GI/L Flashcards

LIP 1
- mucosa = typical of mouth (stratified squamous non-keratinising epithelium - SSNKE)
- @ margin, abrupt transer to skin (stratified squamous keratinising epithelium - SSKE)
- connective tissue (sub-mucosa) - collage and elastin
- deeper layers - glands and striated skeletal muscle (change shape of oral cavity)
- small blood vessl @ sub-mucosa help keep moist

LIP 2: TRANSITION
SSNKE (lower) to SSKE (upper)
LIP 3
- inner lip: SSNKE
- small clumps of salivary tissue
- sebaceous glands (Fordyce’s spots) open to surface rather than hair follicles

HAIR FOLLICLE
- on keratinised surface of lip

TONGUE 1
- SSNKE on ventral (lower) surface
- SSKE on dorsal (upper) surface - constant abrasion
- coarse multi-directional skeletal muscle bundles
extrinsic fibers - skeletal muscle inserted to lower jaw
intrinsic fibers - skeletal muscle inserted to fibrous connective tissue underlying mucosa
mixed sero-mucous salivary glands (SUBLINGUAL)
lymph nodules - particularly @ posterior 1/3 of tongue (linguinal tonsisl)

TONGUE - UPPER SURFACE
- SSKE
- connective tissue
- 2 types of salivary glands
- large bundles of striated muscle
TONGUE - SEROUS GLANDS
- more pink staining (darker than mucous)
- small serous salivary glands
- acini - clusters of grapes
- nucleus on base

MUCOUS GLANDS
- small salivary mucus gland
- michael palin = mucus pale*
mucus glands stain paler than serous!

PAPILLAE AND TASTE BUDS
- dorsal tongue surface - complex folds = papillae
sweet (tip) / slaty (front/side) / sour (further back) / bitter (whole back)
filiform papillae (threadlike) - most common, tall, pointed - @ whole anterior 2/3
fungiform papillae (mushroom-like) @ tip and sides
- @ lateral side fungiform papillae = pale-staining, spindle-shaped taste buds w/ nerves/synaptic vesicles
circumvallate papillae (V-shaped row) @ divide between anterior 2/3 and post. 1/3
this slide - 2 paler staining taste buds embedded in opposing sides of adjacent fungiform papillae

NERVES OF TONGUE
- small nerves lying in sub-mucosa of tongue
- supple close by taste buds

PAROTID SALIVARY GLAND (SEROUS ONLY)
- striated duct (top left)
- surrounded by serous acini
- synthesise alpha-amylase
- secreted via ducts to mouth
- ducts can alter ionic concentrations
- branches of facial nerve pass through gland
- large lymph nodes embedded within gland
secretory cells - pyramidal, spherical nucleus, basal cytoplasm full of rER, apex contains prominent secretory granules (pink staining)
duct cells - simple cuboidal (stratified at distal end)
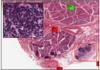
PAROTID GLAND 2
- C (bottom) = nerve
- D = large lymph node
inset - close up of lymph node
parotid saliva contains IgA (from plasma), combines with proteinous pieces so reaches intestine unmodified by amylase
striated duct - from invaginations, indicative of water reabsorption

SUBLINGUAL SALIVARY GLAND (MAINLY MUCUS)
- pale staining secretory cells
- darker staining duct w/ simple cuboidal epithelium
- flattened oval nuclei to base of cells
- branched tubular acinar glands
- sticky mucus rich secretion
major constiuent - polysaccharide

PSNS (parasympathetic nervous system) GANGLION
- PSNS ganglion
- many nerve cell bodies
- involved heavily in secretion regulation
this slide = sublingual

SUBMANDIBULAR SALIVARY GLANDS (MIXED)
- well defined / globular
- branched tubulo-acinar
- interspersed with fat adipose
- mixed secertion - part mucus, part enzyme rich
demi-lunes - serous cells form demi-lunes (half-moons) at closed ends of tubules

