General Medicine: Cardio Flashcards
Patient with BP of 145/96, what investigation findings would confirm a diagnosis of HTN?
ABPM reading of >=135/85
Who should drug treatment be considered in if
>80
<80
>=80yrs + BP >150/90
<80 with evidence of organ involvement OR Q-risk >=10%
How do you manage a patient with BP >180/110
Start drugs immediately
Same day referral if
- retinal haemorrhage
- Life-threatening symptoms
- Suspected phaeochromocytoma
For HTN who gets the following first line
ACEi/ARB
CCB
A: <55yrs, T2DM
C: >55yrs, Black
What do you give after first line treatments for HTN?
A+C/D
A+C+D
If black, give ARB over ACEi
After triple therapy, how d you determine what drug to add for HTN?
LD spironolactone <= K+ 4.5 < a/B blocker
What are the blood pressure targets (clinic + ABPM) for
<80yrs
>80yrs
<80yrs
Clinic <140/90mmHg
ABPM <135/85mmHg
>80yrs
Clinic <150/90mmHg
ABPM < 145/85mmHg
What antihypertensive drug causes
Gout
Cough
High blood glucose
Headaches
Hypotension
Cold peripheries
Postural hypotension
Gout, glucose: thiazide
Cough: ACEi
Headache: CCBs
Hypotension: nd-CCBs
Cold peripheries: B-blockers, bronchospasm
Postural hypertension: doxazosin
How is stable angina different from acute coronary syndrome?
Chest tightness only present on exertion
Settles within 5 mins of rest
What investigation findings would you see for stable angina
cardiac markers and ECG normal
What entails symptom control in stable angina?
Mono: Nd-CCB OR B-blocker
Combo: d-CCB + B-blocker
+ GTN to relieve attacks
What drugs can you give for angina if CCBs or BBs not tolerated?
Nitrates
Ivabradine
Ranolazine
Nicorandil
How do you reduce chances of cardioembolism in stable angina
Aspirin + Statin
What are the risk factors for ACS?
2 non-modifiable
Age, Male
3-4 modifiable
Diabetes
Lifestyle (obesity, smoking, alcohol)
Hypertension
Hyperlipidaemia
How does unstable angina differ from other ACS types
No cardiac markers, no ECG changes
What ECG changes are seen in an NSTEMI?
ST-depression
T wave inversion

Whaat criteria must ST elevation meet for it to be a STEMI?
>1mm in 2 limbs
>2mm in a chest
Outline STEMI management
Aspirin 300mg
<120 mins: PCI
Give prasurgel (clopidogrel if already anticoagulated)
Stent or revascularise (if mutlivessel disease)
>120 mins: Fibrinolysis
Give ticagrelor + aspirin (aspirin +/- clopidogrel if high bleed risk)
Assess PCI need
Outline initial NSTEMI management for
<=3% mortality
>3% mortality
Aspirin 300mg
Fondapirinux (UFH if creat >265)
GRACE <=3% mortality
Ticagrelor + aspirin (aspirin +/-clopidogrel if high bleed risk)
GRACE >3% risk
Angiography: immediate if unstable, <72hrs otherwise
Prasurgel/tigagrelor, + aspirin (UFH during PCI)
What entails secondary prevention in ACS?
Risk factor modification
Aspirin 75mg + clopidogrel >= 12 months
Anticoagulate with LMWH until discharge
B-blokcade
80mg atorvostatin
+ ACEIs if LV dysfunction, HT, or DM
+ if echo <40% function: eplernone
What features carry a particularly poor prognosis for an ACS patient?
Frank pulmonary oedema (38%)
Features of cardiogenic shock (81%)
Chest pain relieved on sitting forwards and a pericardial rub indiate which condition?
Acute pericarditis
What are the ECG changes seen in acute pericarditis?
Widespread ST elevation, ‘saddle shaped’
PR depression is quite specific

What are the causes of pericarditis
Infections: Viral, TB
Tissue damage: trauma, MI (dressler’s)
Cancer
For pericarditis, what is the
Definitive investigation
Treatment
TT echo
NSAIDs + colchicine
How do you treat a tachycardia in a haemodynamically compromised patient?
up to 3 synchronised shocks
+/- amiodarone
What control is typically offered first in AF?
Rate control
- B-blocker (not sotalol) OR nd-CCB (if not in heart failiure) OR digoxin (if sedentary, others CI)
- Combo of 2 above
Who gets rhythm control…
Generally
Before rate control
Generally if…
Symptoms persist despite rate-control strategy
Before rate if
- Reversible cause
- new onset
- Ablation would help
- Clinical judgement
How do you manage acutely presenting AF that is
<48hrs
>48hrs
Unstable
<48hrs: Electrical* OR Flecainide/amiodarone cardioversion
>48hrs: Electrical cardioversion* +/- 4 weeks amiodarone/sotalol before, continuing for up to 12 months
Unstable: Shock
*Anticoagulate for 4 weeks after electrical cardioversion*
What do you offer if rhythm control of AF is not successful/wanted?
Left atrial ablation
4 weeks anticoagulation before
+ 3 months antiarrhythmic treatment after to prevent again
What drugs are used in maintaining rhythm control in AF?
B-blockers
Dronendarone: 2nd line if cardioverted
Amiodarone: If co-existing HF
How do you anticoagulate in acute AF?
Heparin if new acute AF
DOACs if confirmed, high recurrence risk
How is AF anticoagulated post stroke
Aspirin for 2 weeks
Then warfarin/DOAC
How can you distinguish between Fast AF and SVT
SVT regular and has p-waves
How do you treat SVTs
Valsalva manourvre
Carotid massage
Adenosine: Rapid 6mg bolus –> 12mg more –> 18mg more
(verapamil if adenosine contraindicated)
Cardioversion
How is atrial flutter distinguished from other tachycardias?
How do you treat it?
P:QRS complexes 2:1
HR tends to hit 50s (eg 150, 200, 250)
Electrical cardioversion
If fails: Ablate tricuspid valve isthmus
Is this VF or VT?

