GI Path Flashcards
Which has better prognosis: pedunculated or sessile polyps?
Pedunculated– easier to resect
What is the MCC of pseudopolyps in the colon?

Ulcerative colitis
Juvenile polyps: benign or malignant
Rarely malignant; can rarely get Polyposis Syndrome
ID

Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome: hyperpigmentation @ lips/gingiva + harmatomatous polys (benign)
Have increased risk of cancer, but not from polyps themselves
Colonic Hyperplastic Polyps:
- Common or rare?
- Benign or malignant?

Common
Benign but MUST be distinguished from Sessile Serrated Adenomas
When might you suspect Colonic Hyperplastic Polyps may actually be Sessile Serrated Adenomas?

Large (>1cm) in RIGHT colon
– DNA mismatch repair pathway affected
Adenoma of Colon:
- common or rare?
- Benign or malignant?
- Common
- ALWAYS have dysplasia – ALWAYS pre-malignant
Most colon cancers arise from what?
Adenoma of colon- always pre-malignant, but good to find because they can be removed before they become malignant
How can you tell if Adenoma of Colon has invaded?

Stromal desmoplasia
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis

- Rare APC gene mutation
- 100% develop colon cancer
- Wall-to-wall adenomas = FAP until proven otherwise
Main risk factor for Colon Cancer besides genetics?
Diet– better to eat high fiber & fruits & veg
Dirty necrosis

Probably coming from colon
Mucin all up in that peritoneal cavity…

Check appendix!
Yellow tumor in small intestine

Carcinoid
Carcinoid syndrome:

HTN, flushing, diarrhea
MC metastatic site = liver (CT scan)
GIST: prognosis based on? diagnosis?
Prognosis based on size & mitotic rate
CD-117 stain helps confirm dx & prognosis
Appendiceal carcinoids: location? common? prognosis?

@ tip usually
Common
Good prognosis
Appendiceal Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma: morphology

- Mucin + epithelial cells in peritoneal wall
- Pseudomyxoma peritonei (lots of mucin in peritoneal cavity)
ID

Tubulovillous Adenoma
(Intestinal adenomas can be Tubular, Villous, or Tubulovillous)
Morphology of Esophagus with Achalasia
Loss of inhibitory neurons in wall of intestine (enteric)
How are esophageal webs & rings formed?
Post-inflammational scarring (most common)
Tumors
What is the cause of diverticuli?

Esophageal spasms
What is the cause of Mallory-Weiss syndrome?

Persistent vomiting (alcoholics, eating disorder)
Usually not too severe
Cause of Esophageal Varices? Severity?

Portal HTN (from cirrhosis)
Can rupture– 50% mortality :(
What is the main complication of a hiatal hernia?

Reflux –> ulcer –> Barrett’s –> cancer
Histology of Reflux Esophagitis?

Long papillae
Inflammatory cells
What is a histological feature that MUST be present to diagnose Barrett’s Esophagus?

Goblet cells above gastroesophageal junction

ID cause of esophagitis

Herpes:
Multinucleate, fine chromatin cells in epithelium
ID cause of esophagitis

CMV– usually in stroma
White plaques in esophagus?

Candida esophagitis
-- ONLY IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISEED
Concentric rings in esophagus?

Eosinophilic esophagitis – Must have eosinophila (causes contractions of muscularis propria)
Esophageal biopsy:

High-grade dysplasia– still benign but predisposes to cancer
Adeno vs Squamous Cell CA of Esophagus
Adenocarcinoma has Barrett’s surrounding
Squamous cell CA has keratin pearls
Celiac Disease:
- demographics
- Histology
- Mechanism
- Complications
- Management

- White people with HLA-DQ2, -DQ8
- Flat & inflamed histology
- IgG or IgA ab aganst gliadin;
- *IgA** against transglutaminase
- Can cause T-cell lymphoma, adenocarcinoma
- Avoid gluten
Patient has celiac symptoms, but recent diarrhea and trip to Dominica….
Tropical sprue
tx: abx
Whipple’s disease

