Functions Flashcards
What is a function?
reusable block of code that groups together a sequence of statements to perform a specific task

What is function declarations?
binds a function to a name (identifier)
What is Hoisting?
allows access to function declarations before they’re defined.
Ex)
greetWorld(); // Output: Hello, World!
function greetWorld() {
console.log('Hello, World!');
}
//Note: hoisting isn’t considered good practice, we simply want you to be aware of this feature.
What does it mean to ‘call a function’?
Code in the function block { } is executed only when the function is called.
No limits to times functions can be called
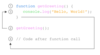
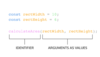
What are parameters?
Parameters allow functions to accept input(s) and perform a task using the input(s).
We use parameters as placeholders for information that will be passed to the function when it is called.
What is an Argument? When does it occur?
When calling a function that has parameters, we specify the values in the parentheses that follow the function name.
The values that are passed to the function when it is called are called arguments. Arguments can be passed to the function as values or variables.

Why is order of arguments important?
order in which arguments are passed and assigned follows the order that the parameters are declared.
Create a function with one argument that prints out:
Thank you for your purchase Cole! We appreciate your business.
Also include how you would call the function with the ‘cole’
function sayThanks(name) {
console.log(‘Thank you for your purchase ‘+ name +’! We appreciate your business.’);
}
sayThanks(‘Cole’);
What do default parameters do?
Allow parameters to have a predetermined value in case there is no argument passed into the function or if the argument is undefined when called.
Ex)
function greeting (name = 'stranger') {
console.log(`Hello, ${name}!`)
}
greeting(‘Nick’) // Output: Hello, Nick!
greeting() // Output: Hello, stranger!
What does the keyword return do?
We can use the keyword return to capture the output of a function to a variable.
By default that resulting value is undefined.\
Ex)
function rectangleArea(width, height) {
if (width \< 0 || height \< 0) {
return 'You need positive integers to calculate area!';
}
return width \* height;
}

What will print out:
function monitorCount(rows,columns){
return rows*columns;
}
const numOfMonitors=monitorCount(5,4)
console.log(numOfMonitors)
20
What are helper functions?
function that performs part of the computation of another function.
Helper functions are used to make your programs easier to read by giving descriptive names to computations. They also let you reuse computations, just as with functions in general.
Ex)
function monitorCount(rows, columns) {
return rows * columns;
}
//function saves the product of two arguments to monitorCount(arg1,arg2)
function costOfMonitors(rows,columns){
return monitorCount(rows,columns)*200;
}
//function saves product of called monitorCount(row,columns) /*note: see line 2*/ times 200
const totalCost=costOfMonitors(5,4)
//we save a called function of costOfMonitors with 2 arg that trigger previous programmed functions, all saved to object called totalCost.
console.log(totalCost)
//prints output value of functions programmed in object: totalCost
What is a function expression?
What is a function with no name ?
define a function inside an expression, we can use the function keyword.
An anonomus function
Ex)
const plantNeedsWater= function(day) {
if (day===”Wednesday”) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
};
console.log(plantNeedsWater(‘Tuesday’))
Note: A function expression is often stored in a variable in order to refer to it.
What is an arrow function?
Quick way to write a function using =>
Ex)
const rectangleArea = (width, height) =\> {
let area = width \* height;
return area;
};
What is consice body?
The most condensed form of the function
1) Functions that take only a single parameter do not need that parameter to be enclosed in parentheses. However, if a function takes zero or multiple parameters, parentheses are required.
2) A function body composed of a single-line block does not need curly braces. Without the curly braces, whatever that line evaluates will be automatically returned. The contents of the block should immediately follow the arrow => and the return keyword can be removed. This is referred to as implicit return.

What is implicit return?
The contents of the block should immediately follow the arrow =>
Implied return
Ex)
const squareNum = (num) =\> {
return num \* num;
};
Same as:
const squareNum = num => num * num;

For following, rewrite using concise body:
const plantNeedsWater = (day) => {
return day === ‘Wednesday’ ? true : false;
};
const plantNeedsWater = day => day===’Wednesday’ ? true : false;