VT
VT: Very Tidy
VF: Very Funny (see pic)

How do you treat ventricular tachycardia?
Unstable: Shock
Stable
Amiodarone/lidocaine/procainamide
Get electrophysiology + ICD if fails
What drug is avoided in VT?
Verapamil
Dampens normal SA node so promotes aberrant circuit .’. risk of Vfib
Slurred QRS, predominant R wave in V1 and Inverted T waves (inferior leads) are features in which condition?
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
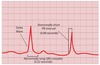
For Wolff-Parkinson-White what drugs do you…
Give
Avoid
Give: Amiodarone, flecainide + refer for ablation
Avoid: Digoxin, verapamil and bisoprolol
Drugs avoided as they cause SA rather than AP depression
How do you distinguish between the AV blocks
1st: Consistent PR >0.2
2 type I: Progressive PR lengthening, dropped beat
2 type II: No progression, 2-3 Ps : QRS
3rd: No association between Ps and QRS
How is sinus bradycardia/complete heart block treated?
Acute:
ABCDE
Atropine 0.5mg IV every 2-3 mins
Correct precipitants
Chronic
24hr taping + pacemaker
What drugs can precipitate bradycardia
B-blockers
nd-CCBs
Digoxin
Ivabradine
a-agonists
What does this show?

Left bundle branch block
WiLLaM
V1: ‘W’/rS
V6: ‘M’/R
What does this show?

Right bundle branch block
MoRRoW
V1: M (RsR)
V6: W (qRS)

What is more worrying LBBB, RBBB
LBBB IS ALWAYS PATHOLOGICAL
RBBB can be normal variant but acute resp/cardiac stuff can have it
How does a chronic heart failure patient present?
Breathlessness: Exertion, lying flat
Coughing: Worse at night, wheezy
Signs: Raised JVP, oedema
For suspected heart failure what is the first line investigation and how does this guide further investigation?
NT-proBNP
400-2000pgml (47-236pmol/L): Raised
>2000pgml (236pmol/L): High
Raised: 6 week echo
High: Urgent
What is the management of chronic heart failure?
4 Pillars of CCF
B-blocker + ACE inihibitor
+ Aldosterone antagonist (spironolactone, eplernone), MONITOR POTASSIUM
+ Sacubitril/valsartan
Failing initial management, what drugs are useful in the following circumstances?
LVEF <35% + sinus >75/min
LVEF <35% + symptoms on other therapy
Coexistent AF
Afro-Carribbean
Ivabradine: LVEF <35% + sinus >75/min
Sacubitril-valsartan: LVEF <35% + symptoms on other therapy
Digoxin: Coexistent AF
Hydralazine: Afro-Carribbean
Acute shortness of breath with pink sputum, bibasal creps and 3rd heart sound indicative of what?
Acute heart failure
What does a firm, smooth, tender liver that can be pulsatile indicate?
Right heart failure
What investigations should you perform in acute heart failure?
BNP to rule it out
CXR cardiothoracic ratio >0.5
Echo to assess ejection fraction
What is the management of acute heart failure?
POUR SOD
POUR away fluids
Sit up
Oxygen
Diuretics (40mg IV furosemide)
Match the features to its cardiomyopathy
Mitral regurgitation, anterior valve motion
Alcohol, B1, reduced output
Scarring procedures
QRS notching in a fatty heart
39 weeks –> 5 months post partum
Stress
HOCM
Dilated
Restrictive
ARVD
Peripartum
Takutsubo
When do you treat aortic stenosis?
How do you treat it?
Symptomatic OR >=40mmHg gradient
Valve replacement if well
Balloon valvuloplasty if unsuitable or children without calcification
What is the cause and treatment of rheumatic fever?
S.pyogenes
Pen V 10 days
What electrolyte imbalance causes
Small T-waves, U waves
PR prolonged
ST depression
Hypokalaemia (or magnasaemia)

What electrolyte imbalance gives the following ECG changes
Prolonged QT
Hypocalcaemia
Twitching, depression, cataracts are all features
What electrolyte disturbance shows the following
Broad QRS
Tall Tented T waves
Hyperkalaemia