@ small intestine
Foamy macrophages– plugs up lymphatics
Caused by atypical mycobacteria in immunocompromised (use Acid-Fast stain)
Lactase (disacccharide) deficiency: histo
NORMAL histo
Abetalipoproteinemia

Rare
See vaculoated epithelium with spur cells in blood (acanthocytes)
Where is helicobacter located?
Antrum of stomach (by pyloric sphincter)
What part of the stomach does autoimmune gastritis affect?
Body of stomach
Actue gastritis: S/S

quick course, can cause hemorrhage
Almost everyone in ICU has mucosal damage
Automimmune chornic gastritis
- @ body & fundus- ab against parietal cells
- More likely to get carcinoid tumors
- less likely to get ulcers than H.pylori
Hyperplastic polyps

- Assoc w/ H.pylori
- Made of foveolar glands
Fundic Gland Polyps

- Chief & parietal cells
- Caused by PPIs
Gastric Adenomas

Assoc w/ FAP or atrophic gastritis w/intestinal metaplasia
Risk of adenocarcinoma increases with size
Tumor Adenoma vs Hyperplastic Polyp
Adenomas have DYSPLASIA
Histology of Diffuse Gastric Adenocarcenoma

Signet rings (lots of mucin pushese nucleus to side)
Diffuse thickening
Grossly: linitis plastica
Malignant vs Peptic Ulcers

Malignant ulcers have masses, heaped edges
Peptic ulcers are benign, clean and “punched out”
Marginal Zone Lymphoma

Look for H.pylori & treat it (can advance to more serious lymphoma)
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma

LCA+ (leukocyte common ag)
50% respond to therapy

Prognosis of Autoimmune Gastritis w/ lots of Gastric Carcinoid Tumors
Good prognosis in stomach, esp with atrophic gastritis
resection usually curative
GI Stromal Tumors
- Large submucosal masses– MC mesenchyma tumor of stomach
- Mostly spindle cells
- Prognosis directly correlated w/size & mitotic activity
- Dx: c-KIT or CD117
- Tx: Imantanib
Infectious bacterial colitis: histology
- Toxin-producing organisms: NORMAL histo
- All others show ACUTE COLITIS (Neutrophils)
C. dificil

- In 3% normal people, 30% hospital pts
- Most important risk factor for developing Pseudomembranous Colitis = abx tx
- see pseudomembranes & inflammatory debris on surface
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: biopsy
NORMAL biopsy, stress related
You have a stressed patient with chronic diarrhea. Endoscopy looks normal. Should you biopsy?
YES– could be microscopic colitis (lymphocytic or collagenous)

Angiodysplasia: gross & complications

- dilated vessels on endoscopy
- causes bleeding in elderly
IBD vs Acute Infectious Colitis

Changes of CHRONIC colitis (gland distortion +/- paneth cell metaplasia) seen in IBD

Chron’s Disease: gross characteristics

- Skip lesions @ small bowel
- Transmural inflammation
- Granulomas
- Fistulas
- Cobblestone

Ulcerative Colitis: gross feats

- Broad ulcers @ rectum
- Pseudopolyps
- Crypt abscesses
- Toxic megacolon

Patient has had IBD for 10 years… what is your concern?
Cancer. look for Dysplasia (screening endoscopy)

Can Chron’s show crypt abscesses?
YES- but more common in UC
Extra-intestinal lesions of IBD?

What causes diversion colitis?
Blind pouch– no fecal flow
Tx: enema with short-chain FAs, or resection to restore fecal flowa
Ischemic Bowel Disease: causes
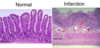
Serious disease– don’t have to be transmural to cause problems
Mucosal Infarction comes before transmural infarct
- Obstruction (increased luminal pressure or kinked /twisted bowel compromises blood supply)
- Acute occlusion of arterial supply (atherosclerosis, thrombosis, emboli)
- Hypoperfusion (shock, marked dehydration, heart failure, vasoconstrictive drugs)
Diverticular disease
Common- caused by low fiber diet
Main complcations: diverticulitis, perforation, infection
Acute Appendicitis requires inflammation of ___?