LYMPH NODULE WITHIN SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND

EPIGLOTTIS
- @ posterior of tongue
- boundary of oropharynx and laryngeal pharynx
- mostly SSNKE
- lower part posterior - pseudo-stratified columnar ciliated epithelium (respiratory)
contains:
- elastic cartilage plate
- lymph nodules (submucosa)
- salivary glands (submucosa)
Box A = buccal surface - faces mouth

EPIGLOTTIS 2
- SSNKE

GI FORMATIVE 1
- this is a tastebud surrounded by squamous epithelium

GI FORMATIVE 2
- mucus acini
- basally located nuclei
- ducts lined by cuboidal/columnar epithelium
this is a sublingual gland

GI FORMATIVE 3
- serous glands @ bottom
- mucus glands @ top
- this is mixed
therefore this is a submandibular gland
(mixed = submandibular)
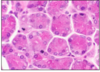
GI FORMATIVE 4
- this is purely serous (granules)
this is parotid gland
therefore contains branches of facial nerve

GI TRACT LAYERS (x4)
- mucosa - innermost. epithelium (folded), connective tissue (lamina propria - w/ lymphoid tissue), smooth muscle ring (muscularis mucosa)
- sub-mucosa - loose connective tissue, glands and lymphoid tissue, many blood vessels, meissner’s plexus (enteric nervous sytem)
- external muscle coat (muscularis externa)- 2 layers of smooth muscle - persistalis -auerbach’s plexus (enteric nervous system)
- serosa - simple squamous epithelium

OSEOPHAGUS
mucosa:
- SSNKE
- thin lamina propria
- narrow muscularis mucosa (thicker @ gastric end)
below diaphragm:
- simple columnar epithelium (same as gastric region of stomach)
- site of pathological change - Barrett’s oesophagus!
sub-mucosa: sero-mucous glands (lubrication), large thin-walled veins (@ distal end - oesophageal variscosities)
muscularis externa:
upper 1/3 = skeletal / middle 1/3 = mixed / lower 1/3 = smooth

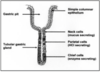
STOMACH
- 4 regions: cardia/body/fundus/pyorus
- cardia and body are histologically similar with respect to glands
- muscosa thrown into folds (rugae)
- simple columnar epithelium punctuated by gastric pits
- muscularis externa is 3 layers thick - additional oblique fibers for churning
gastric mucosa scattered with pale-staining endocrine cells - serotonin, somatostatin, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP).
these regulate breakdown and delivery to duodenum
GASTRIC GLANDS
- tubular @ mucosa
- fill lamina propria
- 3 main cell types
- parietal (HCl + intrinsic factor [B12 absorpition])
- chief cells (digestive enzymes - pepsinogen, zymogen for pepsin)
- mucus neck cells (lubricant - acid resistant mucus)
- full glands @ body and fundus
- no parietal / chief @ cardia and pylorus
STOMACH BODY - GASTRIC MUCOSA
- simple columnar epithelium - produce acid resistant mucin
- gastric pit invaginations (green arrows)
- several tall, straight or brached glands to each pit
- submucosa = loose connective tissue with abundant vessels
- muscularis externa = 3 layers of smooth muscle
muscularis mucosa also contains elastic (black) to stop stomach collapse on empty

PARIETAL (OXYNIC CELLS)
- @ gastric glands of body/fundus
- @ upper part of gland close to pits
- globular - bright pink with H&E
- cell surface invaginated (intracellular canaliculi) w/ many mitochondria (dark staining- grainy appearance)
- rich in carbonic anhydrase
pH - 2
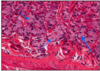
CHIEF (ZYMOGENIC CELLS)
- pyramidal @ deeper gland
- cytoplasm - blue H&E - contains granules (pepsiogen/lipases)
- @ body and fundus
- close to muscularis mucosa
PEPSIN - affinity for collagen

PYLORIC REGION
- cardiac and pyloric glands are shorter
- glands are coiled
- mainly mucus neck cells
- scattered with cells producing gastrin
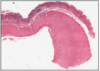
GASTRODUODENAL JUNCTION

