Final Flashcards
(51 cards)
The cranial sutures of the temporal bones where they meet the parietal bones are?

Beveled, like the gills of a fish, indicating articular motility for a respiratory mechanism
Dr. William G. Sutherland state that dural membranes
Act as ‘guy wires’ (for the movement of the cranial bones, holding tension for the opposite motion
Dr. William G. Sutherland Used what to describe the three Cartesian axes held in reciprocal tension
Reciprocal tension membrane system (RTM)
What comprise the Axial skeleton?
Skull Ossicles (Inner Ear)
Hyoid bone
Vertebral Column
Rib Cage

Is the Coxal (Hip) bone part of the axial skeleton?
No.
Illium, Pubis, Ischium
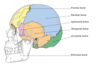
Landmarks of skull Nasion
Mid-point of the frontonasal suture

Landmarks of skull Glabella
Smooth area between the eyebrows at the lower part of the metopic suture

Landmarks of skull Ophryon
Point above glabella
Landmarks of skull Bregma
Junction of sagittal and coronal sutures

Landmarks of skull Vertex
Topmost point of skull
Landmarks of skull Lambda
Junction of the sagittal and lambdoid sutures
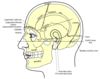
Landmarks of skull Inion
External occipital protuberance

Landmarks of skull Pterion
Junction of the frontal, sphenoid, temporal, and parietal bones

Landmarks of skull Asterion
Junction of the parietal, occipital, and temporal bones
Landmarks of skull Basion
Middle Point of the anterior margin of the foramen magnum
Landmarks of skull Opisthion
Middle point of the posterior margin of the foramen magnum
Landmarks of skull Gnathion
The most inferior point of the mandible, centrally located a the tip of the chin
Bregma is the junction of what sutures
Coronal suture Sagital suture

Lambda is the junction of what sutures
Sagital Suture
Lambdoid Suture

How many cranium bones are there?
22; Does not include 6 ossicles of the ear
8 Cranium
14 Facial
What makes up the Neurocranium bones?
1 frontal bone
2 Parietal
2 temporal bones
1 sphenoid bone
1 ethmoid bone (Crista Galli)
1 Occipital bone

What makes up the Viscerocranium bones?
1 Vomer
2 Nasal
2 Lacrimal
2 inferior nasal concha
1 mandible
2 maxilla
2 palantine
2 zygomatic

What are the ventricles of the brain?
Complex spaces and tunnels through the center of the brain

What is the choroid plexus?
Contained in the ventricles and secretes cerebrospinal fluid