General neuro Flashcards
4 sutures of skull
Which suture closes first?

Metopic (in front), Lamboid (in back), Coronal, Saggital.
Metopic closes first - Male pattern baldness happens first

Which suture is most likely to close abnormally? What are french names for this? (2 names

Saggital (boat shaped head). Scaphocephaly, Dolichocephaly
What two canals are connected to this canal?

Pterygopalatine fossa (PTF) is the canal
Foramen rotundum (posterior), Spenopalatine foramen (medial)
Foramen Rotundum what runs in it? Relation to PTF?
Runs horizonal anteriorly to connect with the posterior aspect of PTF.
R2V2.
Foramen Ovale (relation to Spinosum)
Name these other canals

Shaped like oval on axial scan. Anteromedial.
(stilleto heel visual)

Foramen Spinosum (position, related to ovale)
posterolateral to foramen ovale
Stilleto heel visual
Relation of Vidians, ovale, and spinosum on axial. (visual to help remember Ovale and Spinosum)
From lateral to medial it goes SOV. On axial view, Ovale and Spinosum look like the imprint of a woman’s high heel shoe, which is pointed inwards. (ovale I ball of foot, spinosum is heel). The feet are pointed towards Viridans canal.
On Coronal plane, Anterior cliniod process is seen on slices which contain which foramen?

Foramen Rotundum. (and also likely Vidians canal)

Relationship of Rotundum and Vidians canal on coronal views

Rotundum is lateral, Vidians is medial. V in the middle

Juvenile angiofibroma starts where?
Sphenopalaine foramen. It then extends to Ptf.
JNA is fed by branches of which artery?
ECA
Fetal Pcomm frequencey and clinical significance
Also what is relation of PCOMM to CN3 normally, and what is in fetal pcomm?
30% prevalance. Stroke from ICA may hit both MCA and PCA distribution.
Normally fetal pcomm is medial/superior to CN3, but with Fetal Pcomm, it is lateral/superior
Most common persistent fetal connection b/w vertebrobasilar and carotid systems? Associated complication and associated sign?
Persistent trigeminal artery. This may be prone to aneurysm. Tau sign (seen as the vessel is coming off of the carotid)

Things that connect with pterygopalatine fossa
Rotundum, IOF, greater palatine canal, spenopalatine foramen, infratemporal fossa, viridans canal.
Superior ofbiral fissure contains lots of nerves (Need 3,4,6 for looking)
3,4,6, Lacrimal, frontal, nasocilliary (V1)
Cavernous sinus contains what? What are medial structure

CN2, 3, 4, 6, V1, V2. Internal carotid.
Abducens and internal carotid are medial

What passes through the optic canal?
CN2- opthalmic artery
What passes through the hypoglossal canal? Where is hypoglossal canal in relation to occipital condyle?
Hypoglossal nerve (CN12)
medial and superior to occipital condyle
What traverses the jugular foramen?
Pars vascularis?
Pars nervosa?
Pars vascularis:- Jugular vein- CNs 10 & 11 (go with the vessels)- posterior meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery
Pars nervosa:- CN 9 (Nine is longer, goes alone in Nervosa)- inferior petrosal sinus venous return
What traverses the foramen spinosum?
Middle meningeal artery
What traverses the foramen rotundum?
CN V2 “R2V2”
What traverses the superior orbital fissure?
CNs V1, 3, 4, 6
What traverses the foramen ovale?
CN V3, accessory meningeal artery
Stylomastoid canal
CN 7
What is “dural ring” in ICA course
It is where the ICA enters dural cavity. It is at the border of segements 5 and 6 of ICA. Anything above Dural ring, Like segments C6, C7, is “subarachanoid”
What are the segments of the ICA?
C1 : cervical - C2 : petrous - C3 : lacerum - C4 : cavernous - C5 : clinoid - C6 : ophthalmic - C7 : communicating
2 branches from ICA C2
2 branches from ICA C4
2 branches from ICA C6
4 branches from ICA C7
C2: Carotidotympanic artery, viridian artery
C4: Meningohypophyseal trunk, inferolateral trunk
C6: Opthalmic artery, superior hypophyseal artery
C7: Pcomm, Anterior choroidal, anterior cerebral, middle cerebral
ECA branches (8 branches, some anatomists like freaking out poor med students)
Superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary, superficial temporal
Where does vertebral artey enter the foramen?
C6 level
Facial nerve segments (I love going to makeover parties)
Intracranial, labinthine, geniculate ganglion, tympanic, mastoid, parotid
5 branches of facial nerve
Temporal, zygomaatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical
What is this? What lives here?

Meckel’s cave,
trigeminal ganglion, posterolateral to cavernous sinus
Canal that transmits CN VI to cavernous sinus
Dorello’s canal transmits abducens from prepontine cistern to cavernous sinus
Sinus drainage patterns
Maxillary
sphenoid
frontal
ethmoid (anterior, middle, ethmoid)
Maxillary: MMMiddle meatus
Sphenoid: roof of nasal cavity (through spenoethmoidal recess)
Frontal: middle meatus via the frontonasal duct.
Ethmoid: anterior - middle meatus.
Middle - ethmoid bulla.
Posterior - superior meatus
Name, significance?

