Genetics 3.3 Meiosis & 10.1 Meiosis Flashcards
(18 cards)
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is one of the two ways in which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell can divide. (The other is Mitosis)
Why use Meiosis and not Mitosis?
Meiosis allows the halving of chromosome numbers that allow sexual life cycle with fusion of gametes. This allows genetic variation.
When does Meiosis occur?
Meiosis can happen at any stage during sexual life cycle, but in animals it happens during the process of creating the gametes. Body cells are diploid.
List all stages of Meisosis
- Interphase
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I/Cytokinesis
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
What happens before Meiosis?
During the last stage of interface, DNA is replicated.

What happens during Prophase I (Meiosis)?
- Nuclear membrane breaks down
- Homologous chromosomes pair up to form bivalents/tetrads.
- Homologous chromosomes are held together by points called chiasma
- Homologous chromosomes undergo a process called synapsis whereby sections of DNA are exchanged between homologous chromosomes.
- Crossing over of genetic material between non-sister chromatids can occur at these points, resulting in new gene combinations (recombination)

What happens during Metaphase I?
- Centrioles form on either side of the cell
- Microtubulos grow and attach themselves to the centromeres of homologous tetrads
- Homologous tetrads line up along the equator

What happens during Anaphase I?
- Homologous chromosomes split apart and move to opposite poles
What happens during Telophase I?
- Nuclear membrane reforms 2. Centrioles and microtubules break down 3. Cell splits into two haploid daughter cells as cytokinesis occurs.

What happens during Prophase II?
- Nuclear membrane breaks down

What happens during Metaphase II?
- Chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell 2. Spindle fibres reform and reconnect to the chromosomes

What happens during Anaphase II?
- Spindle fibers shorten and pull sister chromatids apart as they move to opposite poles.
What happens during Telophase II?
- The cell splits in two as cytokinesis happens concurrently.

What is the result of Meiosis?
Because sister chromatids may no longer be genetically identical as a result of potential recombination, the process of meiosis results in the formation of four genetically distinct haploid daughter cells.
Outline the process of crossing over.
Crossing over involves the exchange of segments of DNA between homologous chromosomes.
During synapsis in prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up to form bivalents/tetrads. Portions of non-sister chromatids overlap. The positions in which they are attached are called chiasma.
The chromatids break at chiasmata, reattach to new sister chromatids in a system of reciprocal exchange. The new combinations are known as recombinants.
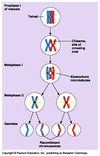
How does meiosis produce genetic variation?
1. Random orientation of bivalents/Independent Assortment:
Bivalents line up along the equator in metaphase I. This means that chromosomes assort independently into two daughter cells during anaphase I. Chromosomes align along the equator independently during metaphase II. This means that chromatids assort independently into daughter cells during anaphase II
2. Chiasma formation:
During Prophase I, genetic exchange occurs between homologous chromosome during synapsis. This creates chromosomes with new combinations of alleles. 3. Offspring of sexual reproduction have two parents (Fusion of gametes)
What are the genetic basis for Down’s syndrome to occur?
Non-disjunction can cause Down syndrome.
The failure of the chromosomes to separate may either occur via:
- Failure of homologues to separate during Anaphase I (resulting in four affected daughter cells)
- Failure of sister chromatids to separate during Anaphase II (resulting in two affected daughter cells)
Thus, both of the chromosomes move to one pole while none to the other.
This results the gametes, sperms or eggs, to have incorrect number of chromosomes.
Down syndrome (trisomy 21) is an example. The person would have three homologous chromosomes #21.
Explain how meiosis results in an effectively infinite genetic variety in gametes
independent assortment:
- variety produced by recombination of maternal and paternal chromosomes
- for each pair of homologous chromosomes, maternal and paternal chromosomes assort to daughter cells randomly
- possible arrangements of chromosomes in haploid daughter cells = (2)nth, where n = number of homologous pairs
crossing over:
- variety produced by recombination within individual chromosomes
- during synapsis, prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair forming bivalents
- portions of non-sister chromatids overlap, break at chiasmata, reattach to new chromatid in a system of reciprocal exchange
- new combinations known as recombinants