MUCOSAL inflammation
Tests if you think pt has Carcinoid Syndrome?
This will be on final
- Urine: 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid (5 HIAA)- serotonin metabolite
- 5HT -> 5HIAA
- Blood: Chromogranin A
Esophagus: dx?

Squamous Cell CA– squamous epithelium on both sides– no Barrett’s
Bipsy of Polyps in stomach (1, 3, 4)

- HYPERPLASTIC polyp
- Fundid gland Polyps
- Adenoma (Dysplasia- stratification)
Stomach- dx?

Helicobacter
- chronic gastritis (MCC = helicobacter)
- yellow picture shows microorganism
Gastric Biopsy
Dx?

adenocarcinoma w/signet rings
Any time you see clear cells in stomach in between normal glands…
Gastric Biopsy

Lots of stroma, but glands are malignant (complex, mitotic activity, necrosis)
Desmoplastic adenocarcinoma- intestinal type
Stomach. Dx?

CLEAR CELLS – signet rings
ADENOCARCINOMA
Stomach. Dx?

Linus plastica
thickening of wall
Adenocarcinoma– diffuse (signet ring)
Benign or Malignant?

Left: malignant
Right: benign
Gastric Mass. Dx?

Marginal Zone Lymphoma
-bland, large lymphocytes
Gastric Mass

Infiltrating into gland
B-cell marker (CD20)
Marginal Cell lymphoma
Stomach Mass

Diffuse Large B Lymphoma
large lymphocytes
*diffuse adenocarcinoma can appear similar– immunostain (LCA, CD45, cytokeratin) to distinguish
Stomach dx?

Benign ulcer

Normal small intestine

Celiac disease
@ small intestine, NO villi, lymphocytes @ surface
Problem: reaction to gliadin, glutan

Whipple’s:
Foamy macrophages in lamina propria

Abetalipoproteinemia
lack of transfer factor –> defx of lipid sol vitamins
acanthocytes

Microscopic colitis
A. Collagenous colitis
B. Lymphocytic colitis

Chron’s– segmental lesions (ends are normal)

Chron’s
linear, sharp fissure-like ulcers

Ulcerative Colitis
broad-based ulcers that form pseudopolyps when they heal

Chron’s Disease
- granulomas
- transmural inflammation

Left: Chron’s
- linear ulcers
Right: Ulcerative Colitis
- broad-based ulcers, pseudopolyps

Low-grade dysplasia

Acute appendicitis:
Must see MUCOSAL inflammation – if it’s just on the serosa - may be coming from elsewhere

Mucosal acute inflammation (acute appendicitis)
Polyp biopsy

Tubuladenoma
dark band of cells down center– piled up nuclei = feature of dysplasia

Villous adenoma
- Long papillary projections
- On cross section- no evidence of invasion

Villous Adenoma
- long projections

Pedunculated Tubulovillous Adenoma

High grade dysplasia:
- complex glands, shared walls, large ugly nuclei
- Not invasive because no desmoplasia
Dx? Bx would show? Gene assoc?

Familial Polyposis
Bx: tubularadenomas
Gene: APC (same as with sporadic colon cancers)

Adenocarcinoma
- complex glands
- reactive desmoplastic stroma

Dirty necrosis- colon

Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
Extracellular mucin w/islets of tumor cells
worse prognosis in colon

Carcinoid
yellow

Carcinoid
Left: Ulcer w/ tumor invading down to wall
Right: Round, monotonous, clumpy chromatin

GIST
prognostic factors: size, mitotic activity
Stain with: CD117 (c-KIT?)

