First Week of Human Development Flashcards
What is a zygote?
When a sperm fuses with an oocyte and contains maternal and paternal genes and chromosomes.
What is gametogenesis?
Gamete formation. Formation and development of specialized generative cells (gametes)
What is a special type of cell division that only occurs during gametogenesis?
meiosis
What occurs during Meisois 1 of spermatogensis?
Primary spermatagoenia become secondary spermatocytes or sister chromatids.
Primary spermatocyte (46 xy) split to become secondary spermatocytes: (23x) and (23y)

What happens during Meiosis II of Spermatogenesis?
Secondary Spermatocytes (23x) and (23y) divide and become 4 spermatids.
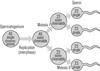
Once the four spermatids are developed how do they transform into mature sperm?
Gradually the 4 spermatids transform into mature sperm thru process of spermiogenesis.
What is spermiogenesis and how long does it take?
Where is the nucleus contained in a sperm?
The head of the sperm.
What is the acrosome?
The anterior 2/3rds of the sperm head that contains the enzyme that allows for penetration of the egg.
What happens to the Corona Radiata when the sperm releases enzymes?
The enzymes facilitate dispersion of the follicular cells allowing sperm penetration of zona pellucida.

What is the middle piece of the sperm do?
Contains mitochondria that fuels energy needed for motility.
What is oogenesis?
Oogonia are transorfed into mature oocytes.
What are the steps of Oogenesis?
- Primary Oocyte (46xx) forms
- Follicular cells develop around it
- Primary oocyte begin first meiotic division before birth
- First Meiotic phase produces a secondary oocyte and a first polar body during puberty.
- At ovulation the secondary ooctye begins the second meiotic division but only progresses if fertilized.
Where does fertilization of the egg occur?
Fallopian tubes
Walls of the ovarian follicle become what?
The corpus luteum.
What does the corpus luteum do?
Secretes estrogen and progesterone.
What does progesterone secreted from the corpus luteum do?
Prepares the endometrium for implantation of the ovum (blastocyte).
What prevents the degeneration of the corpus lutuem during pregnancy?
HCG
What hormone influences the development of the corpus luteum?
LH
What secretes HCG?
The Synctiotrophoblast of the blastocyte


