FMS Week 8 Review Flashcards
(21 cards)
Where do APCs first present the antigens of a microbial agent to a naive T cell in a primary immune response?
in the paracortex of the draining LN
Where do B cells get activated
in the subcapsular sinuses of the draining LN
What hangs out in the LN follicles
B cells
What soluable factors are secreted by infected cells to precent virus spread
Type 1 interferon
a previously healthy 8 year old boy is infected with an upper resp tract virus for the first time. During the first few hours of infection, which of the following events occurs?
The adaptive immune system responds rapidly to the virus and controls viral replication
the innate immune system responses rapidly to the viral infection and limits the spread of the virus
passive immunity mediated by maternal Abs limits the spread of infection
B and T lymphocytes recognise the virus and stimulate innate immunity
the innate immune system responses rapidly to the viral infection and limits the spread of the virus
What cytokines
stimulate inflammation
TNF
IL1
what cytokines
activate NK cells
IL-12
IFN-alpha
IFN-beta
what cytokines are involved in
anti-viral state
IFN alpha
IFN beta
what cytokines
activate phagocytosis
IFN-gamma
TNF
made by: macrophages, T cells
inflammation, fever, neutrophil activation
If you were a neutrophil recruited to a site to kill such a bacterium, which of the following would ENHANCE your ability to phagocytose bacteria?
inflammatory ccytokines
chemokines
IFN-a
opsonins
OPSONINS
chemokines important in attracting there but not in actual phagocytosis
What are the major types of APCs
B cells, DCs, macrophages
MHC class I presentation
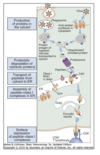
MHC Class II presentation

Which of the following cell types are the most potent at activating naive T cells?
B cells
DCs
endothelial cells
Kupffer cells
macrophages
dendritic cells
the PROFESSIONAL APCs for T cells. Best at activating.
Antigens that are presented in the context of human HLA-A nad B antigens
are usually of intracellular origin
are ususally endocytized
require lysosomal degradation
are often carbohydrates
activate NK cells
Are usually of intracellular origin
Which of the following mechanisms contributes the most to immunoglobulin (ig) and T cell receptor (TCR) diversity
combinatorial diversity: the multiple possible combinations of different V, D, and J segments
junctional diversity: changes in the nucleotide sequences at the junctions between recombines V D and J segments
complexing 2 different chains: heavy and lught chains (Ig) or alpha and beta chains (TCR)
polymorphism in V gene alleles
junctional diversity: changes in the nucleotide sequences at the junctions between recombines V D and J segments
B cell development

T cell development

Positive and negative selection of T cells in the thymus
In the thymus, an extremely diverse array of self peptifdes are presented by both MHC I and II on either thymic epitheliak cells or thymic DCs
Low affinity interactions with self peptide/ MHC lead to selection and differentiation into CD8 or CD4 lineages
T cells that can not recognise MHC undergo apoptosis
T cells that bind with high affiity to self/MHC undergo apoptosis
Consequences
only T cells with a functional TCR become single positive CD8 or CD4 T cells
T cells with high affinity for self antigens are removed from circulation
In both B and T ell development, there is a stage when a pre antigen receptor is expressed. Which of the following accurately describes an important function of these preantigen receptors?
positively select for lymphocytes that have successfully undersone a first round of VDJ recomb requires to express fnal antigen recepts
negatively select for self reactive lymphocytes
instruct the differentiation of lymphocytes into different subsets of effector cells
can select for lymphocytes that can recognise microbial antigens
bind to chemokines to keep the lumphocytes from migrating out of the generaive lymphoid organs
positively select for lymphocytes that have successfully undersone a first round of VDJ recomb requires to express fnal antigen recepts


