Fiscal and Supply side policies Flashcards
What is the fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy involves the manipulation of government spending, taxation and the budget balance. It can have both macroeconomic and microeconomic functions.
What is the budget balance?
The difference between planned government spending and planned government revenue.
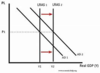
What is a Expansionary fiscal policy?
involves boosting AD by increasing Government spending and lowering taxes. This leads to a budget deficit. ( GS > Revenue)
What is an deflationary fiscal policy?
involves reducing AD by reducing GS and increasing taxes. This is likely to cause a budget surplus. ( GS < Revenue)
When is a deflationary fiscal policy likely to be used?
In a boom or positive output gap, reducing economic growth and increase unemployment, increasing the current account of the balance of payments.
When is an Expansionary fiscal policy likely to be used?
This wil be used in a recession or negative output gap, increasing economic growth, increasing employment, and worsen the current account of the balance of payments.
How can fiscal policy influence AS?
The government could reduce income and corporation tax to encourage spending and investment.
The government could subsidise training or spend more on education. This lowers costs for firms, since they will have to train fewer workers. Spending more on healthcare helps improve the quality of the labour force, and contributes towards higher productivity.
What is an automatic stabiliser?
To help counter swings in the business cycle and maintain economic stability
How would a Automatic stabiliser work in a recession?
Economic growth is negative but an automatic stabliser reduces this fall in growth. With lower incomes people pay less tax and GS on unemployment benefits increase. So the Automatic stabilisers will increase Gov borrowing but at this expense causes a deficit.
How would a automatic stabiliser work in a boom?
In a boom there is high economic growth so the AS will reduce the growth rate and unsustainable boom. The automatic stabiliser will create budget surplus as tax revenues will increase and government spending on benefits falls.
What are 3 things the strength of automatic stabilisers depend on?
- size of gov’t sector
- progressivity of the tax system
- how many welfare benefits are income related
What is an important thing to remember about deflationary fiscal policy?
it reduces demand but doesn’t necessarily cause deflation.
What are two types of tax?
Direct and indirect tax
What is an indirect tax?
Taxes on expenditure.
What are direct taxes?
Direct taxation is levied on income, wealth and profit.
What are some examples of direct taxes?
income tax
- corporation tax
- NIC
- inheritance tax
What are examples of Indirect taxes?
Excise duties
Fuel duties
Carbon tax
What are two types of Indirect tax?
Ad valorem taxes are percentages, such as VAT, which adds 20% of the unit price. This is the main indirect tax in the UK
Specific taxes are a set tax per unit, such as the 58p per litre fuel duty on unleaded petrol.
Why do governments levy tax? 5 reasons
- correct market failure
- raise money for government expenditure
- prevent imports (tariffs) to improve BoP
- redistribute income
- influence AD
What is a progessive tax?
The higher the income you receive the higher proportion of your income will be taxed. e.g. income tax
What is a regressive tax?
As income increases, the proportion of tax they pay will fall, this gives an incentive to work harder and earn more income, but may cause inequality.
What is a proportional tax?
Fixed rate for all taxpayers, regardless of income e.g. NIC
What would supporters of a flat tax say?
It reduces incentive for tax avoidance and invasion, it also increases incentive to earn more.
What is an evaluation of Flat tax?
It brings in less tax revenue overall than progressive tax also dont have vertical equity?