Carcinoid– obstruction of lumen by tumor @ tip
Uniform cells, clumpy chromatin (same histology as the other carcinoid)
Good prognosis

Mucinous Cystadenoma
No invasion, just some stratification

Pseudomyxoma peritonei
look @ appendix!

Left: cholesterol- fat female forty
Right: bilirubin- blood disorders

Acute pancreatitis (lots of hemorrhage)
2 risk factors: alcohol & obstruction
stone would have to be @ ampulla to cause this

Acute pancreatitis
lots of neutrophils, hemorrhage

Fat necrosis
Fat necrosis all over belly? Pancreatitis (activation of lipase)

Chronic Pancreatitis
lots of fibrosis
alcoholics, chronic obstruction

Fibrous adhesion
- usually caused by post-inflammatory (surgery)
- can cause ischemic bowel

Ischemic Bowel
50% fatal– bad prognosis

Diverticular disease
old peeps, low-fiber diet
complications: inflammation, diverticulitis, perforation, rupture

Hemochromatosis

a1-atrypsin deficiency
- blue balls in cytoplasm
- Also get emphysema b/c can’t turn off inflammation quick enough
- Can cause jaundice in newborn

Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- intralobular bile duct under attack of lymphocytes
- check for anti-mitochondrial antibodies

Cholestasis
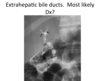
Sclerosing Cholangitis
Extrahepatic ducts –> beaded appearance
Assoc w/ ulcerative cholitis

Esophageal Varices
- portal HTN (mainly from cirrhosis)
- If they rupture & hemorrhage.. 50% mortality

Hemorrhoids

Cirrhosis:
jaundice + ascites

Nutmeg Liver– chronic passive congestion
- due to RHF
- Patients are very ill

Adenocarcinoma
dysplastic stroma, complex glands

Bile Duct Harmatoma
won’t cause problem, but if you seen them while doing sx, might be worried about metastatic disease

Focal nodular hyperplasia
- central scar
- needle biopsy is NORMAL
- not serious

Hemangioma
- most common tumor of liver
- benign

Adenoma
- bland, thin cords, no portal tracts, no central veins
- SERIOUS– can rupture and cause hemorrhage
- often seen in young women on Oral contraceptives

Cirrhosis + Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Green– bile
- Bad prognosis

Hepatocellular Carcinoma
(normal on Left)

Fibrolamellar Variant Hepatocellular Carcinoma
seen in YOUNG
better prognosis (still 50% but better)

Metastatic Disease

Hepatoblastoma
poor prognosis without treatment
with treatment - 80% cure
in young children

Angiosarcoma
- freely anastomosing vascular pattern
- Caused by vinyl chloride, arsenic, thorotrast
- Decades-long latent period
- Very serious
55-year old man with heartburn and sub-sternal chest pain.
See he has Barrett’s
2 years later, comes back with dysphagia. See a mass. What is it most likely to be?
Adenocarcinoma
Biopsy, then Esophagectomy
Esophagus

Barrett’s
GOBLET CELLS
Edge of adenocarcinoma

Dysplasia– looks like tubularadenoma -stratefied
Middle of mass

Adenocarcinoma
Muscle strand surrounded by cancer
What is the major predisposing condition for adenocarcinoma?
Reflux
55-year old woman, stomach pain, GI endoscopy
See ulcer- benign or malignant?

Benign- Peptic Ulcer
debris, granulation tissue, fibrosis– just reactive necrosis
31-year old woman- has had intermittent bloody diarrhea for 10 years
Sigmoidoscopy shows friable, ulcerated colonic mucosa extending from anus -> splenic flexure
Dx?

Ulcerative Colitis
continuous, crypt abscesses, 10 years
56 year old woman with positive stool occult blood test.
Colonoscopy: large mass– probably adenocarcinoma
Biopsy:

Adenocarcinoma

Adenocarcinoma
Within fat (right-hand side)
Large blue blob = lymph node - probably involved because not uniform in color
Resected Lymph node

Cancer- adenocarcinoma


