Gastrointestinal Pharmacology Flashcards
What are the two causes of peptic ulcers? – Aggressive factors that contriubute to their developpment?
What are the body’s defense mechanisms against the development of peptic ulcers?
- Causes
- Helicobacter pylori
- Long term use of NSAIDs (indomethacin and ibuprofen)
- Aggressive factors
- gastric acid & smoking (nicotine stimulates gastric acid)
- Defense mechanisms
- mucus
- bicarbonate
- blood flow
- prostaglandins
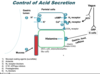
Describe the control of gastric acid secretion.
- When parasympathetic nervous system is activated (drink food/caffeine)
- increases gastrin level – stimulates ECL cells to
- release histamine – stimulates H2 receptor on parietal cells
- increases intracellular cAMP level
- increases activity of proton/K+ ATP pump,
- which increases gastric acid (HCl) secretion
- increases activity of proton/K+ ATP pump,
- increases intracellular cAMP level
- release histamine – stimulates H2 receptor on parietal cells
- increases release of ACh, which acts on M3 receptor on parietal cells
- increases intracellular Ca2+ level, which increases activity of proton/K+ ATP pump
- which increases gastric acid (HCl) secretion
- increases intracellular Ca2+ level, which increases activity of proton/K+ ATP pump
- increases gastrin level – stimulates ECL cells to
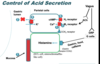
What are the 4 classes of drugs that can decrease gastic acidity?
- H+/K+- ATPase inhibitors
- H2 blockers
- Antacids (weak bases)
- Anticholinergics (not common b/c systemic adverse effects)
What are the PPIs & what is their mechanism of action?
- Drugs
- omeprazole (prilosec, rapine, zegerid)
- Lansoprazole (prevacid)
protom pump inhibitors
- react with H+/K+ ATPase to irreversibly inactivate the enzyme
- lasts lifetime of the pump, so long-lasting
- inhibit both fastign and meal stimulated secretion
Pharmacokinetics of PPIs?
- Prodrugs
- orally administered, absorbed in intestin & activated in parietal cells
- slow onset of action
- bioavailability is decreased by food
- except dexlansoprazole
- Rapid first-pass hepatic metabolism
- CYP2C19
- CYP3A4
Clinical uses of PPIs?
- Peptic ulcer disease: first-line drugs & most widely used
- sever symptomatic GERD
- nonulcer dyspepsia
- Prevention of stress-related mucosal bleeding
- gastric acid hypersecretion: gastrinoma
- Prevent NSAIDS-induced GI side effects
- ie. patients with arthritis
Adverse effects of PPIs?
- well tolerated & relatively safe
- nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain
- Long-term use
- increase Clostridioides difficle-associated diarrhea
- b/c increased gastric pH
- may reduce plasma Vitamin B12, non-heme iorn, Ca2+, Mg2+ levels
- b/c the reduced release of these components from food due to the increased gastic pH
- increase Clostridioides difficle-associated diarrhea
drug-drug interaction PPIs?
- drugs that the bioavailability is affected by intragastric acidity
- itraconazole
- digoxin
- Esomerprazole and omeprazole: CYP2C19 inhibitors
- interact with
- phenytoin
- diazepam
- theophyline
- clopidogrel
- dosage adjustment
- interact with
What are the H2 Histamine receptor antagonists and what is their mechanism of action?
- Drugs
- Cimetidine (tagamet)
- Famotidine (pepcid)
- ranitidine (Zantac)
- mechanism of Action
- competitively and selectively bind to H2 receptors, therefore reduce histamine-induced acid
- therefore, do not COMPLETELY block gastric acid secretion
Clinical uses H2 receptor antagonists?
- Peptic ulcer disease: first-line drugs & most widely used
- sever symptomatic GERD
- nonulcer dyspepsia
- Prevention of stress-related mucosal bleeding
- gastric acid hypersecretion: gastrinoma
- Prevent NSAIDS-induced GI side effects
- ie. patients with arthritis
Adverse effects H2 receptor antagonist?
- extremely safe. Tolerance develops
- cimetidine: ginds to dihydrotestosterone receptors – exaggerated estrogen effects
Drug-drug interaction of H2 receptor antagonists?
- interact with drugs metabolized by
- CYP1A2
- CYP2D6 and/or
- CYP3A4 (azole antifungal agents)
- affect inhibit first-pass metabolism of ethanol
- except famotidine
What is the mechanism of action of antacids?
- neutralize gastric acid
- Mg2+, Al3+, Na+, and Ca2+ salts are the most common
- very rapid, but short duration of action
clinical uses of antacids?
short-term relief of symptoms, used as-needed basis
adverse effects of antacids?
- constipation (aluminum)
- diarrhea (magnesium)
- altered electrolyte balance
- if you combine both calcium & magnesium can reduce both constipation & diarrhea
drug-drug interactions of antacids?
- affects absorption of some antibiotics
- tetracyclines & fluroquinolones
- separate administration time by several hours
Antibiotics used to cur H. pylori infection-induced peptic ulcer
- First line
- clarithromycin
- amoxicillin
- tetracycline
- second line
- Metronidazole
- if allergic to penicillin
- Refabutin
- if clarithromycin or metronidazole resistance
- Metronidazole
What is the drug name & mechanism of action for colloidal bismuth compounds?
- name
- bismuth subsalicylate (pepto-bismol)
- mechanism of action
- coat ulcer and erosions
- stimulate the secretion of prostaglandin, mucus, and bicarbonate
- antimicrobial effects: bind to bacteria and enterotoxins
- reduced stool frequencey and liquidity
Clinical uses of Bismuth compounds?
- nonprescription: treat dyspepsia dn prevent traveler’s diarrhea
- combined with PPI and antibiotics: H. pylori infection-caused peptic ulcer
Adverse effects & contraindications for bismuth compounds?
- adverse effects
- black tongue and stool
- contraindication
- renal insufficiency and allergies to salicylates
Sucralfate mechanism of action?
- pepsin inhibitor
- activated by acid – treating w/ antacid will decrease efficiency
- Mechanism of action (protect mucosa)
- physical barrier
- inhibit pepsin mediated hydrolysis of mucosal protein
- stimulates mucosal prostaglandin and bicarbonate secretion
Clinical uses of sucralfate?
- prophylaxis of stress gastritis
- peptic ulcer
- ulcers not caused by acid: oral mucositits and bile reflux gastropathy
Adverse effects & drug-drug interactions of sucralfate?
- adverse effects
- may develop constipation due to the aluminum salt
- drug-drug interaction
- may reduce the absorption of some oral medications
- time-lapse is important
Draw this




