Further Mechanics Flashcards
(56 cards)
Momentum is always (………..)
Conserved
What does the Linear momentum of an object depend upon?
Mass & Velocity
Is momentum a Scalar or a Vector?
Vector
What is the Momentum equation?
p = mv p - Momentum (kg m s*-1) m - Mass (kg) v - Velocity (ms*-1)
What do we assume is true if momentum is conserved?
There is no external forces acting on the object
Does momentum apply for explosions?
YES
How do you resolve Linear Momentum?
Split it into its Horizontal and Vertical Components
What are the Laws of Momentum?
Momentum before a collision = Momentum after a collision
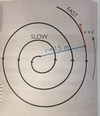
How do you investigate momentum in 2D?
- Weigh two ball bearings and note down their masses - On the table, position two metre rules at right angles to each other, put one of the ball bearings on the table and position a video camera directly above the table so it has a birds eye view. Like the picture! - Start videoing, roll the second ball bearings towards the stationary ball bearings so they collide - Use video analysis software to study the collision - Find the time between each frame and calculate how many frames are in each 0.1s - Use the rulers to find the distance travelled horizontally and vertically of the ball bearings every 0.1s, - use trigonometry to find the magnitude of the balls Velocity before and after the collision - Use Trigonometry to find the directions of these velocities. - You can find momentum is conserved by calculating the total momentum before the collision and the total momentum after the collision
What is an Impulse?
Is the change in momentum
What does Newton’s 2nd Law say?
Force = rate of change of momentum
What are the units of an Impulse?
Ns
The area under a force-time graph is…
Impulse
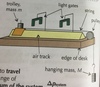
How do you investigate an Impulse (F X Δt = Δp) with an air track and Light Gates?
- Set up the apparatus and connect the lights to a data logger and computer - Release the trolley at one end of the air track and the weight will pull it along - Total mass of the system equals mass of the trolley + hanging mass - Use the data logger to find the Velocity of the trolley at each light gate. - Use this information to calculate the impulse (Δp *system* = m *system* X Δv) - Can also use the data logger to find the time taken for the trolley to travel between the two light gates, use this to find the rate of change of momentum in the system, Δp *system* / Δt - Repeat and take an average value for the impulse - Force acting on the system = Weight of hanging masses, F = Mg - Repeat the experiment with varying masses, every time you change the mass of the hanging mass add it to the trolley to keep the total mass of the system the same - Plot of graph of Force against rate of change of momentum - The graph should be a straight line.
Kinetic Energy is the energy of…
Anything moving
What does Kinetic Energy depend upon?
Mass & Velocity of whatever is moving
What are the 2 Kinetic Energy Equation we MUST know?
KE = 0.5 X m X v*2
KE = p*2 / 2m
V - Velocity of the object
M - mass of the object
P - momentum
How do you derive the equation KE = p*2 / 2m ?
Use KE = 0.5 X m X v*2
And
p = mv
Substitute p in for mv
KE = pv / 2
Rearrange p = mv to give v = p/m and substitute KE = pv / 2
TO GIVE
KE = p*2 / 2m
In what kind of Collision is Kinetic Energy Conserved?
In Elastic Collisions
If after a collision the object stick together or bounce apart is momentum still conserved?
YES
A collision where the total kinetic energy is the same after a collision is called…
An Elastic Collision
A collision where the total kinetic energy is less after a collision is called…
An Inelastic Collision
In a Collision is Energy conserved?
Yes, conservation of energy applies!
In a collision what is meant when it is said that energy is ‘lost’?
It means it is transferred to other forms of energy.