general Flashcards
(24 cards)
Bayesian vs frequentist probability
Bayesian - degree of belief
Frequentist - proportion p of the repetition results in the given outcome with probability p
Random variable
Description of states which are possible, coupled with a probability distribution. Can be discrete or continuous.
Probability mass function P(x)
Maps from a state of a random variable to the probability of that rv taking on that state. Tied to the random variable P(x) != P(y) Sum over all x of P(x) = 1 - normalized
Joint probability distribution
PMF that acts on many random variables at the same time.
Expected value
Of some function f(x) with respect to a probability distribution P(x) is the average, or mean value, that f takes on when x is drawn from P.

Variance
gives a measure of how much the values of a function of a random
variable x vary as we sample different values of x from its probability distribution:
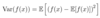
Low variance implies
The values of f(x) cluster near their expected value. The square root of the variance is known as the Standard deviation.
Covariance
Gives some sense of how much two values are linearly related to each other, as well as the scale of the variables:

principle of optimality
Has an optimal substructure.
An MDP problem that can be broken into smaller parts and solved optimally.
Can be broken down into doing the best thing for the next step and the best thing from there onwards.
Bellman expectation equation
One step lookahead
It writes the value of a decision problem at a certain point in time in terms of the payoff from some initial choices and the value of the remaining decision problem that results from those initial choices.

acting greedy (policy)
maximizing short therm reward/.
max of action-value function.

methods to solve an MDP
policy iteration and value iteration
VI: look at all states and update the value function at every state, using the previous iteration. Build a new value func at each state.
Value function
Expected return for a state

How to calculate Incremental Mean

On-policy vs off-policy learning
On-policy learning
- “Learn on the job”
- Learn about policy π from experience sampled from π
Off-policy learning
- “Look over someone’s shoulder”
- Learn about policy π from experience sampled from µ
2 steps of Monte-Carlo Control
Every episode:
1) Policy evaluation Monte-Carlo policy evaluation, Q ≈ qπ
2) Policy improvement -greedy policy improvement
Greedy in the Limit with Infinite Exploration (GLIE)

GLIE Monte-Carlo Control theorem
Theorem GLIE Monte-Carlo control converges to the optimal action-value function, Q(s, a) → q∗(s, a)
SARSA update
Updating Actio-Value functions (Q) with SARSA
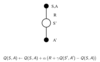
SARSA algorithm for on-policy control

Bootstrapping - bias vs variance trade-off
bootstrapping increases the bias
Q-Learning vs Sarsa



