Formation of the Neural tube and role of SHH Flashcards
Explain what is meant by induction in development
When one cell population or tissie acts on another tissue. The acting tissue is the inductor whilst the other is the responder, which will commit to a specific developmental pathway.
One of the key signalling structures involved in formation of the neural tube is the ???????

Notochord
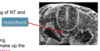
Where is the notochord anatomically in relation to the neural tube?
Ventral

What germ layer is the notochord derived?
Mesoderm
Neural tube (think CNS) is derived from what germ layer?
Ectoderm
The notochord is said to have what type of relationship to the neural tube?
Inductive
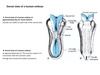
Describe the phyiscal properties of the notochord, what does it go onto become?
Flexible rod like structure. Goes onto form the nucleus pulposus of the spinal cord.
What are the key molecules that are produced by the notochord, and what is their function with regards to patterning of the neural tube?
- Noggin - acts by inhibiting BMP4
- The absence of BMP causes patterning in the overlying ectoderm so it can turn into the neural tube
- Chordin - acts as a BMP4 antagonist
Chordin and Noggin are said to be negative regulators of development.
Inhibition of BMP by noggin and chordin is a key step to the formation of the neural tube. When active, BMP4 ventralises ectoderm and mesoderm. If allowed to remain active, it would make ectoderm turn into epidermis and mesoderm into intermediate and lateral plate mesoderm.
If ectoderm is protected from exposure to BMPs, its default state is to become what type of tissue?
Neural
After gastrulation has occured, the appearamce of the notochord and mesoderm induces the overlying ectoderm to thicken and form what precursor to the neural tube?
The neural plate

What is the name given to the specialised ectoderm that makes up the neural plate?
Neuroectoderm
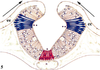
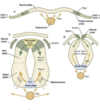
After the neural plate structure is induced. the lateral edges of the plate start to undergo what changes to form the neural tube structure
The depressed midregion of the neural tube is known as what?
- The lateral parts of the neural plate become elevated
- The midregion becomes depressed to form the neural groove
- The folds move towards the midline and fuse together to form the neural tube
- The neural tube becomes separated from the overlying ectoderm, the overlying ectoderm repairs itself.

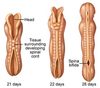
At how many days does neuralation occur?
Days 19-22 (Week 3-Week4)
Describe the changes that occur in cells of the neural fold in preparation for folding, and describe the two “hinge” points that are important for crucial to occur
- Cells take on a wedge-liked appearance
- two points on the neural tube are key for causing neural plate folding; the median hinge point and dorsolateral hinge point
Fusion of neural tube begins in which region, and proceds in which direction?
Cervical
Proceeds in both a Cephalic AND caudal direction simulatenously
After fusion of the neural tube has occured, what are the two holes called seen at the cephalic and caudal ends of the neural tube called?
Anterior neuropore
Posterior neuropore
At what days should the anterior and posterior neuropore close?
Anterior closes at day 25
Posterior closes at day 27
What “master regluator” of development is one of the key signalling molecules involved in differentiation of the neural tube?
Sonic hedgehog
What structure releases SHH for patterning of the neural tube?
Notochord

Sonic hedgehog produced by the notochord can act on the neural tube. As SHH has a relatively short range, it acts to produce what specialised portion of the neural tube? (note this is happening just as neural folding is also occuring)
What is the response of the floor plate as a result of the sonic hedgehog exposure
The floorplate
Floor plate makes it’s own SSH and results in the formation of motor neurones in the ventral part of the neural tube (DAVE)

Aside from patterning of the neural tube, what other important processes is SHH important for?
- development of limb buds
- somite patterning
- can causes cells in the ventral part of the somite, the scleratome, to undergo an epithelial t mesenchymal transition
- This makes them become highly migratory and they can move wrds the signal source (in this case the notochord)
- These cells will go onto form the vertebral column
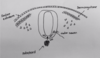
BMPs from the overlying ectoderm of the neural tube also have an important role in neural tube patterning - in particular the dorsal aspect of the neural tube. Explain how this occurs

- BMPs from the ectoderm upregulate PAX3 and PAX7 in order to form the roofplate
- These genes control the formation of sensory neurones in the dorsal aspect of the neural tube (DAVE)
- Therefore, we can say BMPS and SHH have a critical role in establishing the DV axis of the neural tube
There are two factors that are crucial in the formation of the folding hinges of the neural tube. What are they, are at which points are they active?
- SHH - required for the median hinge point
- BMP2 - requied for the dorsolateral hinge point
Although there are 2 potential types of hinge points, they are not always required for folding of the neural tube depending at the level (Upper/interediate/lower) of the spinal cord.
Where in the spinal cord (upper/intermediate/lower) would you expect to find these types of folds?
Upper spinal cord: Primarily Median hinge formation
Intermediate spinal cord: Both Median hinge points and dorsolateral hinge poins
Lower spinal cord: Primarily dorsolateral hinge points

Formation of specific types of hinge points is strongly regulated by signalling molecules. Explain the signalling that occurs which leads to the formation of median hinge points and dorsolateral hinge points
Upper Spine
SHH is strongly expressed, which is able to inhibit noggin. As a result, levels of BMP2 remain high - thus MEDIAN HINGES are formed
Lower spine
SHH is much less strongly expressed. As a result, noggin is free to inhibit BMP 2, and dorsolateral hinges are formed.

The cause of neural tube defects such as spina bifida, where there is improper closure of the neural tube isn’t well understood.
One theory as to why this happens is the result of increased SHH expression within the neural plate. Bearing in mind the effects of SHH and BMP2 on the formation of different hinge types, suggest why increase in SHH could affect this process. Also bear in mind that spina bifida most commonly occurs at the lower back.
- SHH is under normal circumstances is required for the formation of median hinges in the upper spine, so you would expect extra SHH at this region to make any difference
- However, under normal circumstances, SHH is usually at much lower levels, so if for whatever reason there was in an increase in SHH levels at the lower spine, dorsolateral hinges would fail to form
Remeber SHH inhibits noggin, leaving BMP2 to do it’s thing and you get MEDIAN HINGES. If SHH isn’t there, noggin stops BMP2 from doing it’s thing and you get DORSOLATERAL HINGES.
SHH at a cellular level requires two other genes that encode for transmembrane proteins.
Wht are these two proteins, and what family of transcription factors are activated?
Patched, smoothened
Acts on the Gli transcription factors
Describe signalling of SHH and how it controls patched, smoothened and Gli transcription factors

SHH is synthesized as an inactive precursor inside cells. Which lipid is required for it’s activation, and which transmembrane protein is required for it’s delivery to outside the cell?
Cholesterol
Patched

Give examples of conditions that can arrise as a result of abberent SHH signallin