Final Exam Flashcards
(58 cards)
Draw the Wernicke-Geschwind Model of Language, label each primary area (Broca’s, Wernicke’s, Arcuate Fasciculus, Primary Motor Cortex) and the associated function of each area.
- Sounds sensations enter brain through auditory pathway
- Sound images are stored in Wernicke’s area…
- … and are sent to Broca’s area over the arcuate fasciculus pathway
- …for articulation over the motor pathway.
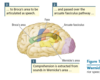
Draw and describe the structural and functional differences between Dorsal and Ventral language pathways.
Ventral: Semantics
Dorsal: Phonemes

Describe the neural web hypothesis of language. How does it differ from the standard model?
- Meaning comes through connections bt/w nodes to comprise neural webs
- Brain organized into neural webs for different aspects of language
- Webs consist of nodes and their 2-way connections

Describe the behavioral characteristics of Wernicke’s and Broca’s Aphasia in terms of fluency and comprehension.
-
Wernicke’s Aphasia (Fluent, yes; Comprends, no)
- Deficits in classifying sounds or comprehending words
- Word salad
-
Broca’s Aphasia (Fluent, yes; Comprehends, no)
- Can understand speech
- Labors hard to produce speech

What causes Kluver-Bucy Syndrome? What are 4 features of the disorder?
Bilateral medial temporal lesions; sometimes seen with herpes encephalitis.
- HYperorality
- HYpersexuality
- Stimulus bound
- Visual agnosia
- Lack of fear response

What are the 6 basic emotions that Ekman discussed?
- Sad
- Happiness
- Anger
- Fear
- Excitement
- Disgust
Describe the Somatic Marker Hypothesis.
Somatic markers: feelings in body associated w/ emotions, (e.g., association of rapid heartbeat w/ ANX or of nausea w/ disgust).
- When confronted with a stimulus of biological importance, the brain & body change
- Reductions in body reactions lead to reduced intensity of emotion
- Emotion is fundamental to survival
- Emotion is necessary for rationale decisions
Describe hemispheric differences in emotional processing
-
R hemisphere: automatic components of emotion
- Generates feelings
- Lesions -> Aprosodia
-
L hemisphere: cognitive control of emotion
- Interprets feelings
- lesions -> flattened mood
- L frontal -> decrease talking
brain areas associated with each of the “dual systems”
- ventral striatum (VS), specifically the nucleus accumbens, associated w/ reward processing
-
PFC associated with cog/ control system.
- vmPFC or orbitofrontal cortex works too

*[Adol Risk Taking Beh] Dual Systems mode? What is it.
IDEA:
- Risk-taking beh. peak during adol b/c activation of an early-maturing reward processing system amplifies affinity for exciting, novel, and risky activities,…
- …while a slower-to-mature, “cognitive control” system is not developed enough to consistently restrain potentially hazardous impulses.
*[Adol Risk Taking Beh] NAcc/Ventral Striatum: location. What does increased activation mean among adolescents?
NAcc/VS: decreased activation translates to less behavioral control.

Name two areas of the brain involved in arithmetic and describe their functions.
- Intraparietal sulcus – numerical processing
- Left angular gyrus – language, number processing, spatial cognition, and previously learned facts
- Fusiform gyrus – visual processing of number symbols
- Prefrontal cortex – working memory and executive functioning

What is dyscalculia? What are the hallmark signs of dyscalculia?
- difficulty in numeracy, not a difficulty in mathematics except for areas that deal with numbers.
Umbrella term to describe mathematical understanding and processing; failure to acquire academic skills related to numbers at an appropriate age.
Hallmark sign:
- inability to subitize (i.e., recognize quickly the quantity of objects in a small group of randomly scattered objects).
List three parts of the brain related to Persistent Complex Bereavement Disorder.
- Posterior cingulate cortex
- Superior frontal gyrus
- Insula
- ACC
- PFC
- Amygdala
What is one way that normal bereavement and complex bereavement differ?
- The patient experienced the death of a loved one at least 6 months previously
- Experience symptoms of intense yearning or sorrow
- Maladaptive adjustment
- It affects functioning at work, school, etc
Burnout is associated with (lesser/greater) empathy-related brain activity. (circle)
Lesser
Name 2 ways to treat or prevent burnout for helping professionals.
Any 2:
- mindfulness
- physical activity
- greater awareness of one’s own emotions
- structural changes that promote autonomy
- decreasing bloated caseloads
- greater flexibility in work setting
- greater contact/collaboration with colleagues
Briefly describe differences between small and large vessel vascular cognitive impairment. Which is more common?
Small vessel (more common)
- small, lacunar infarcts deep in brain (B.G, thalamus, and frontal-subcortical circuits).
- More associated w/ deficits in exec function
- More insidious onset
Large vessel (less common)
- includes strategic infarcts, ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, (efx vary by location).
- Maybe more deficits in VSI and language
Name and describe the three criteria for probable vascular dementia.
-
Dementia: decline from previous function of at least 2 of the following:
- Memory, orientation, ATTN, language, VSI, executive functions, motor control, and praxis
- Evidence for cerebrovascular disease
- Focal signs consistent w/ stroke
- Imaging consistent with cererbovascular disease (i.e. stroke, multiple lacunes, white matter lesions)
-
Relationship between criteria A and B.
- Onset within 3 months of stroke
- Rapid onset
- Fluctuating, stepwise progression
How does verbal memory deficits play into domestic violence?
- Low verbal IQ scores are strong predictors of DV abuse.
Or..
- an inability to communicate in other modes, the abusers opt for violent methods to communicate their volatile internal states.
What brain structure has been linked to potentially be related to the ability to detect empathy in others?
Fusiform gyrus: Prior to the threat of aggression, hyperresponsiveness is present in the fusiform gyrus.
How do executive function deficits reinforce abuse amongst domestic violence perpetrators?
Slow PSI -> component of impaired ability to make decisions, which impairs ability to evaluate behavioral consequences of actions.
What popular theory in flow describes a decrease in neural activity in the frontal lobe?
Transient Hypofrontality

What are 2 of the 4 areas of the neural activity are significantly related to the flow condition? List the directionality as well (i.e. significantly increased or decreased neural activity)
- Putamen (increase)
- Left IFG (increase)
- Medial Prefrontal Cortex (decrease)
- Left Amygdala (decrease)