Haller air cell
Air cell which is inferomedial to orbit. Can obstruct meatus and cause obstruction/sinusitis
Communicating hydrocephalus - 2 causes
SAH, normal pressure hydrocephalus
Ddx - diffusion restriction (6) (stroke + 3 infectious + 2 ‘masses”)
Acute stroke, bacterial abscess, cellular tumors, epidermoid cyst, herpes encephalitis, Creutzfeldt
Ddx for multiple dark spots on GRE (5)
Hypertensive microbleeds,cerebral amyloid angiopathy, familial cerebral cavernous malformations, axonal shear injury, multiple hemorrhagic mets
CNS regions that do not have a BBB
Choroid plexus, pituitary and pineal glands, Tuber Cinerum (controls circadian rhythm, located in the inferior hypothalmus). Area postrema (controls vomiting, located at inferior aspect of 4th ventricle)
Type of brain enhancement patterns (4 intra-axial, 2 extra-axial)
Periventricular, Gyriform, nodular subcortical, ring, pachymeningeal (dural), leptomeningeal (pia-arachnoid.
Periventricular enhancement (enhancement of subependymal surface) 2 neoplastic, 1 infectious, 1 demyelinating
Primary CNS lymphoma, infectious ependymitis (CMV. Linear enhancement along margins of ventricles). Primary lial tumors, multiple sclerosis.
Gyriform enhancement ( I’s - 2 infection, ischemia, or idiopathic)
Herpes encephalitis, Meningitis, Subacute infarct, PRES.
Nodular subcortical enhancement
Hematogenous disseminated metastatic disease. Venous dissemination of mets (pelvic malignancy spread via the Batson prevertebral venous plexus) leads to posterior fossa disease by transit through the retroclival venous plexus.
Ring enhancement (Magic Dr)
Mets, abscess, glioma, infarct, contusion, demyelinating (incomplete ring), radiation
Pachymeningeal enhancement (HaPPy GM)
Intracranial hypotension, postoperative, post lumbar puncture, meningeal neoplasm, granulomatous disease (sarcoid, TB, fungal)
Leptomeningeal enhancement (2 infectious, cancer, anatomic structure)
meningitis, leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (GEMCLOG), viral encephalitis, slow vascular flow
Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis ddx (GEMCLOG)
Glioblastoma, ependymoma, medulloblastoma, Choroid plexus tumor, lymphoma, oligodendrioglioma, germinoma
Ddx Flair hyperintensity in subarachanoid space (4)
Meningitis, leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, SAH, Patient on oxygen or propofol therapy.
3 emergent complications of tumor (3 H”s)
Hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, herniation
Approach to focal brain lesion
Any complications, intra or extra-axial, specific location, enhancement, is there more than 1 lesions, distinctive MRI findings.
Tumors that are hypointense on T2 (type of met. 4 hypercellular tumors)
Mets with desiccated mucin (GI), hypercellular tumors (lymphoma, medulloblastoma, germinoma, some glioblastomas
Tumors that are Hyperintense on T1
Melanoma, fat containing teratoma, hemorrhagic mets (CTMR BB)
4 Glial cells
Astorcyte, oligodendrocyte, ependymal cell, choroid plexus cell.
4 types of herniation
Subfalcine herniation Downward uncal (transtentorial) herniation Upward transtentorial herniation, Cerebellar tonsillar herniation
Downward transtentorial herniation - what lobe is effected
Inferomedial displacement of medial temporal lobe (uncus) through temporal notch
Uncal (downward tentorial) herniation - 4 structure effected
Ipsilateral CN3 (pupillary dilatation and down/out)
Compression of ipsilateral PCA
Upper brainstem sheared (duret hemorrhages)
Compression of contralateral cerebral peduncle (ipsilateral hemiparesis)
Subfalcine herniation (what lobe involved, what 2 things can be compressed)
Cingulate gyrus slides underneath falx rarely causes compression of ACA Foramen of monro obstruction
Upward transtentorial herniation. Main complication
superior herniation of cerebellar vermis due to posterior fossa mass. Main complication is aqueductal compression and hydrocephalus
Cerebellar tonsillar herniation. How can this be fatal.
Tonsils through foramen magnum. Compression of medullary respiratory centers can be fatal.
2 most common Ring enhancing lesions
Neoplasm, abscess.
T 1 hyperintense in the brain (3 common ones, 3 less common, 2 that overlap w/ T2)
A) Gad, fat, proteinacious substance
B) Melanin, mineralization, slow flowing blood
C) paramagnetic stages of blood, calcium
T2 hypointense in the brain (3 main things, 2 overlap with T1, 1 normal findings)
A: Fibrous lesions, highly celullar tumor (lymphoma, medulloblastoma) Dessicated Mucin) B: Paramagnetic stages of blood, calcification C: vascular flow void
Hemorrhagic mets (MR CT and for good measure, BB)
Melanoma, RCC, choriocarcinoma, Thyroid. Also because of how common they are; breast and bronchogenic.
Name these atlanto-axial ligaments
- Ligament that hugs the dens to the atlas
- Ligament that is continuation of PLL to Clivus
- ligament that connects sids of dens to condylar tubercles.
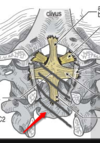
- Cruciate Ligament (made of transvere ligament and other fibers)
- Tectorial membrane
- Alar ligament

describe superior and inferior colliculi (corpora quadrigemina), facial colliculi
Superior and inferior colliculi are at the level of the midbrain. Facial colliculi is at level of pons.
superior colliculi: preliminary visual processing and control of eye movements. (superior is for seeing)
inferior colliculi: auditory processing. (Linferior is for Listening)
Facial colliculi is at the level of the pons and it is the CN7 fibers curving around the abducens nerve.
“extraventricular obstructive hydrocephalus” occurs to obstruction where?
obstruction distal to 4th ventricle outlet foramina.


