Final Exam Flashcards
(116 cards)
To initate cell expansion, P must be greater than ______ based on the Lockhart model

Y
The relative rate of cell expansion of an expanding cell mostly depends on ____ based on the Lockhart model

P and M
The relative rate of cell expansion of an expanding cell mostly depends on ____ at a given turgor pressure based on the the Lockhart Model

m
Cells elongate faster at more acidic conditions is possible due to _____

Greateer activity of expansion
IAA treatment causes a ____

A decrease in pH
IAA treatment causes ______

An increase in coleoptile cell elongation
Stimulated cell elongation by IAA is associated with a decrease in pH

True
In phototropism, auxin promotes ____
Cell elongation in the shaded side
Polar transport of auxin in stem include the following
Directional Movement
Movement from apical to basal
Requirement of Transporters
The organ that is the most sensitive to auxin is _____

Roots
The organ that shows the greatest growth promotion to auxin is _____
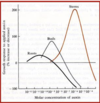
Buds
The number in the figure indicates the concentration of IAA. Predicate which treatment will result in bending?

B and C
The most effective light inducing phototropism is ______ light
Blue
GAs play roles in
Seed Germination
Stem Elongation
Increasing Fruit
Forming Seedless Grapes
In a generalized signaling pathway, GA can be considered as a ligand. It needs to bind to the ____ first to trigger the signaling cascade

Receptor
Both GA and IAA stimulate
Stem Elongation
Function of Cytokinin
Cell Elongation
Senescence
Cell Divison
In tissue culture, a high ratio of Cytokinin and IAA enhcances
Shoot formation
Function of Cytokinin
Enhance cell division
Promote shoot formation in tissue culture
Delay leaf yellowing
For auxin and cytokinin long distance transport through the plant,
Cytokinin through xylem and auxin through cells
In order to induce the root formation in tissue culture, one usually uses
A high ratio of IAA to cytokinin
Among the phytohormones studied, what hormone is also importnat for seed germination, besides ABA
GA
Considering their function in seed germination, GA and ABA act
Antagonistically
Functions of ABA
Inhibition of Seed Germination
Abscission of Leaves
Maintaining Winter Bud Dormancy