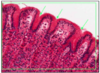
VILLI AND CRYPTS
- intestinal lining - folds - plicae circularis (highest @ jejunum, lowest @ distal colon)
- further SA increase - villi
villi - simple columnar epithelium (enterocytes and goblet cells). short life - but replaced by crypt production
contain - veule, arteriole, lacteal, smooth muscle (milks the villus)
venule and lacteal to liver
crypts of leiberkuhn - between villi, stem cell population, migrate to top and shaved off (takes 5 days)

ENTEROCYTES
- major absorptive cell
- 300 short microvilli on apical surface - brush border
- @ outer surface brush border = glycocalyx (enzymes) - filter most nutrients through this
- water and glucose (some) via intracellular pathways
high concentrations of HEXOSE SUGARS mean brush border stains intensely by PAS

DUODENUM
- 12 inches, few plicae circularis
- villi - broad and leaf like
- few goblet cells
- submucsoa conatins mucus secreting brunner’s glands - alkaline secretion neutralises CHYME
brunner’s gland bottom right
few pale staining goblet cells
long crypts
n.b. submucosal brunner’s glands not found in jejunum/ileum
inner circular layer thicker than outer longitudinal layer of muscularis externa

DUODENUM 2
- crypts form new enterocytes and goblet cells
- dividing cells have very dark staining nuclei or sets of chromosomes
- @ bottom of crypts = DIFFERENTIATED PANETH CELLS
- secrete lysozyme - breakdown of bacterial cell walls
- regulate flora of gut
- bright pink cytoplasmic granules
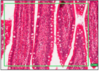
JEJUNUM
- close-packed plicae circularis
- many goblet cells
- long narrow villi (finger-like)
- short crypts
- loose submucosa (almost detached from muscularis externa)
- no brunner’s glands or peyer’s patches
- lymph nodules at lamina propria, but do not penetrate submucosa

ILEUM
- final segment of small intestine, therefore fewer plicae and shorter villi (less absorption)
- goblet cells increase towards distal end
- large peyer’s patches @ submucosa (lymphoid tissue w/ lymphocytes)
- Peyer’s patches erupt through muscularis mucosa to lamina propria

ILEUM 2
- serosa (simple squamous) on edge of longitudinal muscle

VERMIFORM APPENDIX
- from caecum
- simple columnar epithelium
- goblet cells
- no villi
- simple crypts
- lamina propria and submucosa full of lymphoid tissue (declines w/ age)
- no muscularis mucosa
- muscularis externa present
- transverse smooth muscle at muscularis externa = taenia colis - 3 longitudinal bands
- fat filled

APPENDIX 2
- simple columnar epithelium
- rudimentary crypts with few goblet cells
- lamina propria and submucosa full of lymphoid tissue

COLON
- all segment similar histologically
- little folding
- no villi
- mucosa contains close packed crypts with abundant goblet cells and enterocytes
- restricted lamina propria (by crypts)
- prominent muscularis mucosa
- mucosa and sub-mucosa contain a lot of lymph - GALT (gut)
- musuclaris externa - thickened inner circular layer, outer layer drawn into 3 longitudinal bands = taeniae coli
this slide - close packed crypts and abundant goblet cells

RECTO-ANAL JUNCTION
- rectum = similar to colon
- simple columnar epithelium
- anal canal - stratified squamous epithelium, keratinised at distal end (as lip)
- submucosa was FAT, VEIN PLEXUS (anal varicosity)
- smooth muscle of muscularis externa thickened and surrounded by STRIATED MUSCLE of EXTERNAL ANAL SPHINCTER

RECTO-ANAL JUNCTION
- box B - striated muscle of sphincter
- box D - anal glands
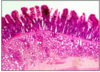
GI FORMATIVE 5
- villous
- sub-mucosa with Brunner’s glands
- duodenal epithelium contains some lymphocytes between epithelium
DUODENUM
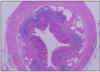
GI FORMATIVE 6
- all of this fits on a microscopic slide therefore not colon
- flat mucosa with no villi
- abundant lymphoid tissue in lamina propria and submucosa
- lacks a muscularis mucosa
- receives lod from superior mesenteric artery
VERMIFORM APPENDIX