What is the treatment for
Hypocalcaemia?
IV Ca gluconate
10% 10ml 10 mins
What is the treatment for hyperkalaemia?
Stabilise: IV Ca gluconate
Shift: insulin/dextrose + salbutamol
Send: Ca resonium/ haemodialysis/diuretics
What is the treatment for hypomagnasaemia?
<0.4mmol/L: IV MgSO4 over 24hrs
>0.4mmol/L: 10-20ml oral salts
Muffled heart sounds, raised JVP and hypotension indicates what cardiac condition?
Cardiac tamponade
How can you differentiate between constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade?
JVP
Pulsus parodoxus
Kussmaul’s sign
Characteristic features
Tamponade // Constrictive pericarditis
X (tampaX) // X + Y
Present // Absent
Rare // Present
Electrical alternans // Pericardial calcification on CXR

How do you treat cardiac tamponade
Pericardiocentesis

Which members of the following drug groups cause QT prolongation?
Antibiotics
Antidepressants
Anti-psychotics
Anti-emetics
Opioid replacement
Anti-arrhythmics
Erythromycin
TCAs, SSRIs (citalopram)
Haloperidol
Odansetron
Methadone
Amiodarone, quinidine, sotalol
What condition presents with severe dyspnoea, often triggered by exertion?
HOCM
Autosomal dominant
Outline PE anticoagulation where
Provoked
Unprovoked or cancer
Unstable
3 Months DOAC (Heparin then VKA if renal impairment) +/3 further 3 months if bleeding risk allows
6 months DOAC
Thrombolysis
How is adenosine administered?
16G cannula in right ACF vein or centrally
How do you treat aortic dissection if its
Proximal/ascending aorta
Distal/Descending
Proximal is type A: ASS
Aortic root replacement
Systolic BP 100-120
Surgery
Type B: BooBs
Bed rest + Beta blockers
As distended neck veins and hypotension are common, how do you distinguish between haemothorax and tamponade?
Haemothorax has reduced breath sounds on affected side
Due to blood build up
How do you treat Mobitz II block?
Pacemaker
Which cardiac drug reduces hypo awareness?
B-blockers
Reduces the physical symptoms (eg shaking)
Which cardiac marker is helpful to look for reinfarction 4-10 days from initial insult?
CK-MB
Only elevated 3-4 days post event whereas troponin is 10 days, so CK-MB will spike again
What pulse changes are seen in aortic dissection?
Absent carotid, brachial or femoral pulses
Arm pressure difference >=20mmHg
What vaccinations are offered in heart failure
Yearly flu
Single pneumococcal
How can AR and MS be differentiated by timing and conditions?
AR: Early diastolic, rheumatic fever
MS: mid-late diastolic, rheumatic fever
How do thiazide and loop diuretics differ in terms of electrolyte imbalances?
Thiazides cause hypercalcaemia
Loop cause hypocalcaemia
J-waves are seen in what acute condition?
Hypothermia
How do ACEis affect potassium levels?
Increase K+ as they reduce Na+
When does tachycardia require DC cardioversion?
Shock
MI
Heart failure
What do if haem instability and on warfarin?
Stop Warfarin
Give vit K
PCC/ FFP if not available
How do you manage a warfarin INR >8.0 if…
Minor bleeding
No bleeding
Both get
Stop warfarin
Give Vit K*, repeat if still high after 24 hrs
Restart warfarin when <5.0
Minor bleed dose: 1-3mg
No bleed dose: 1-5mg, give IV prep orally
How does management of warfarin INR of 5.0-8.0 differ where
Minor
No bleed
Minor
Stop warfarin, 1-3mg vit K, restart at 5.0
No bleed
Withhold 1-2 doses
Reduce subsequent maintenance
DVT causing stroke in patient with systolic murmur?
Atrial septal defect
Allows embolism to bypass lungs to get to brain instead
What causes an S2 that is
Loud
Reverse split
Widely split
Fixed split
Soft
Hypertension
LBBB/Severe aortic stenosis
RBBB
Atrial septal defect
Aortic stenosis
How do tricuspid regurg and mitral stenosis differ?
TR is systolic, MS is diastolic
TR louder on inspiration, MS quieter
Persitent ST elevation following MI indicates what complication?
LV thromboembolism
Blood stagnation in LV causes thombus formation
What anticoagulation is used for heart valves?
Warfarin
Bioprosthetic: 3 months then aspirin if needed
Mechanical: Warfarin with INR of 3.0 (aortic), 3.5 (mitral)
Sudden pan-systolic murmur following MI indicates what?
Acute mitral valve regurgitation
Secondary to flash pulmonary oedema
How to separate pulomary stenosis and aortic stenosis?
Pulmonary louder on inspiration
Aortic louder on expiratory
What post-MI complication can present similarly to cardiac tamponade?
Left ventricular free wall rupture
How can the R-R interval help determine what degree of heart block is present?
If the RR is not constant then its likely Mobitz II
Since there is a dropped beat in there somewhere


