Functional Histology of the Urinary Tract Flashcards
(74 cards)
What is the kidney surrounded by?
A fibrous capsule
What is the kidney organised into?
Two layers, the cortex and the medulla
What does the cortex contain?
The renal corpuscles
What does the medulla contain?
Tubules
Where is the renal blood supply from?
The renal artery
What is the renal artery a branch of?
The abdominal aorta
What does the renal artery eventually become?
The glomeruli and the vasa recta
What are the vasa recta?
The ‘straight vessels’ that run up and down the medulla
Label this diagram

- A - Superficial glomeruli
- B - Interlobular vein
- C - Peritubular capillary bed
- D - Arcuate vein
- E - Arcuate artery
- F - Ascending vasa recta
- G - Descending vasa recta
- H - Henle’s loop of nephron
- I - Interlobar vein
- J - Interlobar artery
- K - Renal medulla (pyramid)
- L - Duct of Bellini
Label this diagram

- A - Convoluted tubules
- B - Cortex
- C - Bowman’s capsule
- D - Glomerulus
- E - Renal corpuscle
- F - Medullary rays
- G - Loops of Henle and collecting tubules
- H - Medulla
What does the kidney nephron consist of?
- Renal corpuscle
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal Convoluted Tubule
What is the function of the renal corpuscle?
It is the blood filtering component of the nephron
What does the renal corpuscle consist of?
- Vascular pole
- Urinary pole
Draw a labelled diagram of the kidney nephron

What does the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle consist of?
- Afferent/efferent arterioles
- Glomerulus
What does the urinary pole of the renal corpuscle consist of?
Bowman’s capsule
What is the renal tubule derived from in development?
The ureteric bud
What happens to the renal tubule during development?
It envelops the growing glomerulus, resulting in a double-layered cover
What is the double layered cover of the renal tubule called?
The Bowman’s capsule
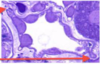
Label this histograph
- A - Bowman’s Capsule + Glomerulus
- B - PCT x-section

Label this histograph
- A - Bowman’s space
- B - Bowman’s capsule
- C - Glomerulus

What is the filtration barrier in the kidney made up of?
- The capillary endothelium
- The visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule
What is the visceral layer of the Bowman’s capsule made up of?
Podocytes
What are podocytes?
‘Cells with feet’