Final Exam Flashcards
(122 cards)
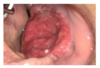
Clinical Description

Multiple white plaques that are mildly corrugated on the anterior floor of the mouth. The plaques have well-demarcated margins that are separated by deep fissures with focal areas of erythema
Differential Diagnosis

Leukoplakia
Squamous cell carcinoma
Proliferative verrucous Leukoplakia
Candidiasis (hyperplastic)
Confirmatory Test

Excisional Biopsy
Histopathological examination of every part of tissue
Management

Tobacco cessation
Low grade dysplasia: Frequent follow-up
High grade dysplasia: assess margins and wider excision if margins transected with frequent follow-up
Clinical Description

Multiple areas of curd-like white plaques on the anterior labial mucosa with coalesced areas.
Differential Diagnosis

Pseudomembranous Candidiasis (Thrush)
Leukoplakia
Verrucous Carcinoma
Confirmatory Test

Clinical findings (oral mucosa in susceptible individual for thrush)
Cytosmear stained with KOH to identify hyphae and spores
Swabs on sabourauds agar medium to grow white, curd-like colonies
Management

Manage drug-induced xerostomia
Better control of diabetes
Nystatin oral rinse
Clotrimazole oral troches
Clinical Description

White plaque on lower buccal mucosa/vestibule that has well-demarcated borders. The plaque is adjacent to a tooth with a cavity. There are areas that appear lifted or peeling (pseudomembrane)
Differential Diagnosis

Chemical burn
Tobacco pouch keratosis
Confirmatory test

Diagnosed clinically (acute onset, pseudomembrane, pain) and history of aspirin in that location
No biopsy required
Management

Do not remove pseudomembrane
Treat tooth
Viscous xylocaine mouth rinse to alleviate pain/burning of chemical burn
Lesions heal spontaneously over 7-10 days with reepithelization
Clinical Description

White lesion enclosing mild erythema on the lower left posterior buccal mucosa adjacent to a metal crown. Lesion exhibits fine radiating white striae
Differential Diagnosis

Lichenoid contact metal reaction
Lichen planus
Lupus erythematosus
Drug-induced lichenoid mucositis
Confirmatory test

Clinical presentation (localized nature of lesion, adjacent to metal restoration)
Skin sensitivity patch test by rheumatologist/dermatologist if patient desires
Management

Asymptomatic do not need treatment
Mild soreness due to superimposed candidiasis (antifungal medications) or excessive inflammatory response (topical steroid)
Replace crown if desired
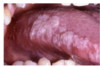
Clinical Description

White plaque on the right lateral tongue with multiple coalescing areas varying in size. Granular corrugated surface with indistinct margins
Differential Diagnosis

Hairy Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia
Tongue chewing (morsicatio)
Cinnamon reaction
Confirmatory Test
RT-PCR for HIV RNA (viral load)
CD4 T-lymphocyte counts (less than 200 cells/ul of blood)
Lesion biopsy (koilocytes in spinous layer, demonstration of Epstein Barr virus in koilocytes)
Management

Benign condition requires no treatment
Clinical indicator of low CD4 T-lymphocyte count (less than 200 cells/ul of blood) - transition point of HIV to AIDS
Indicator to initiate highly active antiretroviral therapy
Clinical Description

Irregular red patch with intermittent white areas on the left posterior soft palate
Differential Diagnosis

Erythroplakia (speckled leukoplakia)
Candidiasis
Thermal Burn
Autoimmune mucositis
Confirmatory Test

Excisional Biopsy
Histopathological examination of tissue
Management

Tobacco cessation
90% high-grade dysplasia or invasive carcinoma
Wide excision with assessment of margins for high-grade dysplasia or carcinoma (wider excision is margins are involved)