General Obs and Gyne Flashcards
What is the risk of developing DMII if you have GDM?
50% risk of developing DMII in the next 20 years if you have GDM
Is GDM related to the same risk of spontaneous abortion, and physical anomalies as DM 1/II?
No, GDM develops usually in the second trimester due to anti insulin factors and higher cortisol levels DM I/II are related to higher anomalies and spontaneous abortion because of first trimester hyperglycemia (important for anomalies) and the pre- conception glycemic control (important for spontaneous abortion)
What is the definition of preterm labour?
Preterm birth is a birth that occurs between 20 weeks and 37 weeks of gestation with preterm labor being labour that occurs during these gestational ages. Labour is defined a regular contractions with cervical change (effacement, dilation).
What is the definition of threatened preterm labour?
regular contractions that do not dilate the cervix OR preterm labour that stops (eg. person dilates to 2cm, then has no further change, they are now “threatened” preterm labour).
What is the definition of cervical insufficiency?
ervical effacement and or dilation with NO contractions /pain.
What are the definitions of braxton hicks contractions?
irregular contractions, usually not painful, producing no cervical changes. Usually improve with rest and hydration.
What are the risk factors for preterm labour?
Risk factors : previous preterm birth, multiple gestations, short cervix on ultrasound (asymptomatic), complicated pregnancies (abruptions, PPROM, chorioamnionitis, polyhydramnios)
How do you diagnose preterm labour?
1)risk factors: previous preterm birth, multiple gestations, short cervix on ultrasound (asymptomatic), complicated pregnancies (abruptions, PPROM, chorioamnionitis, polyhydramnios) 2)Regular painful contractions 3)Fetal fibronectin–> high negative predictive value 4)Cervical exam for dilatation and effacement 5)ultrasound for cervical length
What is the DDX for cramping?
Pregnancy related : True preterm labour ** lots of causes (eg. chorio, abruption etc) Threatened preterm labour Abruption Gynecology related: Fibroid degeneration or ovarian cyst (rupture / torsion) Other systems : Pyelonephritis / UTI dehydration Appendicitis / bowel infections MSK : not usually regular cramping
What are the TORCH infections
Toxoplasmosis Other (Syphilis, varicella-zoster, , parovirus B-19) Rubella CMV Herpes
What populations do you do a fetal fibronectin for?
threatened preterm labour from 24-34 weeks This can direct whether you would give steroids or not
What are the changes to the cervix in labour?
Shortens Dilates Softens Moves more anteriorly
What are the components of Bishops Score? What is this score useful for?
Bishops score is useful in predicting a successful vaginal delivery
If the Bishop score is high, the likelihood of vaginal delivery is similar whether labor is spontaneous or induced [23,46]. In contrast, a low Bishop score increases the likelihood that induction will fail to result in vaginal delivery. The thresholds for high and low scores vary among trials, but a score ≥8 generally predicts a low rate of failed induction and a score of ≤6 generally defines an unfavorable cervix [5].

What are the GBS prophylaxis guidelines?
GBS prophylaxis : if unknown, treat as < 37 weeks (as per SOGC GBS guideline) First line : Penicillin G 5 million U then 2.5Mill U q4h
What are the treatment of preterm labour?
- 1)IV fluids and analgesia
2) Mother and fetal monitoring
3) GBS prophylaxisif unknown, treat as < 37 weeks (as per SOGC GBS guideline) First line : Penicillin G 5 million U then 2.5Mill U q4h
4) Steroids Betamethasone 12mg q24h x2 IM OR Dexamethasone 6mg IM q12 hour x4 - do not use prednisone as it is destroyed by the placenta
- they can be given twice between 24 and 34 weeks
5) Consider tocolysis
a) Indocid (indomethacin)
b) adalat (nifedipine) - the purpose of tocolysis is to allow time for steroids
6) Can’t do Breech delivery before 29 weeks because the head is bigger than the body, so it will get stuck
7) Tertiary care (has 24 hour care < 32 weeks)
8) Obs-gyne care +neonatology
9) Consider MgSO4 for fetal neuroprotection (NMDA receptor blockade)
What is PPROM and how is it confirmed?
Rupture of membranes before 37 weeks
confirmed by
1) Fernings test (Gold standard)
2) Nitrazine
How long is the GBS swab acurate for?
5 weeks
What is the treatment of PPROM?
PPROM IS NOT LABOUR, DON’T TREAT IT AS SUCH
1) IV, CBC, type and screen
2) Fetal monitoring
3) Monitor maternal vital signs for fevers
4) Ultrasound: BPP, presentation, AFI, EFW
5) Steroids
24-34 weeks–> Tocolysis and subsequent steroids to get to 34 weeks
After 34 weeks- tocolysis in this area is a grey zone
6) Tocolysis is not used in PPROM–> higher risk of infection–> higher risk of IVH–> bad outcomes
7) Antibiotics
a) PPROM Antibiotics –> erythromycin +/- ampicillin q 7days
b) Preterm labour antibiotics–> Pen G ( if in labour with PPROM and unknown GBS)
c) if PPROM and then some preterm labour which stops and then goes back to just PPROM
–> erythromycin +/- ampicllin–> PENG–> erthromycin +/- ampicillin
What are the complications of PPROM?
Chorioamnionitis
Abruption
Cord prolapse (esp if not cephalic)
Preterm Labour
When do you deliver with PPROM?
If everything is reassuring : fetal growth, no signs infection or other OB complications
<34 weeks : try to prolong pregnancy (latency Abx) >37 weeks Deliver.
Cephalic : oxytocin induction
Breech / other : cesarean section 34-37 weeks : controversial. Not clinical clerk level.
Calgary : most times you will see delivery with PPROM >34 weeks but cases where pregnancy is prolonged.
What are the treatment for GBS?
First Line–> Pen G 5 000 000 u IV, the 2 500 00 u IV q4h until delivery
IF PEN ALLERGIC (NON ANAPHYLAXIS)
Ancef 2 g IV, then 1 g IV q8h until delivery
IF PEN ANAPHYLAXIS
Clindamycin 900mg IV q8h until del (pen anaphylaxis) – be sure to check sensitivities!
Vancomycin 1 g IV q12h until del (Pen anaphylaxis and clinda resistant!)
When do you treat for GBS?
1) Positive GBS swab
2) Previous infant with GBS disease (sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, death)
3) GBS bacteria in urine during pregnancy at any time
4) GBS unknown if:
a) preterm < 37 weeks, any reason for labour ( PTL, PPROM, iatrogenic)
b) intrapartum temperature > 38.5
c) ruptured membranes > 18 hours and unknown GBS (takes a week to get swab back)
What is the treatment for term ROM and GBS positive?
induce labour
What defines PPH?
Vaginal delivery blood loss > 500ml
C/S blood loss > 1000ml
Is clotting affected in pregnancy?
Clotting factors are not affected by pregnancy
Fibrinogen becomes higher in pregnancy (goes up to 4) so if you check for DIC and it is 2, then you are actually low
What are the four causes of PPH?
Tone
Tissue
Truama
Thrombin
What are the drug therapies for Uterine Atony?
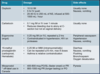
What are the non medical therapies for uterine atony?
Tamponading –> Bakri baloon, folley, packing with gauze