Glass Slide images Flashcards
(142 cards)

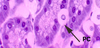
thyroid gland

parafollicular cells
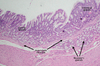
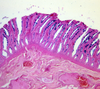
what slide is this?

thyroid

thyroid slide
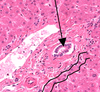
cuboidal follicular cell
What is this? What kind of gland is it (how do you know)?

Sweat gland
simple tubular coiled gland
A simple gland has an unbranched duct (or no duct at all). There is only a single secretory unit

What is this? What cells are found here?

Sweat gland
cells:
- dark cells - near lumen in the center
- pale cells - periphery, clear
- myoepithlial cells - lines periphery, with triangular shaped nuclei

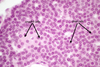
What are these cells (how do you know)? Where are they found?

Myoepithlial cells
1) in sweat gland
line the periphery and have triangular shaped nucleus
2) also found in intralobular ducts
What is top portion of this picture (how do you know)

Sweat gland DUCT
know: b/c has stratified cuboidal epithelium, meanders through dermis to terminate on skin surface
What are the bottom arrows? What type of gland is this?

Sebaceous gland
round or pear shaped, clear or lavender
SIMPLE BRANCHED ACINAR GLAND
What is this? What type of muscle?

Erector pili in scalp slide, between hair follicles
smooth muscle
What muscle can be found between hair follicles?
Erecti pili - smooth muscle

What are thse cells in a sebaceous gland?

stem cells - basophillic
What are these cells? What does this signifify?

Pyknotic cells in sebaceous gland
- pyknotic means condensed nucleus*
- these cells are dying and will soon lyse. Ultimately, cells lyse and their lipid-filled cytoplasm becomes sebum*
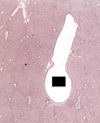
What is this? what does its presence indicate? what type of gland is it?

Islet of langerhans
indicates you are in the pancreas
endocrine gland
what is this? What is secreted here?

Islet of langerhans
a cell -> glucagon
b cell -> insulin
∂ cell -> somatostatin
F or PP cell -> pancreas polypeptide
what is the gland around the “island” in the middle? what type of gland is this?

exocrine pancreas around the islet of langerhans
acini cells are stained bright red
compound acinar gland
what cell is this in the pancreas? (how do you know)
where does its product go?

serous acini cell
brightly red
product enters into intercalated duct
what is this in the pancreas (how do you know)? what does it secrete?

Interlobular ducts:
Low columnar epithelium
Also secrete bicarbonate-rich fluid.
Located between lobules, within the thin connective tissue septa that separate lobules.
what is this in the pancreas? waht does it secrete?

intercalated duct
looks collapsed on itself
produces bicarbonate, stimulated by secretin

what cell is this in the pancreas? what stimulates it?
what does this cell lack?

intercalated ducts
stim. by secretin
lacks secretory granules
what is red? blue (in the pancreas)

red – centroacinar cell – pale staining
blue – serous acinus cell

what is this in the panceas

centroacinar cells
pale staining little round ducts

What is this? what type of gland is it?

Submandibular glanda
predominance of the serous acini
compound tubuloacinar gland. By definition, as in all compound glands, the conducting portion is branched
What is this? What type of acni does it have

Submandibualr gland
mostly serous acni (so look for redish color), but also has mucoous acni and mixed acni