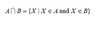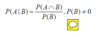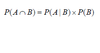General Probability Theory Flashcards
(66 cards)
What is a a sample?
A subset that is drawn from a larger population i.e. r<n></n>
What is a parameter?
Something in the population that we want to estimate.
Why do we do statistics?
To deliver us an estimate of a specific (numerical) parameter in the population based on the information obtained in a sample.
What are the two basic types of statistics?
Descriptive and Inferential
What is descriptive statistics?
It is the DESCRIPTION of characteristics of a set of numbers (e.g. mean, variance, etc.)
What is inferential statistics?
They attempt TO INFER (deduce or conclude (information) from evidence and reasoning rather than from explicit statements) i.e. they are used to estimate a population parameter from a SAMPLE STATISTIC – going back from the sample to infer something about the population
Statistical Inference is based upon what?
PROBABILITY
What is a fundamental concept in scientific research that is linked with probability?
Determining the likelihood of some event occurring in nature.
What is a key assumption or goal of probability?
“The theory of chance consists in reducing all the events of the same kind to a certain number of cases equally possible, that is to say, to such as we may be equally undecided about in regard to their existence, and in determining the number of cases favorable to the event whose probability is sought.” – Pierre-Simon Laplace
What is a random selection?
It is a selection of one unit from a set of N (the population) made in such a way (theoretically at least) that each of of the N units is equally likely to be the unit selected.
What is random selection different than?
Biased Selection
What type of selection process does not give each of the N units an equal chance to be selected?
Biased Selection
Is randomness valid or is it a theoretical construct of questionable validity?
This is difficult to say. Most random number generators on computers are based off of algorithms on the computer clock. It has been shown that if you learn the first number in a sequence you can reliably predict the following numbers based on prescient knowledge of the algorithm.
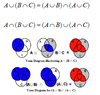
What is set theory?
It is the branch of mathematical logic that studies sets, which are collections of objects. Although any type of object can be collected into a set, set theory is applied most often to objects that are relevant to mathematics. The language of set theory can be used in the definitions of nearly all mathematical objects.
What is a group of distinct objects of any well defined nature?
A set.
Are sets finite (people in the room) or infinite (all integers)
They can be either or.
Elements are?
Members of the set
What is a simple experiment (in set theory)?
A process for generating a set
Define a sample space
Set of all possible distinct outcomes for a simple experiment.
How does one notate a sample space?
“(S)”
What is an elementary event?
A single member of the sample space
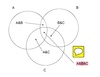
What does this formula state?
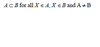
A is a subset of B where X is a member of X and X is a member of B but A does not equal B.
This called a proper subset.
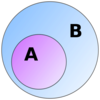
What does this (See below) refer to?
{}
An empty set or a null set.
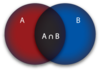
What is the complement?
a complement of a set A refers to things not in (that is, things outside of), A.