Polygon
(#of sides - 2)180
____________________
# of sides
How to find the…
Area of a Rectangle
Length x width
How to find the ….
Area of a Square
side x side
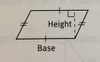
How to find…
The Area of a Parallelogram
Base x Height
How to find the….
Area of a Trapezoid
1/2 x the sum of the bases x height

What is the..
Radius of a Cirlce
A line segment from the center of the circle or the “half way point”
What is the …..
Diameter of a Circle
A line segment that conects form one end of the circle through to the other end
What is the Circumfrence of a Circle
The distance around a circle
C = 3.14 (pie) x Diameter
C = 3.14 (pie) x 2 x Radius
What is an ARC
How do you determine the Arc Length
A propportion of the circumfrence of a circle
Arc Length = ( Nº / 360 ) x Circumfrence
What is an Inscribed Angle?
How do you determine the Arc Length of an Inscribed Angle?
One that opens up from the edge of a circle instead of its center
Arc Length = ( Nº/ 180 ) x Circumfrence
How do you find…
The Area of a Circle
Area = 3.14(pie) x R2
What is the Sector of a Circle?
How do you find the Area of a Sector?
a portion of the circle bounded by two radii and an arc
Area of a Sector = (Nº/ 360) x Area of a Circle
Rectangle
What is the Volume?
What is the Surface Area?
length x width x height
2lw x 2lh x 2wh
What is the formula for
Diagonals in Rectangular Solids?
diagonal2 = length2 + width2 + height2
Cube
What is the Volume?
area of base x height = edge3
aka
V = L x W x H = E3
Cylinder
What is the Volume?
area of base x height
aka
V = (Pie x R2) x Height
Cube
What is the Surface Area?
sum of areas of faces = 6 x edge2
aka
SA = 6E3
Cube
What is the Total Surface Area?
area of bases + LSA
aka
SA = (2 x Pie x R2) + (2 x Pie x R x H)
Slope
Slope Intercept Form
Rise = Change in Y
_______________________
Run = Change in X
y = mx + b
(the slope is m)
How do you calculate the Distance on a Coordinate Plane?
To determine the distance between any two points on a coordinate plane, you use Pythagorean Theorem
How to find the….
Distance Between Two Points

How to simplify these expressions….
(a + b)(a - b) =
(a2 - b2)