GI FORMATIVE 7
- flat surface
- no villi
- numerous straight crypts
- abundant goblet cells
- prominent muscularis mucosa
- stem cells at base of crypts
COLONIC MUCOSA

LIVER
- hepatic portal system receives nutrients
- main cells - hepatocytes functions:
- creation/store energy as glycogen & fat
- synthesise plasma proteins
- de-amination of amino acids and production of urea
- uptake, synthesis, excretion of bilirubin and bile acids
- detox and inactivation of drugs by oxidation, methylation or conjugation
- polygonal lobules of cells
- each lobule with central vein and radiating hepatocytes (cords)
- between cords = sinusoids (blood vessels) - bathe hepatocytes in mix of venous and arterial blood
- blood drains from each lobule via central vein - hepatic

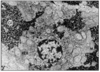
LOBULE
- cords of hepatocytes
- sinusoids (wide, thin, fenestrated capillaries) = 70% portal vein blood, 30% portal artery blood
- portal triads at corners of loules
- arteriole (hepatic artery), venule (hepatic portal vein - nutrient rich blood), bile ductule
- hepatocytes store: glycogen, trigylcerides
- bile ductule = simple cuboidal epithelium
this slide - small muscular arteriole (top left), venule (bottom), bile ductule (top right, simple cuboidal)
hepatocytes secrete nile to extra-cellular bile canaliculi
hepatocytes replicate

SINUSOIDS
- wide, thin walled, fenestrated capillaries
- endothelial cells interspersed with:
- kupffer cells - fixed macrophages
- ito cells - perisinusoidal cells (fat storing)
- too thin to resolve
- sit of meshwork of reitculin (collagen 3)
- separated from heaptocyte cords by space of Disse (no blood cells here, but there is plasma) - albumin/fibrinogen synthesised at liver enters blood @ space of Disse
this slide - cords of hepatocytes with paler staining sinusoids between. nuclei of endothelial sinusoidal cells smaller and darker than that of hepatocytes.
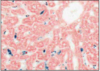
SINUSOIDAL MACROPHAGES
- Kupffer cells in lining of endothelium
- phagocytose blood borne pathogens
- part production of bilirubin (taken up and excreted by hepatocytes)
n.b. demonstrate presence by uptake of coloured dye, contain particulate deposits
this slide - Kupffer cells have taken up blue/black ink. they line cords between pink-staining hepatocytes.
HEPATOCYTE ULTRASTRUCTURE
- GI = glycogen
- Mi = mitochondria
- N = nucleus
- RER = rough endoplasmic reticulum
sinusoidal membrane contains transport mechanisms for pinocytotic release of macromolecules
canalicular membrane is target for bile discharge
well devloped rER - synthesis of plasma proteins
sER - inactivation of drugs (enzymes)
glycogen particule rosesstes and lipid droplets present

GALLBLADDER
- BILIARY TREE = ALL CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM
- smaller vessels = simple
- distal end = stratified
gallbladder
- simple columnar w/ poor brush border
- adapated for water reabsorption (concentrating bile)
- epithelium thrown into folds (not villi!)
- large veins in walls
- smoth muscle at outer surface
- serosa visible at top (simple squamous)
n.b. contracts by CCK released from duodenum in response to fat from stomach

EXOCRINE PANCREAS
- exocrine = 98% of gland
- serous (watery/enzyme rich)
- digestive enzymes from same cell, secretion granules at upper part of cell
- enzymes released as food enters duodenum
- enzymes activated by alkaline environment of duodenum
stimulated by secretin to release ALKALINE FLUID from CENTRO-ACINAR and small duct cells
this slide - centro-acinar cells by green arrows

PANCREAS
- inset
- pacinian corpuscle - pressure sensor in pancreas (and skin)
- nerve plexus - with vagus nerve
also contains islets of langerhans (see SUGER)

EXOCRINE PANCREAS DUCTS
- each acinus has a narrow intercalated duct (ID)
- IDs connect acinus to main duct (MD)
- larger ducts -> 1/2 MDs that enter duodenum with bile duct
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM (stratified at distal end, as GB)
n.b. duct cells produce most of the fluid in secretion
PORTAL TRIAD


