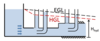
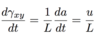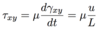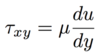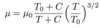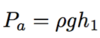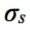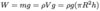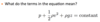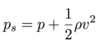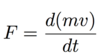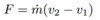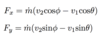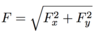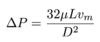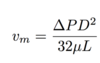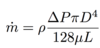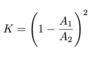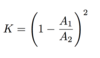Fluid Mechanics Flashcards
(299 cards)
A solid is matter that…
retains it’s shape (lump of metal)
A liquid is matter that…
deforms to the shape of its container and forms a free surface (glass of water, cup of tea, ocean, etc)
A gas is matter that…
occupies the full extent of its container (i.e. air in a balloon etc.)
A fluid is a substance which is…
either a liquid or a gas
A fluid is a matter that deforms continuously under the action of…
Shear stress
Define a system
A quantity of matter or region of space chosen for study
What resides outside the system?
The surroundings
The system is enclosed by its ____?
Boundaries
Define real and solid boundaries
Real: Solid boundaries
Imaginary: Notional surfaces that define a control volume
A system can be…(3 things)
Open, close or isolated
What is not allowed and what is allowed to cross the boundaries in a closed system?
- Mass is not because mass is fixed
- Energy is
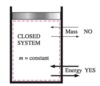
Boundaries are permitted to ____ in a closed system?
Move
What is allowed to cross in an open system?
Mass and energy
What can cross boundaries in an isolated system?
No mass or energy can cross the boundaries
Properties can either be…(2 things)
Intensive or extensive
Define intesive properties
Intensive properties are independent of the size of the system
Define Extensive properties
Extensive properties are dependent on the extent of the system
Give two examples of inentisive properties of a system and why
Pressure and temperature - they are independent of the size of the system
Give two example of extensive properties of a system and why
Mass and volume - they are dependent of the size of the system
Define density and it’s equation and units
The mass per unit volume of a substance

Define specific volume of a substance
- Specific volume defined as how much volume holds 1 kg of fluid mass
- The specific volume is the reciprocal of the density, i.e.
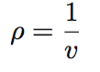
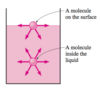
Define Continuum fluid
Homogeneous, continuous matter with no gaps
When is the assumption of continuum okay?
When the size of the system is large with respect to the spacing between molecules
What is the collision and rebound amongst molecules in the system represented by in the continuum?
Thermodynamic pressure, p (M/m2)